Terrorism - sunshinepasaquian
advertisement

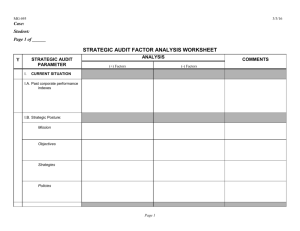
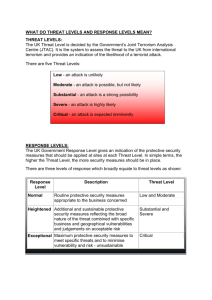
F/SUPT HERBERT B CEZAR Director Fire National Training Institute (FNTI) It is the premeditated, threatened, actual use of violence, force, or by any other means of destruction perpetrated against person/s, property/ies, or the environment. It is committed by any person or group of persons, whether natural or juridical, who, with intent to create or sow danger, panic, fear or chaos to the general public or a group of persons or particular person, or to coerce or intimidate the government to do or to abstain from doing an act. Threatening or causing death or serious bodily harm (on person or persons); Threatening or causing serious risk to health or safely of (the public or any segment of the public; Threatening or causing substantial damage or wanton destruction or resorting to arson on critical infrastructure or property, public or private; Threatening or causing serious interference with or serious disruption of an essential service, facility or system, whether public or private, other than a result of lawful advocacy, protest, dissent or stoppage of work; Hijacking or threatening to hijack any kind of aircraft, electric or railroad train, locomotive, passenger bus or oilier means of mass transportation, or public conveyance, or piracy of ship or sea vessel; Taking or threatening to kidnap or deprive any person of his/her liberty; Assassinating or threatening to assassinate, or kidnapping or threatening to kidnap the President or the Vice President of the Philippines, the President of the Senate, the Speaker of the Mouse of Representatives or the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court; Killing or violently attacking an internationally protected person or depriving the liberty of such person in violation of the Convention on the Protection and Punishment of Crimes Against Internationally Protected Persons, including Diplomatic Agents, and oilier international agreements; Attacking or threatening to attack the cyberspace, by destroying the actual machinery of the information and communication infrastructure, disrupting the information technology underlying the internet, government or private networks or systems, or committing any unlawful act against networks, servers, computers or other information and communication systems; Wilfully destroying the natural resources in land, water and air, such as forests or marine and mineral resources, or intentionally causing oil or toxic spillages, or other similar acts of destruction against the environment that threatens ecological security; Unlawfully manufacturing, processing, selling, acquiring, possessing, using, diverting, supplying or transporting chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear agents, or equipment and instruments used in their production, distribution, release or spread that would endanger directly or indirectly the safety of one or more individuals, or to cause mass destruction or great damage to property; or Unlawfully manufacturing, selling, acquiring, supplying, disposing, using or possessing explosives, bombs, grenades, projectiles, devices or other lethal weapons, or substances or machinery used or intended to be used for the manufacture of explosives in furtherance of, or incident to, or in connection with an act of terrorism defined herein. BALI BOMBING October 2002 WORLD TRADE CENTER September 2001 2005 Valentine’s Day Bombings “Mini-9/11 in the Philippines” Bus exploded into flames at least 3 persons killed Bomb detonated at a bus terminal 1 person killed Blast hit outside Gaisano Mall at least 3 persons killed SUPERFERRY14 BOMBING February 2004 “the WORLD's fourth deadliest terrorist strike since September 11, 2001, and ASIA's worst since the Bali bombings of October 2002”. -TIME MAGAZINE AUGUST 2004 LIST OF BOMBING ACTIVITIES THAT TRANSPIRED IN 2006 July 11, 2006 Mumbai, India eight coordinated explosions during the evening rush hour 190+ killed and hundreds injured. July 10, 2006 Sao Paulo, Brazil bomb Injures exploded inside a subway train More than 10 injured July 5, 2006 Yakhroma, Russia bomb exploded at a Muslim prayer house no casualties reported June 26, 2006 Suicide Attack in Colombo, Sri Lanka A top Sri Lankan general was killed along with several others June 24, 2006 Bangkok, Thailand two bombs exploded near the Thai Rak Thai (TRT) party headquarters June 23, 2006 Sharif Aguak, Mindanao bomb exploded near a public market 5+ people killed and 10 injured June 20, 2006 an explosion that occurred on a Makati street One injured June 13, 2006 pillbox bomb exploded inside Camp Bagong Diwa no reports of injuries a SWAT van sustained damage June 11, 2006 Lipa, Batangas grenade