Forces
advertisement

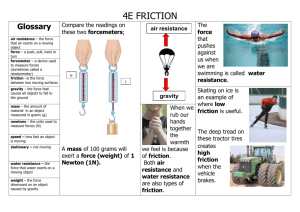
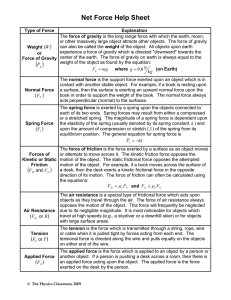
Forces Ch. 12.1 What is a force? • Any push or pull on an object = FORCE • Forces cause objects to move, accelerate, and/or change speed or direction • Use scales to measure forces • The SI unit is a NEWTON – 1 N=1 kg ● m/s2 • Use arrows (←, ↑, →, or ↓) to show which way the force is acting Combining Forces • Put forces together to show an end result • If forces are the SAME direction à ADD • If forces are DIFFERENT direction à SUBTRACT • NET FORCE à overall force acting on an object after all forces combine • BALANCED FORCE à net force is = and there’s NO change in motion – ex: arm wrestling standoff, tug of war • UNBALANCED FORCE à object will accelerate (move) – ex: WINNING arm wrestling or tug of war – http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/forcesand-motion-basics Friction • Any force that opposes motion of objects as they move past each other = FRICTION Static Friction • Acts on an objects that are NOT moving. Sliding Friction • opposes the direction of motion. One object is sliding. Rolling Friction a force acting on rolling objects Fluid Friction – opposes motion through a fluid Gravity • Force acting btwn 2 masses is GRAVITY – causes objects to accelerate downwards Projectile Motion • CURVED PATH of motion – combination of initial forward velocity and downward vertical force of gravity – http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/projectile-motion/ projectile-motion_en.html Concept Check • How is the motion of an object affected when a force acts on it? • How does air resistance affect the acceleration of a falling object? • Describe why a projectile follows a curved path.