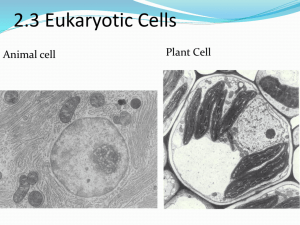
1.2 Eukaryotic Cells IB HL Biology Essential Idea Eukaryotes have much more complex cell structures than prokaryotes Eukaryotic Cells Algae Fungi Plants Animals Eukaryotic Properties More complicated than prokaryotic Nucleus with a nuclear membrane Many membrane-bound organelles with distinct functions 10-100 m Eukaryotic Cell Structure Nucleus – double membrane control centre Store DNA chromosomes in form of chromatin DNA replication and transcription Nucleolus – in the nucleus Made of RNA Makes ribosomes Eukaryotic Cell Structure Ribosomes Ribosomes – link amino acids into proteins like enzymes Made in the nucleolus Made of RNA and protein ~ 20nm Size = 80s Eukaryotic Cell Structure Endoplasmic ReticulumFolded membrane that carries materials through cytoplasm Make proteins for secretion to outside the cell Rough ER (rER) Covered in ribosomes Makes proteins Smooth ER (sER) No ribosomes Synthesize fats and lipids Eukaryotic Cell Structure Golgi apparatus – folded membrane for storing, processing and packaging proteins from rER Mitochondria – double membrane with enzymes on cristae (folds) What kind of cell would have lots of mitochondria? Why? Create vesicles (small sac) Exocytosis - sac fuses with cell membrane and empties contents outside of cell Inside called matrix Produce large amount of ATP for cell by cell respiration Power plant of cell Lysosome Created by Golgi Apparatus Vesicle filled with hydrolytic enzymes Breakdown and recycle cell parts and biomolecules Eukaryotic Cell Micrographs Mitochondrion Golgi apparatus Nucleus Lysosome Liver Cell Micrographs Rough ER Mitochondrion Free ribosome Liver Cell Micrographs Mitochondrion Rough ER Cell membrane Nucleus 2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultra structure of the liver as an example of an animal cell Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotes Smaller Single, circular DNA DNA in cytoplasm (no nucleus) Small ribosomes (70S) Usually no extra membranes: no mitochondria, ER, golgi, chloroplasts, vacuole, etc. Eukaryotes Larger, containing multiple mitochondria Multiple strings of DNA organized by proteins DNA in nuclear membrane Large ribosomes (80S) Many extra membranes forming compartments for special jobs for many organelles Plant & Animal Cells Animal Cell Plant and animal cell differences Plant Animal Cell wall (cellulose) For structure, support and regular shape. No cell wall Large central vacuole May have small temporary vacuoles Autotrophs Heterotrophs Chloroplast photosynthesis No chloroplast Carbs stored as starch Carbs stored as glycogen (some fat) Centrioles (mitosis) No centrioles Structures outside the cell: Cell wall of plants Primary cell wall Non-living Cell wall is made of cellulose (carbohydrate) Cellulose makes microfibril bundles with other molecules Supports Cell shape Overall plant shape (opposes gravity) Storage of carbohydrates Prevents the cell from absorbing too much water and bursting (lysis) Structures outside the cell: Animal Extracellular Matrix Glycoproteins proteoglycan Plays a role in Support Adhesion Movement Helps in embryonic development IB Objectives Eukaryotes have a compartmentalized cell structure. Skill: Drawing of the ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells based on electron micrographs Skill: Interpretation of electron micrographs to identify organelles and deduce the function of specialized cells. Task: Venn Diagram of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells