931-An Introduction to Acids and Bases
advertisement

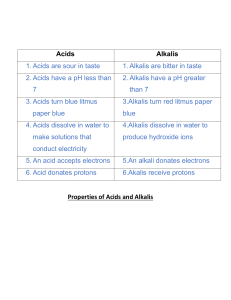
Answer these questions in the back of your book. What is a chemical reaction? What is a physical reaction? What is an acid? What is an alkali? What is a base? What does neutral mean? What does neutralisation mean? Objectives To be able to test chemicals and decide if they are acid/alkali/basic/neutral. To be able to record chemical reactions in word and symbol equations. Facts about acids Weak acids, like lemon juice and vinegar, taste sour. Strong acids are corrosive and can “eat away” at metal, stone and flesh! Acids turns blue litmus paper red. Acids have a pH of less than 7. Acids can be neutralized with alkalis. Facts about alkalis Alkalis feel soapy and are used in household cleaning materials. Strong alkalis are caustic. Alkalis turn red litmus paper blue. Alkalis have a pH of more than 7. Alkalis can be neutralized with acids. pH scale http://www.phschool.com/atschool/science_activity_library/images/acids_and_bases_phscale.jpg Testing the pH of chemicals Practical There are a wide variety of indictors Universal Indicator Litmus Phenolphthalein Methyl orange Neutralisation Compounds of alkali metals called salts can be made by reacting solutions of their hydroxides, which are alkaline, with acids. The general equation is: Names of salts When we replace the hydrogen in an acid by a metal, we get a salt. Acid Name in salt Example Hydrochloric Sulphuric Nitric Symbol equations No atoms are created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. There should be the same number of atoms of each type of element each side of the equation. Nitric acid + potassium hydroxide potassium nitrate + water State symbols (s) (l) (g) (aq) You try Measure 20cm3 of hydrochloric acid into a beaker. Add a few drops of UI soln. Using a pipette, add sodium hydroxide to the acid. Observe please note that an indicator can be used to show when acidic and alkaline solutions have completely reacted to produce a neutral salt solution. Write a word and balanced symbol equation for the reaction (can you add state symbols?). Plenary – true or false? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bases and alkalis are the same. Acids have a pH of less than 7. Neutralisation reactions always produce water. Symbol equations must always be balanced. (aq) means liquid. Homework – complete the following: Hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide Sulphuric acid + potassium hydroxide Nitric acid + Lithium hydroxide Hydrochloric acid + potassium hydroxide Sulphuric acid + sodium hydroxide