Production Planning
advertisement

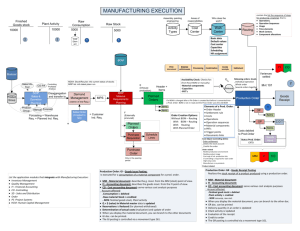
Production Planning Mixer Snack Bar Line Mixer Form Bake Pack Mixer Production (200) Mixer Finished Goods Warehouse (300) Raw Material Warehouse (100) Work Centers for Fitter Snacker Production Master Data Company Code Valuation Area Plant Work Center Material Master Routing Capacity Planning Production Orders Bill of Material Product Costing Navigating Material Master Views Click on tabs to select Use direction arrows to scroll Use icon to get list Material Types A Material Type is used to classify materials: Defines material attributes like: Valuation (value of material as market changes) Procurement (internal, external or both) Controls screen sequence and number assignment Can restrict access using authorization groups A number of material types are pre-defined Abbreviations are abbreviations of German terms Users can create their own material types Usually best to copy a pre-defined type, then modify Material Types in Exercises ROH: Raw material Externally purchased only, no sales view Oats, Wheat Germ, Honey, Cinnamon, etc. HALB: Semifinished Product No purchase or sales view Dough for NRG-A and NRG-B bars FERT: Finished Product Produced internally, has sales views, no purchasing views NRG-A and NRG-B bars Other Material Types HAWA: HIBE: VERP: LEER: KMAT: ERSA: DIEN: NLAG: UNBW: FHMI: WETT: PROD: IBAU: Trading Goods Operating Supplies Customer returnable packaging Empty containers Configurable material Spare parts Services Non-stock, non-valuated material Non-valuated, stocked material Production resources/tools Competitive products Product group Maintenance assembly Documentation in Material Master The SAP R/3 system documents all changes to the material master: Click for documentation Documentation in Material Master Master Data – Bill of Material BOMs are represented as single-level relationships between a material and its components and sub-assemblies ## NRG–A (case) BOM for NRG-A ## Dough NRG–A (lb) ## Oats (lb) ## Wheat Germ (lb) ## Cloves (lb) ## Cinnamon (lb) ## Canola (gal) BOM for Dough NRG-A ## Nutmeg (lb) ## Honey (gal) ## Carob Chips (lb) ## Raisins (lb) ## Vit/Min Powder (lb) Routings Routings define the relationship between a material and the sequence of workcenters (operations) that are required to produce the material Also specifies where sub-components and sub-assemblies are needed in producing the material 10 20 30 40 50 60 Functions of Production Orders (part 1 of 2) Status Management: Tracking, User-defined status Scheduling Calculation of Capacity Requirements (detailed) Costing/Collection of Costs Availability Checks (material, capacity, PRTproduction resources and tools) Printing of Paper Orders/related documents Assembly drawings and instructions Inspection instructions Storage regulations Material Staging: withdrawal of materials used in production, e.g. components and sub-assemblies Functions of Production Orders (part 2 of 2) Confirmations: quantities, activities, times Goods receipt: receipt of completed materials Period-end closing: Process cost allocation, overhead costs, surcharges, WIP (work-in-process) calculation, variance calculation, order settlement Archiving and retrieval Many more: rework, serial numbers, as-built, quality control, etc. Production Orders capture actual data— costs, dates, etc. Status Management (part 1 of 2) Status Management is one tool that can be used to manage released production orders A status can allow, allow with warning, or block a business transaction Two status types are available System status: internal, predefined, fixed number User status: freely definable, set by user Status Management (part 1 of 2) Status Status detail Planned Orders vs. Production Orders Planned Orders are for PLANNING Production Orders are for EXECUTION Planned Order 3 weeks in future Planned Orders 2 weeks in future Planned Orders 1 week in future Production Orders released today Planning Execution Master Data for Production Orders Master Data is data that does not change frequently Master Data for the production order comes from: Material Master Bill of Material (BOM) Work Center Routing Production Resources/Tools (PRT) Materials like gages, fixtures, test equipment Can also be items like drill bits that can be consumed in production but aren’t consumed INTO the product Most Production Order data comes from BOM and Routing Archiving & Deletion Order Request 1 16 Order settlement Order Creation 2 Availability Checks 15 Variance Calculation Goods Receipt 3 Production Order Cycle 14 13 WIP Determination 4 Machine Reservation 5 Order Release 6 12 7 11 Confirmation Upload from PDC system 10 8 Download to PDC system Print Order 9 Material staging Material withdrawal posting Routing Selection Different routings can be selected for a product depending on a number of criteria like: Raw material used Lot size Product features/configurations (variants) A complicated, automatic selection process can be configured Bill of Material (BOM) The system selects the FIRST Valid BOM it finds Validity can depend on: Date (engineering changes) Customer Serial number Material Material Material Material Assignment Assigned via BOM: All materials assigned to first operation OP OP OP OP OP …….. 0010 0020 0030 0080 0090 Assigned via Routing: Materials can be assigned to specific operations Material Material OP OP OP OP OP …….. 0010 0020 0030 0080 0090 Material