module aims, assessment and support
advertisement
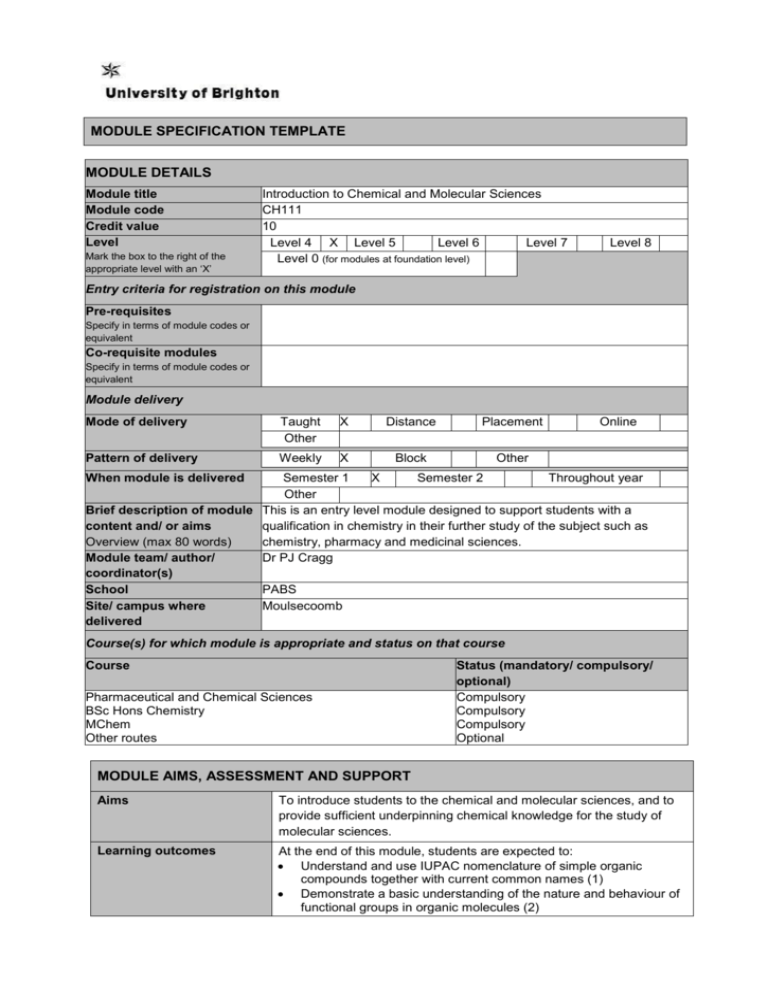
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Introduction to Chemical and Molecular Sciences CH111 10 Level 4 X Level 5 Level 6 Level 7 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other X Distance Placement Pattern of delivery Weekly X Block Other Online When module is delivered Semester 1 X Semester 2 Throughout year Other Brief description of module This is an entry level module designed to support students with a content and/ or aims qualification in chemistry in their further study of the subject such as Overview (max 80 words) chemistry, pharmacy and medicinal sciences. Module team/ author/ Dr PJ Cragg coordinator(s) School PABS Site/ campus where Moulsecoomb delivered Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course Pharmaceutical and Chemical Sciences BSc Hons Chemistry MChem Other routes Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Optional MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims To introduce students to the chemical and molecular sciences, and to provide sufficient underpinning chemical knowledge for the study of molecular sciences. Learning outcomes At the end of this module, students are expected to: Understand and use IUPAC nomenclature of simple organic compounds together with current common names (1) Demonstrate a basic understanding of the nature and behaviour of functional groups in organic molecules (2) Content Show an appreciation of the importance of stereochemistry and its relationships with molecular properties (3) Demonstrate an appreciation of basic properties of elements and their simple compounds, including trends within the Periodic Table, and their relationship to biological and pharmacological properties (4) Understand the principles of thermodynamics and kinetics and their application to chemical and biological systems (5) Demonstrate an understanding of equilibrium constants and their applications in acid-base equilibria (6) Show an appreciation of buffers and buffering capacity in terms of the Henderson Hasselbach equation (7) Organic chemistry Introduction to organic chemistry. Structure and bonding in organic compounds, molecular properties and introduction to reactivity. Functional groups: IUPAC and common names for alkanes, alkenes, aromatics, alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, ketones, aldehydes. Physical and chemical properties (including pKa values, stereochemistry, conformations, configurations, enantiomers, geometric isomers, R/S and Z/E nomenclature, definition of diastereoisomers). Inorganic Chemistry Introduction to inorganic chemistry. Inter- and intramolecular interactions. Lewis dot structures and the octet rule. Descriptive main group chemistry - periodicity, diagonal relationships, biological and medicinal importance of the elements. Physical Chemistry Introduction to the 1st and 2nd laws of thermodynamics. Hess’ law and thermodynamic potentials. The equilibrium constant and its applications in acid-base equilibria, extraction and partition coefficients. BronstedLowry and Lewis definitions of acids and bases. The HendersonHasselbach equation, pKa, pH of buffers. Introduction to chemical and enzyme kinetics: reaction rates and calculus description; rate constants; rate expressions; kinetic and thermodynamic control. Learning support Clugston and Flemming, Advanced Chemistry, Oxford University Press, Current Edition, or Silberberg, Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, McGraw-Hill, Current Edition, or similar Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities Approximately 33 hours lectures/tutorials, 64 hours private study, 3 hours assessment Allocation of study hours (indicative) Study hours Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. 33 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 67 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not work-based learning or a year abroad. TOTAL STUDY HOURS Assessment tasks 100 Details of assessment for this module Student performance will be assessed through a phase test (45 minutes) and final examination (2 hours). Phase test (MCQ) 40% (L.O. 1-7) Final exam (MCQ + short answers) 60% (L.O. 1-7) Types of assessment task1 % weighting Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN Written exam COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise 100 EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Dr I Pulford Senior Lecturer, University of Glasgow 01/10/09 31/12/14 QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval 2002 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision 2009 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of approval for this version 2013 Version number 5 Modules replaced CH101 and PY128 Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Yes No 1 Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task. X






