Coming Out as Kinky
advertisement

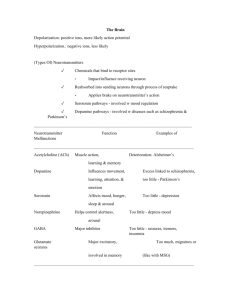
COMING OUT AS KINKY GEARUP 2015 Cal Domingue, MFT 7/10/15 Agenda • • • • • • • Mindfulness Emotions: their role Happiness Identity Groups Coming Out Exercise 2 MINDFULNESS Many styles • Grounded in Hakomi • Present: sounds, sensations, posture – Reactions, thoughts feelings • Loving Observer, compassionate witness EMOTIONS: THEIR ROLE Anthropology / Sociology • • • • Emotions are an evolutionary response Means of social communication Critical to group survival Each emotion has a role Emotions • Shame – Conformity to group rules (social norms) – Survival vs. straight white male dominance • Love / joy – Creates connections, interdependencies • Fear – Warn of danger, pay attention • Anger – Be strong, defend / attack Emotional Intelligence • Self-Awareness: recognize feelings as they occur • Managing emotions: appropriate reactions; modulate negative affect • Self-Motivation – focus on a goal, emotional self-control; deferred gratification; controlling impulsivity • Recognizing emotions in others: empathy • Relationships: skill in navigating others’ emotions HAPPINESS What is Happiness • Dave Robson: 5 Pillars – Know yourself; passion; trust your heart – Build awareness; positive mindset • Uplift Program: Murray & Fortinberry – Connection to others; self-esteem – Connection to your body, nature, spirituality • Dalai Lama – – – – – We have a right to be happy; happiness = a sense of wellbeing How we perceive our situation; how satisfied we are Impacted by our mindset and perceptions Basic physical needs must be met: food, clothing, shelter Love, affection, closeness, & compassion bring happiness Happiness: common threads • Basic needs met – Plan to provide for yourself • A choice • An attitude • Involves self-awareness – What actions bring you satisfaction (accomplishment) – What actions bring you joy – What interactions bring you joy – How are these impacted by your sense of self? July 27, 2013 Gifted Adults GPGC 2013 55th Reunion Copyright 2013 Cal Domingue, LMFT 11 IDENTITY Cultural biases • The Western mind favors the self-contained – Elevates individual and self-identity – Not good at implementing interdependence • Hinduism & Buddhism – interdependent co-origination – Experience of divisions, locations, and selfidentity are illusions, generated by the body, senses and the mind Four Take Home Messages 1. There are no single human beings – alone we die 2. The brain is a social organ – evolved for group survival 3. The cortex is shaped post-natally via social interactions 4. The brain can be changed, regulated and helped to heal in relationships Aspects of Identity • • • • • • • Cultural identity Ethnic identity National identity Religious identity Gender & sexual identity Labeling others & ourselves in categories Associating with certain groups – Comparison: comparing groups 15 GROUPS Identity in groups 1a : sameness of essential or generic character in different instances b : sameness in all that constitutes the objective reality of a thing : oneness 2 a : the distinguishing character or personality of an individual : individuality • The distinctive characteristic(s) belonging to any given individual, or shared by all members of a particular social category or group 17 Group & Identity • Others’ actions & thoughts have impact – Do we fit in? – Socialization and peer pressure • Other people’s attitudes – Acceptance or rejection of how other people attempt to influence the individual • GroupThink – Attitudes, who belongs, hazing, … 18 Belonging / Tribe • Majority / minority – In-group / out-group • Visible / hidden – Self-categorization – Categorization by others – Match or different? • Establishment of an easy-to-understand and consolidated sense of self or identity Brain: Mirror Neuron Systems • Sensory-Affective Link-up for Attunement – Imitation & Skill Building – Resonance & Coordination • Experiencing the other as a part of the self – Shared Emotion / Emotional Contagion – Sympathy – Empathy Brain: Social Engagement System • Tenth Cranial Nerve Network – Allows finer tuning of arousal than sympathetic – parasympathetic balance • Allows us to stay connected • Helps with matching emotional response to the social situation Engagement in Community • Initial Attraction – Phenylethylamine, norepinephrine, dopamine • Later stages of long relationships – Oxytocin, serotonin Neurochemicals • Serotonin: serenity, optimism, spiritual experiences • Norepinephrine: physical & mental arousal; heightens mood • Dopamine: motivation, pleasure, reward • Opiates: Modulate pain, reduce stress, bliss • Phenylethylamine (PEA) - “love drug”, modulates dopamine & norepinephrine • Anandamide: mood, appetite, memory, pain perception – binds & activates same receptors as weed • Oxytocin: bonding, emotional attachment, loyalty Kink / Leather / BDSM • Pain – physical & emotional processed same – Regulation: endorphins, noradrenaline, opiates, serotonin • Endogenous – produced by our bodies • Intense doses of same chemicals that cause pleasure • Community interactions / group scenes – Initial attractions: PEA, norepinephrine, dopamine – As relationships lengthen: oxytocin, serotonin Kinky Brains • Touch us in our vulnerability & strength • Brain pathways etched deeply through life – Brings intense focus to them – Opportunities to transform – Provide missing experiences COMING OUT Gay / Bi / Trans Coming Out • Series of Circles – Self – Private: friends, family – Public: colleagues, acquaintances, activities • Environments – Others who are same – Individuals / gatherings – Work – Social