Engineering Graphics & Design
advertisement

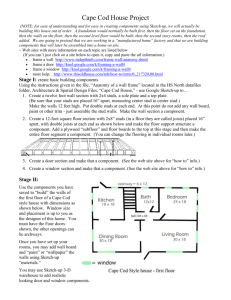
Engineering Graphics & Design Civil content NATIONAL CURRICULUM STATEMENT Grade 10 – Drawing basic floor plans of dwellings incorporating scale and dimensioning techniques. Grade 11 – Drawing single-level dwellings including foundation to ceiling using appropriate sections, scale and dimensioning techniques. Grade 12 – Drawing all aspects of single-level dwellings including foundation to roof, electrical wiring diagrams and plumbing using appropriate sections, scale and dimensioning techniques. Content Grade 10 Grade 11 Grade 12 Floor plan Elevations Sectional elevation Site plan & schedule of spec’s Foundation Foundation Foundation to floor slab to ceiling to roof GRADE 10 Brick and Block sizes Wall types Foundation DPC – Floor DPC - Wall Floor slab Floor plan Elevations Fixtures GRADE 11 Windows Doors DPC (Doors & Windows) Section of walls Detailed Elevations GRADE 12 Roof / Trusses Eaves (Open – Close) Site plan Plumbing Drainage Wiring Schedule of specifications EGD - CIVIL GRADE 10 BRICKS AND BLOCKS A block is defined as any building unit with a length greater than 300mm or a width of more than 130mm, any building unit smaller than this is called a brick. Brick size Block sizes Walls Walls are divided into different categories according to the purpose of the wall. Seeing as we only expect the pupils to design a one storey house the two most important walls can be divided into the following: a) load bearing walls and b) non loading bearing walls. a) Load bearing walls has a thickness of at least 220mm and mostly used for the shell of the house. These walls will usually carry the weight of the roof. There are two types of walls in this category namely, one brick walls and cavity walls. Cavity walls are mostly used along the coastal areas of the country or where there is high rainfall. The one brick wall is mostly used in drier areas like the interior of the country. The cavity is never less than 50mm and must be free of any cement. b) Non load bearing walls are usually used for the inside of the house to divide the house into rooms. They are also called half brick walls (110mm). Walls To strengthen walls we use welded wire mesh (brick force) and wall ties (see drawing). There must be at least 3 wall ties in every square meter of wall. Wire mesh is mostly used to strengthen the wall above doors and windows. The norm is to place wire mesh in between at least two courses above openings. These wall ties and wire mesh must be coated with a anti-rust coating (galvanized or plastic coating). There are two methods of drawing a wall when it is sectioned. The one method is used when the scale of the drawing is 1:20. In this instance we will indicate the individual bricks. When the scale of the drawing is smaller than 1:20 we will indicate the wall only as outlines. Walls Foundations Foundations must always be in solid ground. The foundation is one of the most important parts of the building. The following guidelines are given: 1. Foundations may not be thinner than 200mm. 2. Foundations for half brick (110mm), non load bearing walls may be 400 x 200mm. 3. One brick (222mm), load bearing wall may be a min size of 600 x 200mm. 4. Cavity (270mm), load bearing wall may be a min size of 730 x 230mm. 5. Foundations must be at least 150mm below the natural ground level (NGL) Foundations are also influenced by the soil structure (sandy, clay & rock). Foundations The floor of a house must be done on at least 150mm of compacted hardcore. Hardcore is defined as sand and small stones that will compact to a firm surface. Plant material and bricks must be removed when preparing the ground for compacting. To prevent moisture and water from seeping through the floor a SANS approved damp proof course (DPC) must be placed below the concrete floor. Before laying the concrete floor (slab), the cavity in a cavity wall must be filled with a weak mixture of concrete. The top level of the floor must be at least 