Chapter Nine Management Information System Importance of this
advertisement

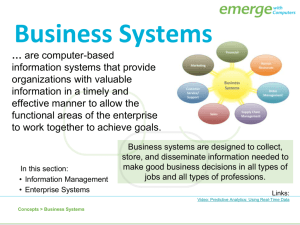
Chapter Nine Management Information System 157 Importance of this Chapter This chapter introduces basic idea about data, information, information system, role of information system and overview of some major enterprise applications. Management Information System (MIS) plays a vital role in management administration and operations of an organization. Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Get an overview on data, information and information system Know why information systems and information technology are so important for running and managing a business today? Get idea about Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Decision Support System (DSS), Business Intelligence System(BIS)and Supply Chain Management (SCM). Management Information System (MIS) is an information system that evaluates, analyzes and processes an organization's data to produce meaningful and useful information on which the management will take right decision to ensure future growth of the organization. 9.1. Data and Information Data are streams of raw facts representing events occurring in organizations or the physical environment before they have been organized and arranged into a form that people can understand and use. When data is processed, organized, structured or presented in a given context, to make it useful then it is called information. A brief example contrasting information and data may prove useful. Supermarket checkout counters scan millions of pieces of data from bar codes, which describe each product. Such pieces of data can be analyzed to provide meaningful information, such as the total number of bottles of dish detergent sold at a particular store, which brands of dish detergent were selling the most rapidly at that store or sales territory, or the total amount spent on that brand of dish detergent at that store or sales region. Figure 9.1: Relation between data and information 158 9.2. Information System An information system can be defined technically as a set of interrelated components that collect (or retrieve), process, store, and distribute information to support decision making and control in an organization. Figure 9.2: Functions of an Information System 9.2.1. Components of Information System The main components of an information system are Hardware is a device such as a processor, monitor, keyboard or printer Software is a program or collection of programs that enable hardware to process data. Database is a collection of related files or tables containing data. Network is a connecting system (wired or wireless) that permits different computers to share resources. Procedures are the set of instructions about how to combine the above components in order to process information and generate the desired output. 159 People are those individuals who use the hardware and software, interface with it, or use its output. 9.2.2. Role of Information System in Business Information systems are a foundation for conducting business today. In many industries, survival and the ability to achieve strategic business goals are difficult without extensive use of information technology. Businesses today use information systems to achieve six major objectives: operational excellence; new products, services, and business models; customer/supplier intimacy; improved decision making; competitive advantage; and dayto-day survival. 9.2.3. Information Technology Information technology (IT) consists of all the hardware and software that a firm needs to use in order to achieve its business objectives. This includes not only computer machines, storage devices, and handheld mobile devices, but also software, such as the Windows or Linux operating systems and the many thousands of computer programs. Problem Please send this portion to rashed@iubat.edu Solution of given problem Please send this portion to rashed@iubat.edu Exercise Please send this portion to rashed@iubat.edu 9.3. Major Enterprise Applications Enterprise applications are specifically designed for the sole purpose of promoting the needs and objectives of the organizations. These applications provide business-oriented tools supporting electronic commerce, enterprise communication and collaboration and web-enabled business processes both within a networked enterprise and with its customers and business partners. Most commonly used enterprise applications are: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Decision Support System (DSS) Business Intelligence System (BIS) Supply Chain Management (SCM) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Firms use enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to integrate business processes in manufacturing and production, finance and accounting, sales and marketing and human resources into a single software system. Information that was previously fragmented in 160 many different systems is stored in a single comprehensive data repository where it can be used by many different parts of the business. Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Firms use customer relationship management (CRM) systems to maintain their relationships with their customers. CRM systems provide information to coordinate all of the business processes that deal with customers in sales, marketing, and service to optimize revenue, customer satisfaction, and customer retention. This information helps firms identify, attract, and retain the most profitable customers; provide better service to existing customers and increase sales. Decision Support System (DSS): Decision support systems are interactive software-based systems intended to help managers in decision making by accessing large volume of information generated from various related information systems involved in organizational business processes, like, office automation system, transaction processing system etc. DSS uses the summary information, exceptions, patterns and trends using the analytical models. Decision Support System helps in decision making but does not always give a decision itself. The decision makers compile useful information from raw data, documents, personal knowledge, and/or business models to identify and solve problems and make decisions. Business Intelligence System (BIS): Business Intelligence System is a contemporary term for data and software tools for organizing, analyzing, and providing access to data to help managers and other enterprise users make more informed decisions. The goal of BIS is to allow for the easy interpretation of the large volumes of data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights can provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability Supply Chain Management (SCM): Supply chain management (SCM) systems help to manage relationships with their suppliers. These systems help suppliers, purchasing firms, distributors, and logistics companies to share information about orders, production, inventory levels, and delivery of products and services so that they can source, produce, and deliver goods and services efficiently. The ultimate objective is to get the right amount of their products from their source to their point of consumption in the least amount of time and at the lowest cost. These systems increase firm profitability by lowering the costs of moving and making products and by enabling managers to make better decisions about how to organize and schedule sourcing, production, and distribution. Problem 161 1. What is MIS? Write down the purpose of MIS. The Management Information System (MIS) is a planned system of collecting, storing and disseminating data in the form of information needed to carry out the functions of management. The purpose of MIS is the smooth running of the business by providing information about the organization. Employees from different levels will then evaluate this information so that decisions can be made to ensure that the business remains competitive and successful. 2. Why we need Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Business integration and automated data update Linkage between all core business processes and easy flow of integration Flexibility in business operations and more agility to the company Better analysis and planning capabilities Critical decision making Competitive advantage Use of latest technologies 3. How do customer relationship management systems help firms to achieve customer intimacy? Customer relationship management (CRM) systems integrate and automate customer-facing processes in sales, marketing, and customer service, providing an enterprise-wide view of customers. Companies can use this knowledge when they interact with customers to provide them with better service or to sell new products and services. These systems also identify profitable or nonprofit able customers or opportunities to reduce the churn rate. The major customer relationship management software packages provide capabilities for both operational CRM and analytical CRM. 4. What are the characteristics of Business Intelligence System? It is created by procuring data and information for use in decision-making It is a combination of skills, processes, technologies, applications and practices It is an extension of Executive Support System or Executive Information System It collects, integrates, stores, analyzes, and provides access to business information It is an environment in which business users get reliable, secure, consistent, comprehensible, easily manipulated and timely information It provides business insights that lead to better, faster, more relevant decisions. 5. What are the objectives of Supply Chain Management (SCM)? To decrease inventory cost by more accurately predicting demand and scheduling production to match it. 162 To reduce overall production cost by streamlining production and by improving information flow. To improve customer satisfaction. Exercise: 1. 2. 3. 4. Differentiate between data and information. Why information systems are so important in business today? What are main components of an information system? What is decision support system? 163