Year 8 Revision Summer 2015 Be Scientific You should know
advertisement

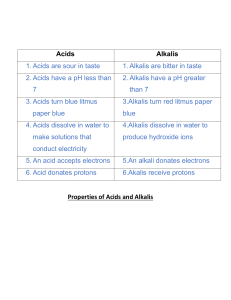
Year 8 Revision Summer 2015 Be Scientific You should know: • • • • • • • • Science safety rules. Meaning of hazard warning symbols. Name and use of simple scientific apparatus. How to light a Bunsen burner and adjust flames. How to use basic measuring equipment. Units of measurement. To recognise a fair test. How to draw and label scientific diagrams. Dissolving You should know: Some solids are soluble, others are insoluble. The meaning of the terms – solute, solvent, solution, saturated solution. Three ways to speed up dissolving. Solubility of solid solutes increases as the temperature of the solvent increases. Separating techniques You should know: How to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid by decanting and filtering. How to separate a soluble solid (solute) from a solvent by evaporation. How to separate a solvent from a solution by distillation. How to separate two immiscible liquids. How to draw and label diagrams of the apparatus used in separating techniques. Acids & Alkalis You should know: Acids are sour, soluble substances. Alkalis are soluble and the chemical opposite of acids. Strong acids and alkalis are corrosive. Neutral substances are neither acidic nor alkaline. Indicators change colour in acids and alkalis, Colours of Litmus, Universal Indicator and Red Cabbage solutions. The pH scale. Every day uses of neutralisation. Water You should know: The stages in the water cycle. Tests for water - cobalt chloride paper, anhydrous copper sulphate. Three ways to speed up evaporation. Evaporation causes cooling of the surroundings. Water travels up narrow tubes – capillarity. How to detect microbes using petri dishes filled with agar jelly. Causes of water pollution. Stages in water treatment. How to make a model filter. Water finds its own level. Water pressure increases with depth. Streamlined shapes move through water fastest. Living Things You should know: • The seven characteristics of living things. • How to classify living organisms – vertebrates/invertebrates. • Names and features of (a) the five vertebrate groups (b) arthropods. • The stages in insect life cycles. . How to use a key.