15 Fats
advertisement
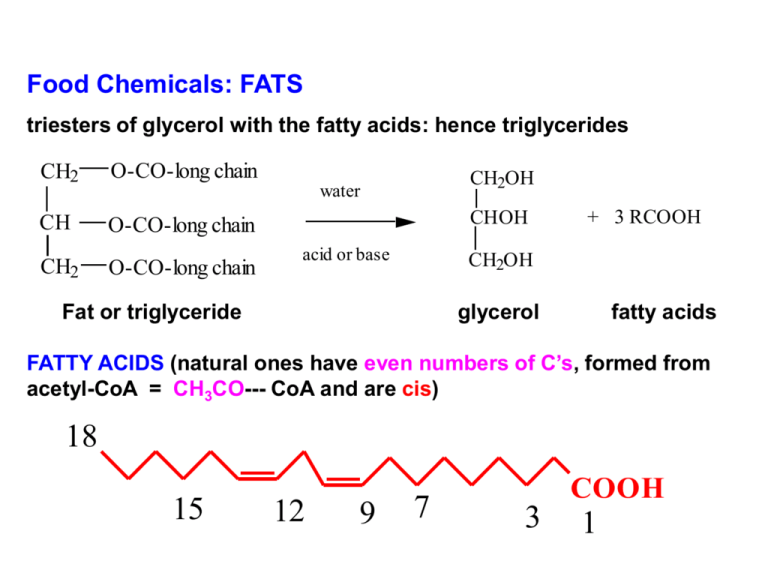
Food Chemicals: FATS triesters of glycerol with the fatty acids: hence triglycerides CH2 O-CO-long chain CH O-CO-long chain CH2 CH2OH water O-CO-long chain CHOH acid or base + 3 RCOOH CH2OH Fat or triglyceride glycerol fatty acids FATTY ACIDS (natural ones have even numbers of C’s, formed from acetyl-CoA = CH3CO--- CoA and are cis) 18 15 12 9 7 COOH 3 1 18 15 12 #C’S # DB'S 4/6 8/10 12/14/16 18 18 18 18 20 20 22 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 0 4 0 9 7 COOH 3 POSITIONS NAME Butyric/caproic Caprylic/capric Lauric/myristic/palmitic Stearic 9(-10) Oleic 9;12 Linoleic 9;12;15 Linolenic Arachidic 5;8;11;14 Arachidonic Behenic 1 SOURCE Butter Coconut Palm Beef fat Olive Oil Soy Bean Fish/Liver Peanut Fish/Liver Canola (Rapeseed) Systematic names: Butyric acid Caproic acid Capric acid Lauric acid Palmitic acid Stearic acid Arachidic Behenic = butanoic acid = hexanoic acid = decanoic acid = dodecanoic acid = hexadecanoic acid = octadecanoic acid = eicosanoic acid = docosanoic acid 4C 6C 10C 12C 16C 18C 20C 22C butane hexane decane dodecane hexadecane octadecane eicosane docosane DHA = docosahexaenoic acid 22C – 6 C=C (at 4,7,10,13,16,19 positions) - found in fish oils, membranes of eyes, brain Linoleic acid is essential in our diets (we can make the others) Arachidonic acid: COX enzymes convert to prostaglandins, etc. Iodine # = g I2 per 100g of oil (a measure of unsaturation) OIL % SATD % MONO % POLY IODINE # Coconut Butter Palm Lard Margarine Olive Peanut CANOLA Cottonseed Corn Fish Soybean Safflower Sunflower Linseed 93 6 1 57 44 36 46 7 10 15 21 7 26 14 73 49 61 22 29 12 30 32 52 57 14 10 11 24 14 19 62 76 70 8-10 25-40 37-54 45-70 80-85 75-95 85-100 ~115 100-117 115-130 120-180 125-140 130-140 130-145 170-205 All natural fatty acids are all cis: but can be isomerized to trans trans-isomers are higher melting than cis-isomers: solid fats vs. oils Saturated fats (no double bonds): pack better, higher Mp = SOLIDS Can increase mp of OIL by HYDROGENATION and/or ISOMERIZATION to get solids = margarine The more double bonds, THE HIGHER THE IODINE NUMBER a) BUTTER has IN=30, mostly C4-C6-C8 short chain saturated acids: IN varies with the milk source (diet of the cow) b) SOYA OIL has IN=120-140, mostly C18 with 2-3 double bonds: part hydrogenated, part isomerized to get Margarine, IN ~85 (NOTE: olive oil also has IN=90, but is all cis and thus is an OIL) CANOLA OIL used to be mostly C22 but selective plant breeding has produced modern Canola strains that are mostly C18: 7% satd; 61% mono unsaturated; 32% polyunsaturated Now mostly (91%) C18: C18-1 = Oleic (55%) C18-2 = Linoleic (26%) C18-3 = Linolenic (10%) so 0.91 x 26% = 21% Linoleic in Canola w-6 and w-3 oils 6 COOH 1st double bond at C-6 from end = w-6 COOH 3 1st double bond at C-3 from end w-6 FATTY ACID w FATTY ACID w g-Linolenic acid aLinolenic acid Plant Oils Fish oils Modern diets are high in w-6, about 10x the w-3, while old diets were about 1:1 Current theory is that w-3 gives lower blood triglyceride levels PLUS 1g of w-3 per day has been shown to give a 20% reduction in heart-related deaths Lack of w-3 leads to heart disease, thrombosis, atherosclerosis Modern Canola has about 11% w-3 while decreasing Erucic acid C22-1(13-14) to <1% Erucic acid was prevalent in old rapeseed oil and has been implicated in heart lesions As a matter of interest see: Monsanto vs. Schmeiser – a well-documented court case where Monsanto sued Schmeiser for patent infringement when he saved seeds from a Round-up Ready (a genetically modified Canola strain) Canola that had blown into his field from neighbouring areas