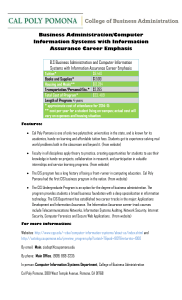
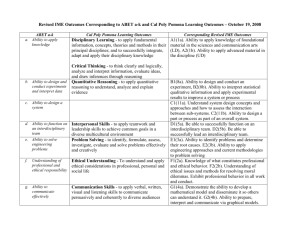
Selection of a Minimum Attractive Rate of Return (MARR)
advertisement

Selection of a Minimum Attractive Rate of Return Click here for Streaming Audio To Accompany Presentation (optional) EGR 403 Capital Allocation Theory Dr. Phillip R. Rosenkrantz Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering Department Cal Poly Pomona EGR 403 - The Big Picture • Framework: Accounting & Breakeven Analysis • “Time-value of money” concepts - Ch. 3, 4 • Analysis methods – – – – Ch. 5 - Present Worth Ch. 6 - Annual Worth Ch. 7,7A,8 - Rate of Return (incremental analysis) Ch. 9 - Benefit Cost Ratio & other methods • Refining the analysis – Ch. 10, 11 - Depreciation & Taxes – Ch. 12 - Replacement Analysis – Selection of the MARR EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 2 Selecting a MARR • MARR is generally the maximum of the: – Cost of borrowed money – Cost of capital – Opportunity cost EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 3 Sources of Capital • Money generated from the operation of the firm (retained profits and cash flow generated from depreciation). • External sources of funds: – Short term borrowing - banks (generally unsecured). – Long term borrowing - banks, insurance companies, pension funds, bonds (secured). – Permanent - sale of company stock. EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 4 Cost of Funds Cost of capital is the after tax weighted ROR of borrowed funds from all sources. Total capital invested (millions) $ 100.00 Bank loan Mortgage bonds Common stock and retained earnings Capital Structure % 20% $ 20.00 20% $ 20.00 60% $ 60.00 Cost of capital Tax rate Interest paid ROR 40% Taxes AT Interest cost $ 1.08 $ 0.84 9% 7% $ $ 1.80 1.40 $ $ 0.72 0.56 11% $ 6.60 $ - $ 6.60 $ 9.80 $ 1.28 $ 8.52 8.52% EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 5 Investment Opportunities • There are many investment opportunities in an active firm and often limited capital. • Opportunity cost is the ROR of the best opportunity foregone. Capital available $ 1,200.00 Project Number 2 4 3 5 1 6 8 9 7 11 10 12 Cost $ 50.00 $ 100.00 $ 50.00 $ 200.00 $ 150.00 $ 100.00 $ 250.00 $ 300.00 $ 200.00 $ 400.00 $ 300.00 $ 1,200.00 Estimated ROR 45% 40% 38% 35% 30% 28% 25% 20% 18% 15% 10% 8% ROR of Select Capital to Rejected Projects be Invested Projects 1 $ 50.00 1 $ 100.00 1 $ 50.00 1 $ 200.00 1 $ 150.00 1 $ 100.00 1 $ 250.00 1 $ 300.00 0 $ 18% 0 $ 15% 0 $ 10% 0 $ 8% $ 1,200.00 Opportunity cost 18% EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 6 Adjusting MARR to Account for Risk and Uncertainty • Increase MARR to avoid marginal projects. • Assess the projects using techniques other than economic analysis. Additionally, MARR might be adjusted to reflect imminent inflation. EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 7 Selecting a MARR • MARR is generally the maximum of the: – Cost of borrowed money – Cost of capital – Opportunity cost • If a project we are considering does not generate a greater return than these would cost, then we should put our money into these rather than the project. EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 8 Representative Values of MARR Used in Industry Group Small project Struggling One year payback One year payback = 60 % ROR = 60 % ROR Limited funds Stable Adequate funding Payback with a variable life Large project 12 to 15% After-tax In addition to these two factors,many other factors also affect interest rates: a public vs. a private organization, debt/equity position, risk posture, etc. EGR 403 - Cal Poly Pomona - SA16 9