You should know
advertisement

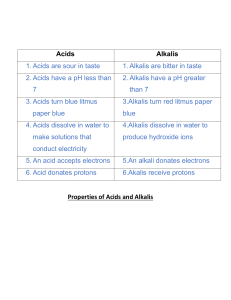
Year 10 Chemistry Revision Term 1 Acids and Alkalis (Year 8) You should know: The names of acids and alkalis. Acids are sour, soluble substances. Alkalis are soluble and the chemical opposite of acids. Strong acids and alkalis are corrosive. Neutral substances are neither acidic nor alkaline. Indicators change colour in acids and alkalis. Colours of Litmus and Universal Indicator. The pH scale. Every day uses of neutralisation. States of Matter (Year 9) You should know: • The names and properties of the three states of matter. • How to change from one state into another. • The particle (kinetic) theory of solids, liquids and gases. • How to explain the properties of solids, liquids and gases using the particle (kinetic) theory. • How diffusion occurs. • The definitions of the words element, compound, atom, molecule. • The names, symbols, description and uses of certain elements. • How to relate the properties of a material to its uses. Acids, Bases and Salts (Year 10) You should know: • The names and formulae of common laboratory acids. • Acids are substances which want to replace their hydrogen with a metal. • A base is a metal oxide or metal hydroxide. • An alkali is a soluble base. • The names and formulae of common laboratory bases. • How to explain the terms strong, weak, concentrated, dilute with reference to acids and alkalis. • The colours of a range of indicators in acids, alkalis and neutral solutions. • The properties of acids. • How to name salts. • How to write word equations to describe chemical reactions. • How to make salts by (a) reacting an acid with a metal (b) reacting an acid with an insoluble base (c) reacting an acid with an alkali. • A titration is an accurate neutralisation reaction. Gases You should know: • How to make and test oxygen. • The definition of combustion. • Oxides are formed when substances burn in air. • Metal oxides are basic and non-metal oxides are acidic.