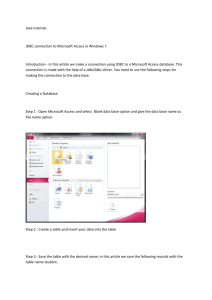
Java JDBC
advertisement

Java DataBase Connectivity
JDBC
java.sql.*
1
Java DataBase Connectivity
• Draft release of JDBC spec (3/96)
• Java API for executing SQL statements
(Since JDK 1.1)
• Primary focus is to link with RDBMS and
OORDBMS systems
• JDBC certification requires compliance with
ANSI SQL-2 spec.
• Initial support for access to ODBC through
JDBC-ODBC bridge
2
What does JDBC do?
• Establish a connection with a database
• Send SQL statements to the database
• Process the results.
3
Client Server Models
4
JDBC Architecture
• Implemented in 2 specific layers
• Driver layer
– Product / Vendor specific driver
implementations that convert JDBC syntax.
• Business Layer
– JDBC DriverManager and associated classes
that connect Java Applications to appropriate
drivers.
5
JavaSoft Framework
6
JDBC Drivers
• JDBC-ODBC Bridge
– A “quick startup” was needed, and there were many ODBC
compatible DBMSs in use.
• Native-API Driver
– Relies on client access to database-access API. Only
partially implemented in Java, and uses API binary code.
• JDBC-Net Driver
– Uses JDK network protocols to connect to server, which
then translated request into DBMS.
• Native Protocol - All Java Drivers
– Uses DBMS network protocol to connect to database.
7
JDBC Interfaces
(java.sql.*)
• java.sql.Driver
– acceptsURL, connect, getPropertyInfo
• java.sql.Connection
– createStatement, commit, prepareStatement, rollback
• java.sql.Statement
– execute, executeUpdate, getResultSet,
getMoreResults
• java.sql.PreparedStatement
– SetDate, setFloat, executeQuery, executeUpdate
8
JDBC Interfaces
(java.sql.*)
• java.sql.CallableStatement
– getByte, getTime, registerOutParameter
• java.sql.ResultSet
– getBytes, getMetaData, next
• java.sql.ResultSetMetaData
– getColumnName, getPrecision, isReadOnly
• java.sql.DatabaseMetaData
– allTablesAreSelectable, getColumns,
getDatabaseProductName,
supportsMultipleTransactions
9
Company table from zoo.mdb
10
SQL Queries
• SELECT * FROM zoo.company;
– Will select all fields for all records from the “company” table in
“zoo” database
• SELECT * FROM company WHERE state_cd =
OR;
– Will select all fields for records that have a state code of “OR”
• SELECT company_name, state_cd, postal_cd
FROM company where postal_cd > 60000;
– Will select 3 fields for all records that have a zip code larger
than 60000
11
SQL Queries
• SELECT company_name, phone_nbr FROM company
where company_name LIKE ‘%Artist%’;
– Will select 2 fields for all company names that contain the string
“Artist” preceded or followed by 0 or more char.
• String sql1 = “SELECT company_name, phone_nbr
FROM company where company_name LIKE ‘%” +
inputVar + “ %’ ”;
– Above query changed to allow dynamic definition of comparator.
•
INSERT INTO state_codes (state_cd, state_desc)
VALUES ('MO', 'Missouri');
– Will insert into the state_codes table a new record, with two fields state_cd, and state_desc, with values “MO”, and “Missouri”
12
JDBC Statement Types
• Statement (createStatement method)
– Used for simple SQL statements
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection(newurl);
Statement stmt = con.createStatement( );
String stmt = “Select * from retail_item where
retail_item_nbr = “ + somejavavariable;
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(stmt);
13
JDBC Statement Types
• PreparedStatement (prepareStatement method)
– Used for SQL statements that require 1 or more input arguments.
– Precompiled and stored for future use.
PreparedStatement pstmt =
con.prepareStatement("UPDATE EMPLOYEES
SET SALARY = ? WHERE ID = ?");
pstmt.setBigDecimal(1, 153833.00);
pstmt.setInt(2, 110592);
14
JDBC Statement Types
• CallableStatement (prepareCall method)
– Extension of PreparedStatement that can also
execute SQL stored procedures and process
results.
15
JDBC Connection process
• Get Connection implementation from
DriverManager
• Get Statement from connection
• Execute Statement
• Process ResultSet returned from query
• (For other statements check return value for
number of rows affected)
• Repeat for as many Statements as needed.