Media Generational Considerations The times, they are a’changing Younger • Less need for LGBT? • Less persecution (for some) • More comfort in mainstream, w/o need to establish specific identity • Need 2 B deeply seen Older • Strong need for LGBT • History of persecution for identity • Closet: hidden in mainstream • Integrated: Out in mainstream • Need 2 B deeply seen Reasons to Come Out (or Not) • Safety – What do others think – How do they react? • Consequences: job, isolation, rejection • Less need for specific identity (age-related) • Self-Acceptance – Integration: levels – Shame vs. privacy • Finding tribes: belonging in groups • Being seen& accepted for all of who we are Being Seen - Deeply • • • • Mirror neurons Experiences flood us with neurochemicals Community mirrors: fairs, weekends, parties Transformational opportunities Kinky & Happy • • • • Understanding what it means to you Understanding how it manifests in you Meeting individual needs What beyond that? – Partners, fun, growth – Adapting to changes • Goals – Emotional, psychological, spiritual, physical July 27, 2013 Gifted Adults GPGC 2013 55th Reunion Copyright 2013 Cal Domingue, LMFT 31 Kinky Community • Group Think • What’s OK? • What’s included? – Types of play – Roles • Dress • Hazing / ritual / process Coming Out Specific desires / preferences / roles • Dealing with attitudes including: – Slaves are simply property, not people (some) – Attitudes about masculinity • Internalized & in the community • Are tops somehow more masculine (better) • Dirty, dark side – Nastiness as part of the appeal – ‘Owning’ as positive what others demean • Gay, queer, black, etc… Coming Out about Fetishes • Animal play: puppies, pigs, ponies, … • Holes: – Which ones: ass, mouth, piss slit, – What do you put in them? Body parts? Toys? – Yours or theirs, or both? • Other body parts & practices – Finding others, place in community – Influenced by GroupThink & attitudes Coming Out about Limits • Is more better? – Not being shamed or forced by this belief • Some limits OK, not others? – For yourself – For the community Coming Out about Quirks • • • • Coming out as individuals Nerdiness Emotions & needs, shyness Disabilities or physical limitations, etc - • Community pressure to conform? • Community acceptance for all? EXERCISE Silent Gaze • Find partner – Sit facing each other – Establish mindfulness, closed eyes – Open eyes, in silence look into each others eyes • Notice what happens in yourself – – – – – Tension / relaxation Thoughts, emotions, sensations Easy or challenging Opening or blocking Want / desire / Come Out • Some aspect of kinkiness – Specific to that person – Not evident to community Summary • Define your challenges – Technological as well as personal • Set realistic expectation – Mastery is not achieved overnight • Keep your eye on the goal – Mentorship programs QUESTIONS? THANK YOU! BRAIN & NEUROBIOLOGY Attachment System • Affective Regulation via Proximity • Experiencing the other as a part of the self • Shaping neural structure via experience Social Neural Plasticity • Prenatal / Childhood epigenetic processes • Ongoing Neuroplasticity – Changes in attachment patterns – Healing early deficits Limbic System • Amygdala- regulates fear, anger, startle reflex • Hypothalamus- hormonal balance, appetite, sleep, wakefulness • Thalamus – pacemaker for cortical activity • Hippocampus- short term recall, context of emotional memory • Anterior Singulate Cortex- reward system, emotional processing Brain influences • Meditation: brain changes opposite of depression & anxiety • Negative emotions : right frontal lobes • Positive emotions: left frontal lobe • Advanced meditators – More left cortical activity – Lower cortisol, reduced startle response Serotonin • Serenity, optimism, spiritual experiences • Dysregulation: depression, eating disorders, suicidality • Regulates sleep, appetite, pain, mood • Effected by some anti-depressants • Hallucinogens alter serotonin in areas of brain affecting integrating sensory stimuli Norepinephine • Physical & mental arousal; heightens mood • “Fight or flight”: heart rate, blood pressure, etc. • Medications: target alertness, attention; alter blood pressure Dopamine • Arousal: motivation, pleasure, reward • Apathy, anhedonia, parkinsonism • Schizophrenia, mania, delusions, hallucinations • Meds: anti-psychotics, mood stabilizers Neurosteroids • Cortisol – Stress response, blood glucose, mood • Estrogen – Mood, neurotropic factor • Progesterone – Mood changes (mostly in women) • Testosterone – Aggression, dominance, ‘Type A’ behavior Opiates • Modulate pain, reduce stress, bliss • Suppress physical functionality: breathing, dependence • Endogenous: “runners high”, cutting, BDSM Other Factors • Phenylethylamine (PEA) – Amphetamine, found in chocolate, “love drug” – Modulator of dopamine & norepinephrine • Anandamide – Binds & activates same receptors as weed – Mood, appetite, memory, pain perception • Oxytocin – Bonding, emotional attachment, loyalty Oxytocin • Ability to trust: same brain circuits for love, friendship, generosity • Physically released when hug lasts more than 10 seconds • Released in social situations where we trust and love – – – – Trust: step-by-step process. Eye contact made; respond with smile Smile back; hold out our hand We trade gestures gestures, facial expressions and tones of voice: increase attunement (Mirror neurons, other structures) • Each tiny interaction builds trust by getting the oxytocin flowing • Also a signal that it's okay to trust a stranger – Whose actions resemble those of members of our tribe – Who’s like us