Martinez-Moyano & Luna - System Dynamics Society
advertisement

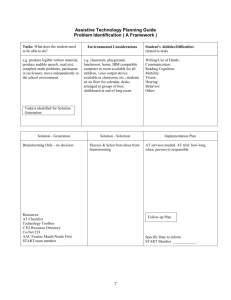
Generic Structures that Guide the Implementation of IT-Based Innovations in the Public Sector Sharon S. Dawes - CTG Anthony M. Cresswell - CTG Laura Black - MIT David F. Andersen - RC George P. Richardson - RC Luis F. Luna - RC Ignacio J. Martinez - RC Agenda • The opportunnity • How the idea was depeloped • The group modelling session – Pre-meeting activities – Meeting activities – Post-meeting activities • What is next The Opportunity • Past fall, MIT students visit to Albany – Laura Black presented to us her work with technology and Cross-Boundary Collaboration • The Center for Technology in Government at the University at Albany, – worked since 1993 to study just this process through implementation of Technology-Based Innovations in the Public Sector – Gateways to the Past, Present, and Future: Practical Guidelines to the Secondary Uses of Electronic Records How The Idea Was Developed Jan/2001 Mar/13/2001 Mar/20/2001 Mar/29/2001 Apr/13/2001 DFA starts talking with potential participants – Paper proposal Meeting with Tony Cresswell (CTG) – Group modelling approach Meeting with all the KDI team – Initial interest in the project Meeting with modeling group – HIMS project selected / session scheduled First modeling meeting – More than a paper Modelling Session Pre-meeting Activities • Create Script (Richardson and Andersen, 1995) – Roles • • • • • Facilitator Modeler/Reflector Process Coach Recorder Gatekeeper DA GR GR LL / IM AC • Get CTG approval • Create Concept Model • Complete logistics Meeting Activities 8:30 · · · · Review Agenda for the day Purpose, discussion and clarification Concept Model: a fast overview of final product Boundary Clarification – stakeholders, actors, sectors in the model, key variable (especially stocks) elicitation, key variables and the reference mode 10:20 BREAK 10:30 · · · · Stock mapping Feedback loop mapping Modeler Feedback Next steps and future tasks The Modelling Group David Andersen Donna Canestraro Meghan Cook Anthony Cresswell Mark LaVigne Ignacio Martinez Theresa Pardo George Richardson Fiona Thompson Luis Luna Rockefeller College Center for Technology in Government Center for Technology in Government Center for Technology in Government Center for Technology in Government Rockefeller College Center for Technology in Government Rockefeller College Center for Technology in Government Rockefeller College Concept Model People productivity Tasks to do Progress rate Finished work People on project Trust People Fraction of people assigned to project Trust building rate Trust built per task accomplished Trust erosion Time for trust to break down Concept Model Project and Trust Progress 600 450 300 150 0 0 10 20 Tasks to do : Final1 Finished work : Final1 Trust : Final1 30 40 50 60 Time (Day) 70 80 90 100 Task Task Task Concept Model Project definition Fraction remaining B People productivity Tasks to do Progress rate Effect of trust over productivity Finished work R People on project Trust People Fraction of people assigned to project Trust building rate Trust built per task accomplished Trust erosion Time for trust to break down Concept Model Project and Trust Progress 600 450 300 150 0 0 18 Tasks to do : Trust Normal Finished work : Trust Normal Trust : Trust Normal 36 Time (Day) 53 71 Task Task Task Concept Model Project definition Fraction remaining People productivity Tasks to do Progress rate Finished work Effect of trust over productivity People on project Trust People Fraction of people assigned to project Trust building rate Trust erosion R Trust built per task accomplished Time for trust to break down Concept Model Project and Trust Progress 600 450 300 150 0 0 10 20 Tasks to do : Normal Finished work : Normal Trust : Normal 30 40 50 60 Time (Day) 70 80 90 100 Task Task Task Key Variables Elicitation • Number of interactions or meetings • Level of the people involved • Trust – Providers role to the state – Providers trust to Bob and CTG – Providers trust among them – Individual trust • Feedback from work (evidence of listening) • Percent of HIMS developed • Level of engagement (at meetings) – Ownership • Level of leadership • CTG involvement amount and role • Providers appreciation about the value of HIMS to themselves