250mm above the natural ground level. Take note of where the dpc is placed in the wall above the floor. Foundations A - HALF BRICK WALL A - HALF BRICK WALL 106 106 DAMP PROOF COURSE 85 DPC DPC DPC 200 COMPACTED HARDCORE COMPACTED HARDCORE NGL NGL 45° 200 400 400 Foundations B - ONE BRICK WALL C - CAVITY WALL 222 280 DPC DPC WEEP HOLE DPC COMPACTED HARDCORE 230 45° 200 NGL 600 730 Dimensions and areas of rooms Minimum area 6 m². Minimum linear dimension 2,1 m between walls. Habitable room. Height of ceiling. Minimum 2,4 m. Passages and bathrooms. Minimum ceiling height 2,1 m. Minimum floor area of a house 30 m². Lintel height of windows and doors 2,1 m Floor plan 7350 1110 RWG RWG 270 2500 1800 BEDROOM 1 270 270 1300 1770 1030 270 130 900 130 2770 270 2740 270 3800 270 645 3010 270 1030 270 395 4340 270 270 900 900 1170 1000 270 475 1000 900 900 480 900 130 600 270 475 3770 2280 2140 2410 7350 PLAN VIEW SCALE 1:100 270 270 3120 1820 12450 2070 1680 1200 900 130 270 270 MB RWG 4140 900 280 2420 1150 520 1550 1800 RWG 270 DB 520 4360 14.1 m² 1800 LIVINGROOM 1800 780 270 460 900 2000 130 1800 900 1180 1280 270 KITCHEN 130 270 275 12450 460270 655 900 130 900 BIC BIC 270 1860 900 130 580 6650 BIC BEDROOM 2 5800 1800 BEDROOM 3 Bathroom & Kitchen WASH CLOSET (WC) ZINK ZINK 470 1200 435 535 290 490 1235 360 WASH BASIN (WB) SHOWER (SH) BATH 800 712 420 860 570 1703 Elevations NGL NGL NGL NGL NORTH ELEVATION EAST ELEVATION SCALE 1:100 SCALE 1:100 NGL NGL NGL NGL SOUTH ELEVATION WEST ELEVATION SCALE 1:100 SCALE 1:100 EGD - CIVIL GRADE 11 Windows Windows provide light and fresh area to enter a room. There must always be cross ventilation in a room. The only door and window in a room is not allowed to be in the same wall. Windows are usually placed in such a way that the top of the window and the top of the door is at the same level. Take note of how dpc is placed around the window to prevent water from entering the house. Ventilation and illumination Any room must have a window. Window size Min 10% of floor area 5% opening including door. Must have cross ventilation. 1702 2255 1164 990 1733 HEIGHTS OF 984 IS ALSO AVAILABLE. 597 Wooden Windows WIDTHS OF 3200 IS ALSO AVAILABLE. 2648 1702 2255 1164 990 1733 HEIGHTS OF 984 IS ALSO AVAILABLE. 597 Wooden Windows WIDTHS OF 3200 IS ALSO AVAILABLE. 2648 359 1022 1511 949 654 533 949 HEIGHTS OF 1245, 1540 AND 1854 ARE ALSO AVAILABLE. Steel Windows WIDTHS OF 305, 2000 AND 2489 ARE ALSO AVAILABLE. 1511 Doors STANDARD GARAGE DOOR 2032 2125 STANDARD WOODEN DOOR 813 2440 Doors SLIDING DOORS ALUMINIUM 2090 2134 WOODEN 1830 SIZES AVAILABLE 1830 x 2134 2430 x 2134 3048 x 2134 3658 x 2134 1490 SIZES AVAILABLE 1490 x 2090 1790 x 2090 2090 x 2090 2390 x 2090 2990 x 2090 Window 106 126 HALF BRICK WALL 280 68 242 222 CAVITY BRICK WALL ONE BRICK WALL BRICK ON EDGE BRICK ON EDGE DPC DPC 222 300 68 280 Section NGL EGD - CIVIL GRAAD 12 ROOF TRUSSES DPC RAFTER CEMENT ROOF TILES TRUSS PLATE BATTEN KING POST TIE STRUT TILTING BATTEN CORNICE WALL PLATE BRANDERING TIE BEAM CEILING ROOF TRUSSES 21 0 2 1 2 20 1750 1750 1750 7000 KING POST TRUSS 1750 ROOF TRUSSES 28 28 87 87 3333 3333 10000 W - TRUSS 3333 ROOF TRUSSES 28 28 28 87 87 87 3000 3000 3000 15000 DOUBLE W - TRUSS 3000 3000 ROOF TRUSSES 23 23 23 09 09 09 4000 4000 12000 FAN TRUSS 4000 ROOF TRUSSES SIZES TIE BEAM RAFTERS KING POST TIE STRUT WALL PLATE 114 x 38 or 156 x 38 or 228 x 38 114 x 38 or 156 x 38 76 x 38 or 114 x 38 76 x 38 or 114 x 38 76 x 38 or 114 x 38 114 x 38 ROOF The last two courses, below the roof truss, in a cavity wall are closed up to strengthen the wall. A 4mm galvanized wire is used to tie down the roof onto the wall plate. This galvanized wire is build into the wall between three and six courses below the wall plate. The wall plate is a piece of wood (114 x 38) placed on the last course of the inside wall. The tie beam of the roof truss rests on this wall plate. The spacing of the roof trusses depends on the roofing material that will be used. The following is a guideline for the spacing