Final Exam Review & Recap
advertisement

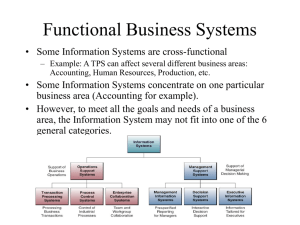
Final Exam Review & Recap CSIS-114 Reading • • • • • • Chapter 1 pp 3-30 Chapter 2 pp 39-58 Chapter 5 pp 67-91 Chapter 7 pp 99-124 Chapter 8 pp 133-161 Chapter 10 pp 169-209 The final exam is cumulative so review early reading But, Concentrate on these pages System Types Basic Types Operation Support • TPS • PCS • ECS Management Support • MIS • DSS • EIS Enterprise Types • ERP • SCM • CRM Special Types • Expert Systems Core Types • DBMS Information Technologies - major highlight Database Technology (Chapter 5) – Relational model reduces redundancy and dependence by providing a centralized data framework Data Mining (Chapter 10) – Innovative techniques used to discover patterns and correlations hidden in massive data sets. OLAP: Online Analytical Processing (Chapter 10) – Technologies allow large amounts of data to be processed and analyzed interactively instead of with pre-developed reports. Artificial Intelligence (Chapter 10) – Category of technologies that simulate human-like ability to solve problems, learn, and “think.” Information Technologies - examples from lab Database Technology – Lab 4: Databases vs. Spreadsheets – Lab 5: Tables, Records, Relationships, Queries, etc. Data Mining – Lab 9: Using advanced queries to discover the best transaction (Decision Support). Best transactions were difficult to find with basic reports and graphs. OLAP: Online Analytical Processing – Lab 10: Pivot Charts let us slice and dice the data to develop an expert system that would predict when Dr. B will play. Information Technologies - student presentation examples Data Mining – Dan Haemmerle talked about advanced Scout; data mining in basketball, and other applications like casinos.” Artificial Intelligence – Chris Allen, Travis Smith & Guillaume Dufau talked about the Lexus that could parallel park itself (Human-like ability) Systems for Functional Areas - examples from class Accounting Systems – Frank Leone and Robyn Freeman talked about Quickbooks an out-of-the-box, inexpensive system perfect for small businesses. – Be sure to read pp 121-122 While functional systems are still around, systems that integrate different functional areas are more valuable. Why? Systems for Functional Areas - examples from class Marketing Systems – Tara Maloney and Todd Crounse talk about the major components: (1) Managing Customers, (2) Targeted Marketing, (3) Automating the Sales Force – Be sure to read pp 111- 116 – Mathias Besse and Bryan Li talked about a CRM system (SalesForce?), a CRM is really an Enterprise Marketing System that integrates other functional areas. – Be sure to read pp 135-142 Enterprise Systems - Functional Areas CRM: Customer Relationship Management 1. Marketing 2. Accounting, Finance, HR, Operations ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning – All functional areas are equally represented SCM: Supply Chain Management System 1. Accounting, Operations 2. Finance, HR, Marketing Enterprise Systems - Types or Categories CRM: Customer Relationship Management 1. MIS, TPS, DSS, ECS ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning 1. EIS, DSS, MIS 2. TPS SCM: Supply Chain Management System 1. TPS, DSS, PCS 2. MIS Components and Goals - read all of Chapter 8 CRM: Customer Relationship Management 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Contact Management Marketing Customer Service Retention & Loyalty Programs Sales Management Goals: – – – Acquire More Customers Enhance Sales Retain Customer Loyalty Components and Goals - read all of Chapter 8 ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning 1. Production Planning (DSS, PCS play roles) 2. Sales Distribution and Order Management (TPS) 3. Logistics Integration (TPS) 4. Human Resource Planning (DSS, MIS) 5. Accounting and Finance (MIS) By integrating all the components into a single portal, an ERP can also fit into the EIS category. Goals: – – – Increase Efficiency Decrease Production Costs Increase Enterprise Agility Components and Goals - read all of Chapter 8 SCM: Supply Chain Management System 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Forecast and Demand Planning Customer Order Fulfillment Distribution Network and Warehouse Operations Transportation and Shipment Management Strategic Sourcing and Procument Goals (similar to ERP but more specific): – – – Increase Efficiency (Rapid Demand Fulfillment) Decrease Inventory Costs (Just-in-time Inventory) Improve Collaboration with Parters Unique system because it could integrate multiple enterprises. Key Concepts - Role of IS’s • Competitive Advantage – Companies use IS’s to leverage advantages – Force competition to invest in IS’s or sink • Strategic Advantage – IS’s transform data into valuable information that help companies make better “big” decisions. – Misconcept: IS’s only help make “small” operational decisions. Key Concepts - Role of IS’s • Business Improvement vs. Business Process Re-engineering – Better information lead to incremental continuous improvement in each functional area. This is why functional systems are still valuable. – Integrating system and information allows companies to completely re-engineer at the highest levels (BPR). This is why Enterprise systems are so valuable. Key Concepts - Role of IS’s • Business/Enterprise Intelligence – In large businesses, no single person could process all the available information to make intelligent decisions. – IS’s all a large group of people to get the right information so that the company has a collective intelligence that is great than the sum of its parts. • Enterprise Agility – IS’s allow information to move faster from the operational level to the strategic level and vice versa enabling companies to move faster.