Boundary Clarification 01/98 01/01 CTG ends its participation Business case/ smart IT tools Prototype Common service eval model Common data HIMS Leadership Financing Further develop Implementation Structure Elicitation component growth Common understanding of what and how Use of SMART IT tools CTG involvement Feasible prototype components Structure Elicitation component growth Common understanding of what and how Use of SMART IT tools Feasible prototype components Capacity to collaborate Willingness to collaborate Collaboration Trust CTG involvement Responsibiliy for collaboration Leadership Provider Engagement Structure Elicitation Pressure to be accountable Personal prior experience Demonstrated results Expectations Welfare reform pressure Bob activity component growth Opportunity to act Common understanding of what and how Use of SMART IT tools Feasible prototype components Capacity to collaborate Willingness to collaborate Collaboration Trust CTG involvement Responsibiliy for collaboration Leadership Provider Engagement Structure Elicitation Pressure to be accountable Personal prior experience Demonstrated results Expectations Welfare reform pressure Bob activity Bob used negative experience component growth Opportunity to act Common understanding of what and how Use of SMART Role of IT tools corporate partner CTG involvement Responsibiliy for collaboration Feasible prototype components Capacity to collaborate Willingness to collaborate Collaboration Trust Leadership BHS and QA engagement Provider Engagement Structure Elicitation Pressure to be accountable Personal prior experience Demonstrated results Expectations Welfare reform pressure Bob activity Bob used negative experience component growth Opportunity to act Common understanding of what and how Use of SMART Role of IT tools corporate partner CTG involvement Responsibiliy for collaboration Feasible prototype components Capacity to collaborate Willingness to collaborate Collaboration Trust Leadership BHS and QA engagement Provider Engagement Reflector Feedback Uncommitted providers Gaining commitment Loss of commitment Committed providers Reflector Feedback + Involvement of the State (BHS, QA) + Perceived Potential Involvement of CTG + Involvement of providers + Building + Perceived threat Level of commitment of the committed + Eroding R1 Uncommitted providers Gaining commitment + Loss of commitment Committed providers + Positive word of mouth Reflector Feedback + Positive prior expectations (process) +/- Feasible Prototype Components +/Satisfaction in demostrated results + Negative expectations (process) R2 Collaboration + + - + + + Involvement of the State (BHS, QA) + Perceived Potential Involvement of CTG + Involvement of providers + Building - + + Perceived threat Level of commitment of the committed + Eroding R1 Uncommitted providers + + Gaining commitment + Loss of commitment Committed providers + Positive word of mouth Reflector Feedback + +/- Feasible Prototype Components +/Satisfaction in + demostrated results + + R2 Collaboration + + - + Positive prior expectations (process) + + Involvement of the State (BHS, QA) + Perceived Potential - + + Perceived threat + Perceived validity of + the process Involvement of CTG Negative expectations (process) + Involvement of providers + Building Level of commitment of the committed + Eroding R1 Uncommitted providers + + Gaining commitment + Loss of commitment Committed providers + Positive word of mouth Reflector Feedback + - + Infeasible Prototype Components Vision + + Common + Understanding R2 + Collaboration + + + - + + + Involvement of the State (BHS, QA) + Positive prior expectations (process) Negative expectations (process) - + + Perceived threat Perceived Potential Trust + Perceived validity of + the process Involvement of CTG + +/+ +/- Satisfaction in + demostrated results + + Feasible Prototype Components + Opportunity/pressure to act + Involvement of providers + Building Level of commitment of the committed + Eroding R1 Involvement of Corporate Partner Uncommitted providers + + Gaining commitment + Loss of commitment Committed providers + Positive word of mouth What Is Next • • • • • Formulate the Model Second Meeting on May, 8th Poster in Atlanta Meeting Paper in SD Review or other Journal Obtaining funding to model other CTG projects • Dissertation