Chapter 3 - westerncivilizationwhs
advertisement

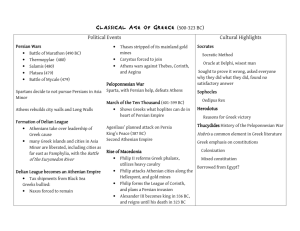
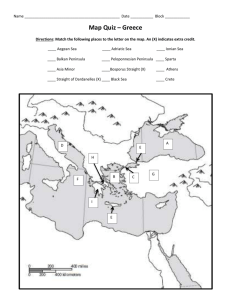
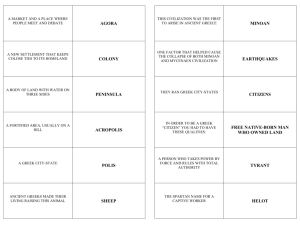
Chapter 3 The Civilization of the Greeks Timeline Early Greece Geography Mountains Sea Minoan Crete (c. 2000 – 1450 B.C.) Knossus Catastrophic Collapse (c. 1450 B.C.) Map 3.1: Ancient Greece (c. 750 – 338 B.C.) The First Greek State: Mycenae Mycenae Flourished between 1600 – 1100 B.C. Indo Europeans Powerful monarchies Fortified palace complexes Warrior society Trojan War Mycenae destroyed c. 1190 B.C. The Greeks in a Dark Age (c. 1100 – c. 750 B.C.) Period of Decline Farming revived (c. 850 B.C.) Migrations to Ionia Revival of some trade Use of iron Adoption of Phoenician alphabet Homer The Iliad • Trojan War The Odyssey Heroes The World of the Greek CityStates (c. 750 – c. 500 B.C.) The Polis Town or city and surrounding countryside Acropolis Agora Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities New military system Hoplites and Phalanx Colonization and the Growth of Trade Migration and Colonies Effects of Colonization Increased trade and industry Map 2.2: Greece and its Colonies in the Archaic Age Tyranny in the Greek Polis Tyrants Outside the law Favored interests of merchants and traders Tyranny in Corinth Decline of Tyranny (end of sixth century B.C.) Sparta Origins in Laconia Perioikoi and Helots Conquest of Messenia Lycurgan Reforms (c. 800 – 600 B.C.) Development of a military state (early 6th c. B.C.) Barracks and military life Spartan women Spartan society The Spartan State Two kings Ephors Assembly Isolationism Peloponnesian League Athens Attica Economic Problems Solon Economic reforms Political reforms Tyrants The Reforms of Cleisthenes Ten Tribes – Cross section of population Council of 500 (50 from each tribe) Democracy Greek Culture in the Archaic Age Influences Lyric Poetry Sappho of Lesbos Hesiod Works and Days Theognis of Megara Celebration of aristocracy The High Point of Greek Civilization: Classical Greece The Challenge of Persia Ionian Revolt (499 – 494 B.C.) Persian Invasion (490 B.C.) • Battle of Marathon (490 B.C.) Xerxes • • • • Renewed Persian invasion (480 B.C.) Battle of Thermopylae (480 B.C.) Battle of Salamis (480 B.C.) Battle of Plataea (479 B.C.) Map 3.3: The Persian Wars The Growth of an Athenian Empire in the Age of Pericles Delian League (organized 478 – 477 B.C.) Pericles Democracy • Magistrates • Ostracism Athenian Imperialism Control over Delian League The Great Peloponnesian War (431 – 404 B.C.) & the Decline of the Greek States Thucydides Spartan fear of Athens Athens – Naval Power; Sparta – Land Power Plague (430 B.C.) Death of Pericles (429 B.C.) Destruction of Athenian Fleet (405 B.C.) Athens Surrenders (404 B.C.) Greek States continue to fight among themselves Map 3.4: The Great Peloponnesian War (431 – 404 B.C.) The Culture of Classical Greece The Writing of History Herodotus (c. 484 – c. 425 B.C.) • The Persian Wars Thucydides (c. 460-c. 400 B.C.) • History of the Peloponnesian War Greek Drama Tragedies • Aeschylus (525-456 B.C.) • Sophocles (c. 496-406 B.C.) • Euripides (c. 485-406 B.C.) Comedies • Aristophanes (c. 450-c. 385 B.C.) Outdoor theater at Epidaurus The Arts: The Classical Ideal Architecture Temples Mathematical ratios found in nature Sculpture Ideal Beauty Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian Orders The Temple of Athena on the Island of Aegina Fifth-century B.C. Doryphoros The Greek Love of Wisdom Philosophy (“Love of Wisdom”) Sophists The art of the argument Socrates (469 – 399 B.C.) Socratic method Plato (c. 429 – 347 B.C.) The Republic The Academy Aristotle (384 – 322 B.C.) Politics Greek Religion Religion and Daily Life Festivals Gods and Goddesses Mount Olympus Olympic Festivals (began in 776 B.C.) Oracle of Apollo at Delphi Remaining Columns at the Oracle to Apollo Delphi Daily Life in Classical Athens 150,000 citizens – 43,000 adult males with political power Slavery Agricultural Economy Trade Artisans Lifestyle Family Life Women Male Homosexuality Discussion Questions What role did geography have on Greek history and civilization? What brought about the Dark Ages in ancient Greece? What were the main causes behind the development of democracy in Greece? Why was the polis the preferred form of government in ancient Greece? How did the Persian Wars lay the seeds for the Peloponnesian Wars? What were the defining features of Greek art? How did Plato’s Republic challenge democratic ideals? What impact did Greek philosophers have on the Western intellectual tradition? What function did festivals and public rituals play in Greek religion? Web Links Ancient Greek Sites on the World Wide Web Dēmos: Classical Athenian Democracy Encyclopedia Mythica: Greek Mythology Didaskalia: Ancient Theater Today Cultural Map of Hellas The Ancient City of Athens