JDBC Basics
advertisement

JDBC Basics
Setting Up a Database
Data modeling:
- Entity types: different types of data to be stored in DB
- Relationship types: associations between related entity types
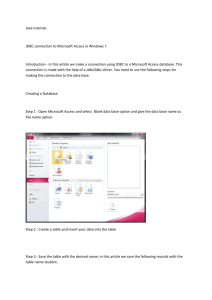
Use MS Access:
- Create a database:
o create tables
o set referential constraints (relationships between tables)
o enter initial data if applicable
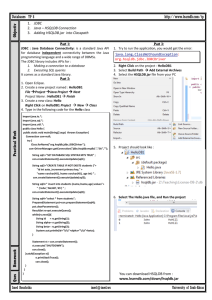
- Set up a data source on your (server) machine
o start | settings | control panel | administration tools | data source (odbc)
o add (a new user data source)
o select access db (.mdb) file and provide a name
Establishing a Connection
Import java.sql and java.net APIs
import java.net.URL;
import java.sql.*;
Loading Drivers
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
Making the Connection
String url = "jdbc:odbc:Grocery prices";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
Creating JDBC Statements
A Statement object is what sends your SQL statement to the DBMS. You
simply create a Statement object and then execute it, supplying the
appropriate execute method with the SQL statement you want to send. For a
SELECT statement, the method to use is executeQuery . For statements that
create or modify tables, the method to use is executeUpdate .
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
Executing Statements (actually, SQL queries)
- Insertion:
sqlString = "insert into FoodPrice (StoreKey, FoodKey, Price) "
+ "values (3, 6, '$3.99')";
insertStmt.executeUpdate(sqlString);
-
Selection:
sqlString = "select FoodKey, Price from FoodPrice " +
"order by Price";
selectStmt.executeQuery(sqlString);
JDBC-1/3
Retrieving Values from Result Sets
When executing a SELECT statement, JDBC returns results in a ResultSet object:
ResultSet prices = selectStmt.executeQuery(sqlString);
Using the Method next: works like the hasNext method of the Iterator type
while (prices.next()) {
// process each row in the result set
}
Using the getXXX Methods: you may retrieve fields in any type using getString
// hard-coded for a resultset with two fields in each row
for (int i=1; i<=2; i++)
// be careful: index starting with 1, NOT 0!
System.out.print(prices.getString(i) + " ");
Updating Tables
-
update:
String updateString = "UPDATE FoodPrice " +
"SET Price = '$0.75' " +
"WHERE FSKey = 3";
-
delete: apply to a whole record in a table, not just a few fields in a record
String deleteString = "DELETE FROM FoodPrice " +
"WHERE FSKey = 3";
Using Prepared Statements
When to Use a PreparedStatement Object
If you want to execute a Statement object many times, it will normally reduce
execution time to use a PreparedStatement object instead.
Compare the following equivalent code segments:
- Using normal statement:
String updateString = "UPDATE COFFEES SET SALES = 75 " +
"WHERE COF_NAME LIKE 'Colombian'";
stmt.executeUpdate(updateString);
-
Using prepared statement:
PreparedStatement updateSales = con.prepareStatement(
"UPDATE COFFEES SET SALES = ? WHERE COF_NAME LIKE ?");
updateSales.setInt(1, 75);
updateSales.setString(2, "Colombian");
updateSales.executeUpdate();
Useful Links
Sun’s online tutorial is a good starting point.
java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/jdbc/index.html
Jeff Schmitt's JDBC Page
http://triton.towson.edu/~schmitt/java/jdbc/
JDBC-2/3
A sample application
import java.net.URL;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
public class InsertTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String driver = "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver";
String url = "jdbc:odbc:Grocery prices";
try {
Class.forName(driver);
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
//get the metadata; not used in this sample
DatabaseMetaData dma = con.getMetaData();
// retrieving info from db
Statement selectStmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet prices =
selectStmt.executeQuery("select FoodKey, Price " +
"from FoodPrice " +
"order by Price");
while (prices.next()) {
for (int i=1; i<=2; i++)
System.out.print(prices.getString(i) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
selectStmt.close();
// inserting data into db
String insertSql = "insert into FoodPrice " +
"(StoreKey, FoodKey, Price) " +
"values (3, 6, '$3.99')";
Statement insertStmt = con.createStatement();
boolean failed = !(insertStmt.execute(insertSql //,
//Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS
));
System.out.println("Insertion failed: "+failed);
insertStmt.close();
con.close();
} //load the Bridge driver
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Check out groceries.mdb under lab9 for details about the database used for this
sample app.
JDBC-3/3