• Commit changes (if necessary)
• Close statement
16
Company table from zoo.mdb
17
JDBC Application
import
import
import
import
import
java.lang.*;
java.util.*;
java.sql.*;
sun.jdbc.odbc.*;
java.io.*;
public class sample1b
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
int id, zip, nextRecord;
float amount;
java.sql.Date dt;
String status, name;
String result;
18
JDBC Application
try {
//connect to ODBC database
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
String url = "jdbc:odbc:Zoo";
// connect
Properties p = new Properties();
p.put("user", "student");
p.put("password","sql");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"student","sql");
// create Statement object
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String sqlselect = "Select company_id, company_name, postal_cd"
+ " from company";
// run query
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sqlselect);
19
JDBC Application
// process results
while(rs.next()) {
result = "";
id
= rs.getInt(1);
zip
= rs.getInt(3);
name
= rs.getString(2);
result = result.valueOf(id) + " ";
result += result.valueOf(zip) + " ";
result += name;
System.out.println("Values are: " + result);
}
System.out.println("\n\n");
//create next (insert)query
String sqlSelect2 = "INSERT INTO company
(company_id,company_name,address_1,city,state_cd,country_cd,
postal_cd,phone_nbr) "+ "VALUES (9,'Bobs ISP',
'345 Main St','Grants Pass', 'OR', 'USA',97526,
'(541)582-1234')";
20
JDBC Application
int ct = stmt.executeUpdate(sqlSelect2);
System.out.println("Insert row: " + sqlSelect2.valueOf(ct));
sqlselect = "Select company_id, company_name, postal_cd"
+ " from company";
// run query
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sqlselect);
// process results
while(rs.next()) {
result = "";
id
= rs.getInt(1);
zip
= rs.getInt(3);
name
= rs.getString(2);
result = result.valueOf(id) + " ";
result += result.valueOf(zip) + " ";
result += name;
System.out.println("Values are: " + result);
}
21
JDBC Application
//create last (delete) query
System.out.println("\n\n");
sqlSelect2 = "DELETE FROM company WHERE company_name = 'Bobs ISP' ";
ct = stmt.executeUpdate(sqlSelect2);
System.out.println("Deleted row: " + sqlSelect2.valueOf(ct));
sqlselect = "Select company_id, company_name, postal_cd"
+ " from company";
// run query
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sqlselect);
// process results
while(rs.next()) {
result = "";
id
= rs.getInt(1);
zip
= rs.getInt(3);
name
= rs.getString(2);
result = result.valueOf(id) + " ";
result += result.valueOf(zip) + " ";
result += name;
System.out.println("Values are: " + result);
}
22
JDBC Application
//save your actions
con.commit();
//close connection
con.close();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
23
Sample JDBC Results
D:\data\cs423_fs00\java\jdbc examples>java sample1b
Values are: 1 99141 Some Shirt Company
Values are: 2 98272 Good Candy Company
Values are: 3 11455 Penns Pens
Values are: 4 56899 Close To You Magnets
Values are: 5 98151 Cute Critters
Values are: 6 98565 Seattle Signs
Values are: 7 59909 The Artist Group
Values are: 8 89980 Yummys
Values are: 0 64110 Bobs PCs
Insert
Values
Values
Values
Values
Values
Values
Values
Values
Values
Values
row:
are:
are:
are:
are:
are:
are:
are:
are:
are:
are:
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
0
9
99141
98272
11455
56899
98151
98565
59909
89980
64110
97526
Some Shirt Company
Good Candy Company
Penns Pens
Close To You Magnets
Cute Critters
Seattle Signs
The Artist Group
Yummys
Bobs PCs
Bobs ISP
24
Sample JDBC Results
Deleted row: 1
Values are: 1 99141
Values are: 2 98272
Values are: 3 11455
Values are: 4 56899
Values are: 5 98151
Values are: 6 98565
Values are: 7 59909
Values are: 8 89980
Values are: 0 64110
Some Shirt Company
Good Candy Company
Penns Pens
Close To You Magnets
Cute Critters
Seattle Signs
The Artist Group
Yummys
Bobs PCs
D:\data\cs423_fs00\java\jdbc examples>
25
Setting up ODBC in Windows
(NT, 2000, XP, Vista, 7(?) )
1.Verify that ODBC Data Sources (ODBC) is
loaded in Control Panel / Administrative
tools
26
Setting up ODBC in Windows
2.Open Data Source Administrator and add
source
27
Setting up ODBC in Windows
3.After selecting database type, add Source
name, and select specific database image.
28
Setting up ODBC in Windows
4.Add login Name and password
29
Transaction Support
• Consists of one or more statements that have been
executed, completed, and then either committed or rolled
back
• Default mode for statements is auto-commit
– Each statement becomes a “transaction”
• Can be disabled to support controlled commit or rollback
(for multiple statement transactions).
–
–
–
–
con.setAutoCommit(false);
con.commit();
con.setSavepoint();
con.rollback();
• Transaction support defined in DatabaseMetaData
30
Summary
• JDBC Allows Java programmers to build
customized interfaces to standard database
management systems through a number of
approaches.
• JDBC uses a standardized instruction syntax
(SQL) to send queries to databases
• The JDBC-ODBC bridge allows Java to use an
existing database connectivity method to gain
easy access to existing databases.
31