of trusses. ROOF Trusses – (see resource pack) Slope Min 15°- max 30° Class A & C (A = Fibre cement. B = Metal plates). Slope Min 17°- max 35° Class B = Concrete tiles. Spacing of trusses: 760mm concrete tiles; 1400mm Metal plates Min pitch Sheeting material 5° - 22° Concrete & Clay tiles 17.5° (with underlay) ROOF Take note of how the roof truss is secured to the wall in the drawing provided. It is good practice to always place dpc below the battens on the roof truss. The drawings of the construction of roof trusses explain how to draw the different roof trusses. You will note that the tie beam and the rafter are always divided into equal parts. This is only a few of the roof trusses that are available on the market. Unplaned wood is indicated with two lines drawn diagonally from one corner to the other. Planed wood (PAR) is indicated by drawing freehand annual rings on the wood. EAVES CLOSED EAVES OPEN EAVES Sectional elevation DOUBLE ROMAN CEMENT TILES ON 38 x 38 BATTENS AT 340 c/c ON D.P.C. SHEETING ON SABS ENG. TRUSSES AT MAX. 760 c/c ON 110 x 38 WALL PLATE. 2100 2700 2700 6,4mm GYPSUM CEILING BOARD ON 38 X 38mm BRANDERING AT 450mm c/c. 25mm SCREED ON 85mm CONCRETE SLAB ON P.V.C. SHEETING ON 150mm COMPACTED FILL. DPC NGL 230 230 NGL 700 3450 400 SECTIONAL ELEVATION 2530 700 ERF NR 2351 1500 23679 BUILDING LINE RE1 1500 IE2 6526 10107 ERF NR 2304 SITE PLAN SCALE 1 : 100 ROWAN STREET 23679 ERF NR 2305 1500 27222 IE1 3000 27222 ERF NR 2303 PROPOSED NEW DWELLING 73.8m² SEWERAGE The drainage of a building must always be indicated on the site plan. All the roding eyes (RE) and the inspection eyes (IE) must be shown. A drainage pipe must have a roding eye every 25m. The fall of a drainage pipe must be a minimum of one meter for every sixty meters of pipe (1:60). Plumbing must be shown on the elevations. ELECTRICAL On the plan view the positioning of lights, plugs and switches are indicated. The position of the main board and the distribution board are also shown in the plan view. Schedule of specifications The schedule of specifications is where the draftsman will describe the different materials that will be used in the building proses, eg. Roof type, spacing of trusses, windows to be used, guttering, facias, ect. The schedule of specifications is usually printed to the side of the drawing page in a specially demarcated block. The name and contact detail of the draftsman must also be printed at the bottom of this block. The name of the owner of the property must also be printed. The street address and plot number of the proposed new dwelling must also be printed on the drawing. Some municipalities also wants the plot numbers of the neighboring plots to be printed on the site plan. Plan layout The following information should be drawn on a house plan: Floor plan – Drawn to a scale of 1:100 or 1:50. Outside and inside walls. Door and window openings. Fixed furniture such as sanitation, washing troughs, cupboards etc. All dimensions of rooms as well as the overall measurement of the building. Room descriptions. Electrical distribution. Floor levels. Layout of rooms such as kitchens and bathrooms as well as the positions of wardrobes. Sectioning drawing Foundation and floor levels. Height of walls and position of damp course (DPC). Roof truss construction and coverage detail. Natural ground level. Ceiling height. Door and window heights. Elevations North-; West-; East-; and South elevations Outside finishing detail of walls All window and door openings Gutter and down pipe detail Plumbing detail Site Plan Stand size, borders and dimensions. Stand number and adjoining stands. Servitudes and building lines. Vehicle entrance position. Sewer connection point and position of sewer line. Scale. Arrow to indicate position of true north. General information Name of Client. Name of architect or draftsman. Information about the area of the dwelling as well as the coverage area on the stand. Electrical distribution symbol explanation. Street name, stand number, township name etc.