Name: Period: _____ Date - East Hanover Schools Online
advertisement

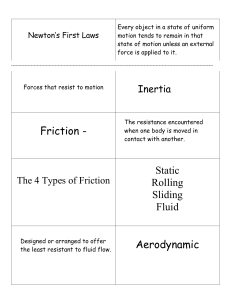
Name: __________________________________ Period: _____ Date: ____________ Chapter 5 Study Guide 1. Know what a reference point is and how you know something is moving. Reference point: an object that appears to stay in place An object is in motion when it changes position over time, in relation to a reference point. 2. Know the difference between speed and velocity. (including the SI unit for speed) Speed is distance traveled divided by time and velocity is the speed + direction. SI unit for speed/velocity: meters/seconds (m/s) 3. Be able to identify when an object is accelerating and when it is not. Three ways to accelerate: 1. slow down 2. speed up 3. change direction 4. Know the formulas (to solve for) speed, velocity, acceleration and time (use the speed triangle). Speed = distance / time Distance = speed x time Time = distance / speed Acceleration = final velocity – starting velocity -------------------------------------------time 5. Be able to read and analyze graphs for speed and acceleration. (what will it look like if there is an increase in speed, decrease in speed, stopping, constant speed, etc). Time vs distance straight line = constant speed Curved line down (slowing down) Velocity vs time going up (accelerating) going down (decelerating) 6. Be able to find net force on an object (example: What is the net force on an object when you combine a force of 15 N west with a force of 10 N east?) Same direction: add forces together Different direction: subtract the smaller force from the larger force and take the larger force’s direction (15 N west – 10 N east = 5N west) 7. Know what type of force is needed for an object to start moving and if forces are always acting on object, even if they aren’t moving. You need an unbalanced force to start moving. Forces are ALWAYS acting on objects, whether moving or not moving. 8. Know two types of friction and be able to give an example of each. Sliding Kinetic friction: present when pushing a box across the floor Rolling kinetic friction: riding a bike Fluid kinetic friction: skydiving Static friction: when pushing a heavy box that does not move 9. Know the two factors that determine the amount of friction and how friction affects rolling objects. (example: a golf ball after it is hit) Two factors: 1. amount of force applied 2. roughness of the surface Friction will begin to slow down/oppose motion once an object begins to roll. 10. List three ways to reduce friction. 1. use lubricants 2. switch from sliding to rolling 3. make the surfaces smoother 4. decrease force 11. Know at least two differences between mass and weight. (especially the definition of mass) Mass: measured in kilograms, measured with a balance, always constant, amount of matter in an object Weight: measured in Newtons, measured with a scale, changes depending on gravity 12. Know what gravitational force is related to. (use law of universal gravitation) and they change gravity. Gravity is related to the mass of the objects and the distance between them Increase distance = decrease in gravity Increase mass = increase in gravity