inside a bag exploded outside of a market at least nine people injured June 11, 2006 Commonwealth Avenue, Quezon City homemade bomb exploded near a parked bus no reports of injuries; bus sustained significant damage June 11, 2006 Plaza Lawton, Manila explosion hit a police station June 9, 2006 Pampanga grenade attack on the residence of a PGMA supporter June 6, 2006 Makati City improvised explosive device detonated outside the Great Pacific Life Bldg no reports of injuries March 29, 2006 Digos City, Davao del Sur bomb exploded inside a bus at least 17 people were injured the bus and three nearby vehicles sustained damages March 27, 2006 a bomb exploded in Jolo, Sulu 9 people killed, 20 others injured February 20, 2006 an explosion occurred inside the gates of Malacañang, Manila no reports of damage or injuries February 18, 2006 Jolo, Sulu a bomb exploded at a karaoke bar located several meters from an army base where US soldiers are participating in joint exercises with the AFP 1 person killed; 28 others injured January 30, 2006 Ermita, Manila a small improvised explosive device detonated in front of the Court of Appeals Bldg no reports of damage or injuries Any inimical act and/or unwanted event, which may bring about adverse results. Types of Threats Typhoon NATURAL Volcanic Eruption Earthquake Flood Erosion MANMADE TERRORISM Sabotage Technical or Financial Fraud Coup d’ Etat/Rebellion Labor Strike War TECHNOLOGICAL Plant Breakdown Breakdown or Failure of Protective Devices Environmental Hazards Subjects of Threats Nation Person Organization Infrastructures Community Key Assets Operations Areas of Threats Transport Terminals Business Facilities Public Conveyances Medical/Health Facilities Telecom Facility Emergency Service Facilities Power Facilities Road Infrastructures Water Supply Facilities Religious Institutions Government Buildings Educational Institutions Movie Houses & Malls Markets A condition used to describe the openness or weakness of a subject of a threat. The condition of vulnerability is directly influenced by the strength or weaknesses of a security or protective program. The chance that a given threat will occur and bring about adverse consequences. Importance of a subject of a threat as defined by its nature. Importance is directed towards: a. The subject of a threat itself b. Community and citizenry c. Any or all aspects of National Security Tangible and intangible outcome or consequence of a threat occurrence, such as loss, injury, disadvantage or gain. The product of threat probability and the sum of impact of a threat occurrence that can be inflicted against a target of an identified threat. The systematic and logical study of a given threat, its likelihood of occurrence and the severity of its impact, purposely for the formulation and implementation of an effective and efficient security program to detect, control or prevent losses. the probability that an undesirable event or threat may actually take place and inflict adverse consequences, including the failure to achieve goals and objectives. One is at RISK when: there is a threat the threat is probable to occur consequences if threat occurs 4TH STEP 3RD STEP 2ND STEP 1ST STEP The 1st Step of Risk Analysis involves the identification and profiling of a threat. Who offers the threat? Why the threat? THREAT Objectives of the source of threat? Likely specific targets? Modus Operandi? Helps in designing an effective and efficient security or protective program. are specific conditions that identify a threat. Also, they directly or indirectly influence the potential of a threat to exist or be present. Criticality or Nature of the Subject of Threat Internal & External Environment Historical Incidents/Events Nature & Criticality of Facility Operational Significance Financial or Business Significance Security Classification Work or Input-Output sensitive areas processes and Critical infrastructures and key assets (plus costs) Financial Status and Financial Operations Implications to national economy, politics, etc. security, Environment EXTERNAL Politico-socio-economic situations Geography, topography, etc Demography Presence of PNP, AFP and Emergency Response Agencies and their capabilities Presence of sources of threats in the area Global Situation INTERNAL Structural Design Landscaping Facility Occupants Facility Contents Security Personnel & their capabilities Presence of sources of threats inside the facility Organization Historical Event Historical Event Internal Incidents Security Dept External Incidents Government Private • Near-miss events • Actual events Other Depts RATING LEVEL 1 – 2 Very Low 3–4 Low 5–6 Medium 7–8 High 9 – 10 Very High Example: RATING 1. The facility provides electricity in entire Luzon. - 7 2. The facility