2.3 Eukaryotic Cells - IBDPBiology-Dnl
advertisement

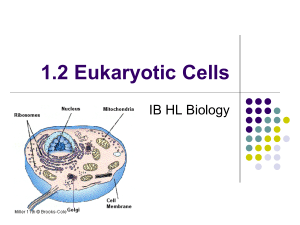
2.3 Eukaryotic Cells Animal cell Plant Cell Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. The diagram should show ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER), lysosome, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, cytoplasm and nucleus. Annotate the diagram from with the functions of each named structure Electron micrographs of liver cell Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleoplasm Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Golgi apparatus Electron micrographs of a plant cell Cell Wall Chloroplast Nucleoplasm Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Plasma membrane Cell vacuole Function(s) of cell Organelles ribosomes – protein synthesis rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) – synthesis of proteins to be secreted lysosome – holds digestive enzymes Golgi apparatus – for processing of proteins mitochondrion – for aerobic respiration nucleus – holds the chromosomes Comparison between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell DNA in cytoplasm / nucleoid / no nucleus DNA in nucleus / nucleus present naked DNA protein associated with DNA circular DNA linear chromosomes/DNA molecules Mitochondria present no mitochondria 70S ribosomes present 80S ribosomes present no membrane bound organelles internal membranes form organelles pili present plasmids sometimes present cell wall present flagella solid pili absent plasmids absent cell wall only present in plants/fungi flagella flexible/membranebound Differences between plant and animal cells Animal Cells Plant Cells Structure Cannot produce its own food X Chloroplast Can produce its own food. Flexible, can easily change shape. X Cell Wall Rigid, cannot easily change shape. Does not store large amounts of liquid. Smaller size of cell. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen. X Central Vacuole Stores large amounts of liquid (juice). Larger size of cell. Storage of carbohydrates Carbohydrates stored as starch. Roles of extracellular components Plant cell wall composition: cellulose microfibrils Functions: provides physical protection prevents excessive water uptake precluding bursting in hypotonic environment produces turgor pressure which holds whole plant up against the force of gravity Maintains the shape of the cell Animal extracellular matrix animal cells secrete glycoprotein that form the extracellular matrix Functions: Support – bone and cartilage cells are embedded in the matrix adhesion between cells - skin cells sit on a sheet of proteoglycan (protein + polysaccharide ) cellular movement