Physics Concepts: Inertia, Motion, Force, Energy Reference
advertisement
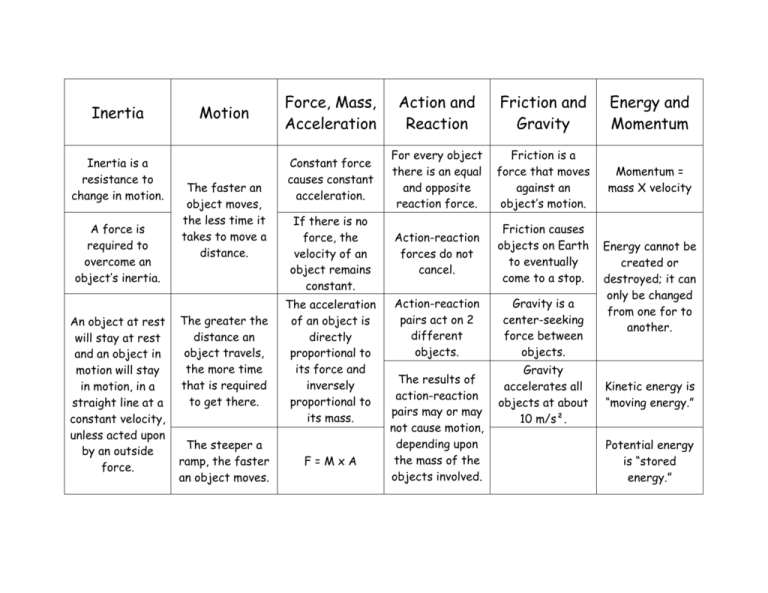
Inertia Inertia is a resistance to change in motion. A force is required to overcome an object’s inertia. An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion, in a straight line at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an outside force. Motion The faster an object moves, the less time it takes to move a distance. The greater the distance an object travels, the more time that is required to get there. The steeper a ramp, the faster an object moves. Force, Mass, Acceleration Action and Reaction Friction and Gravity Energy and Momentum Constant force causes constant acceleration. For every object there is an equal and opposite reaction force. Friction is a force that moves against an object’s motion. Momentum = mass X velocity If there is no force, the velocity of an object remains constant. Action-reaction forces do not cancel. Friction causes objects on Earth to eventually come to a stop. Action-reaction pairs act on 2 different objects. Gravity is a center-seeking force between objects. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to its force and inversely proportional to its mass. F=MxA The results of action-reaction pairs may or may not cause motion, depending upon the mass of the objects involved. Gravity accelerates all objects at about 10 m/s². Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be changed from one for to another. Kinetic energy is “moving energy.” Potential energy is “stored energy.”