is located in an NPA-infested area. - 9 3. The facility was attacked by NPA’s in 2003. - 8 = 8 Average Threat Potential The 2nd Step of Risk Analysis involves the identification and measurement of the weaknesses of the existing security or . protective program of a subject of a threat, as against the strength of the same security or protective program. Allows risk owners to know the strength of their existing Security Program, what needs to be corrected and what more are necessary to be put in place in defense against an identified threat. Vulnerability directly influences the probability of a threat to actually take place. WEAK SECURITY STRONG SECURITY Increases probability of threat occurrence Reduces probability of threat occurrence are specific security conditions that weakens or strengthens the security/protective program of a target of threat. absence of security or protective measures inadequacy of security or protective measures defective security or protective measures to empirically estimate the vulnerability of a target of threat. RATING Example: LEVEL 1–2 Very Low 3–4 Low 5–6 Medium 7–8 High 9 – 10 Very High RATING 1. No security guards are employed. - 7 2. Perimeter fence is below standard of 8 feet. - 9 3. Personnel Control Policy is not strictly enforced. - 8 Average Vulnerability = 8 The 3rd Step of Risk Analysis The probability that an identified threat is going to actually take place is measured using empirical parameters and tool. specific conditions that influence the probable occurrence of an identified threat. Threat Factors (Threat Potential) Vulnerability Factors PROBABILITY = Average Rated Threat Factors X Average Rated Vulnerability Factors 100 EXAMPLE: Probability of Terrorist Attack to occur THREAT FACTORS RATIN VULNERABILITY G RATI NG 1. Facility located in NPA - 7 1. Facility does not have - 9 2 . - 8 2 . - 7 = 8 area Facility already attacked once AVERAGE = 7.5 fence PROBABILITY = PROBABILITY = Facility does not have guards 7.5 XAVERAGE 8.0 100 0.60 or 60% PROBABILI TY LEVEL 0.00 Improbable 0.01 - 0.20 Very Low 0.21 - 0.40 Low 0.41 - 0.60 Moderate 0.61 - 0.80 High 0.81 - 1.00 Virtually Certain DESCRIPTION Given no changes, threat will not occur. Least chance of occurrence. Occurrence is less likely. There is 50:50 chance of occurrence. Occurrence is much greater. Given no changes, threat will certainly occur. The 4th Step of Risk Analysis The possible impact of a threat occurrence and their severity are identified and measured. GENERAL IMPACT Failure to achieve organizational goals & objectives Loss of lives Destruction or loss of infrastructures & key assets Destruction, disruption or loss of systems/operations Income losses Loss of information and competitive edge Loss of image, goodwill and reputation Adverse implications to all or any aspects of National Security OTHER IMPACTS THAT NEED TO BE CONSIDERED Geographic dispersion of potential damages Temporal extension of potential damages Requirements of restoring the situation to the state before the damages occurred (i.e., reforestation and detoxification of water) Violation of individual, social or cultural interests and values generating social conflicts and psychological reactions from those who feel inflicted by the risk consequences systems/operations PUTTING VALUE TO IMPACT Quantitative Lives lost & Cost Downtime period & cost Lost income Replacement Cost Restoration Cost Cost of property destroyed Qualitative Reputation Goodwill Patronage loss Morale loss Effects to others IMPACT SEVERITY = Average (Quantitative + Qualitative) X SAMPLE CASE QUANTITATIVE RATING 1. Building destruction worth P10.0M - 5 2. Income loss/day equal to P2.0M - 4 3. Death & injuries - 5 QUALITATIVE 1. Stoppage of services - 5 2. Loss of reputation/image - 4 3. Patronage loss - 5 AVERAGE IMPACT/LOSS RATING = 4.70 PROBABILITY = 0.60 IMPACT SEVERITY = (14 + 6 14) X 0.60 = 3.0 Probability RATI NG 1 2 3 4 LEVEL DESCRIPTION Improbab Effect is insignificant. le Can be covered by normal contingency services. Low Short discontinuance of operation. Noticeable impact on earnings. Moderate Requires attention of top management. Very Serious Major impact on balance sheet account. Requires changes in investment policy. Threat Potential Rating 8.00 Threat TERRORIST ATTACK Level: HIGH Vulnerability Rating Threat Probability Impact 0.60 4.70 Level: MODERATE Level: FATAL 8.00 Level: HIGH Impact Severity 3.00 Level: MODERATE In a complex and rapidly changing world, the day can instantly turn from friendly to hostile in a least expected time and with serious consequence … …thus, constantly “penetrating the fog of the future”, and managing the dangers beyond is a vital priority for all of us! F SR/SUPT HERBERT B CEZAR Director Fire National Training Institute (FNTI)