Trans-fats (US and CAN require labelling) Modern margarine has some cis-bonds isomerized to trans to increase ‘solidity’: Hard margarine ~12% trans-fats Soft margarine ~5% trans-fats Becel 0% trans-fat but still ~12% saturated fat Current hypothesis: trans fats increase LDL’s a few % = a small increase in risk of heart attack Ban on use of trans-fats in restaurants comes into effect in BC in September ’09 (already adopted, then abandoned in Calgary) DISADVANTAGES of unsaturated fats: easier to oxidise -CH=CH-CH-CH=CH| H -CH=CH-CH-CH=CH• Allylic hydrogen is easily oxidised to a free radical which further reacts with oxygen to cleave the chain and produce SMELLY short chain fatty acids (under-arm sweat and rancid butter smell) An ANTIOXIDANT (usually ArOH) can supply a H• back to this free radical and reform the fat, before it has had time to react with oxygen: the resulting phenoxy radical ArO• is stable. NOTE: Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is 2-t-butyl-4-methylphenol and it is commonly added to cereals for the same reasons (next page) Hence need to protect fats with antioxidants: OH OH O HO OMe BHT BHA butylatedbutylatedhydroxytoluene hydroxyanisole allowed at 0.01-0.02% VITAMIN E a-tocopherol too expensive for food Note: in these the ArO• is highly crowded which makes it less reactive FLAVINOIDS eg. epicatechin are found in green and black teas, red wines and also have antioxidant properties: reduced heart disease? OH HO O OH ANTHOCYANINS R2, R5, R7 virtually always OH and other R groups may be OH Powerful anti-oxidants found as pigments in berries, flowers, vegetables, outer skins: blueberries, blood oranges, jalapeno peppers, purple onions, red apple skins, many others OH OILS: Vegetable oil production 80-100 Mtons/y mostly as Soy, Palm, Canola (about ~20% each) plus minor amounts of coconut and peanut oils Soft margarine has Low fat soft margarine has 80% fat 40%fat 16% water 56% water!!! Fats don’t dissolve in water, so have to emulsify them COO- Na+ -OOC -OOC COOCOO- -OOC -OOC -OOC COOCOO- A piece of dirt (grease): hydrocarbon tails embed in grease; water surrounds the COO- groups and the grease ‘dissolves’” For fats can use phospholipids: eg. Lethicin (egg yolks) C17H31COO-CH2 | C17H31COO-CH | + CH2OPO3CH2CH2NMe3 greasy end binds fat Remember bile acids transport fats thru the intestine for use Cholic acid: ionic end binds water Similarly mono- or diglycerides bind fats to sugars: C17H31COO-CH2 | CH-OH | CH2-OH greasy end binds fat this H-bonds to sugar -OH’s so used in shortenings, cakes and cookies: can get up to 40% sugar in a cake without it being ‘crunchy’; fats make cookies more ‘crumbly’ FAT SUBSTITUTES Some are ‘modified’ starches, have the texture of fat but 4 kcal/g rather than 9 kcal/g OLESTRA CH2OH H O H OHH HO O H OH CH2 O H HO H HO CH2 OH HO each -OH of sucrose is converted to a -OCO(CH2)6,7,8CH3 H the resulting molecule cannot pass through the intestine, so is not absorbed: because it is so ‘greasy’ it can lubricate the intestines too much so ‘anal leakage’ can occur carrying with it some fat soluble vitamins Natural Waxes are long chain acid / long chain alcohol esters: CH3(CH2)24/26COO(CH2)29/31CH3 = beeswax Carnauba wax (used for car polish and coatings on ‘no-mess’ candies like Smarties, M+M’s) contains some pendant HO~~~~COOH that polymerize and give it its hardness CANNOT DIGEST THESE Jojoba oil is an unsaturated ‘wax’ that is not metabolised: under study as a frying oil CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)mCOO(CH2)nCH=CH(CH2)7CH3 m = 9,11; n=10,12 chain lengths vary Used in cosmetics as a moisturizer and in many skin and hair care products; also under investigation as a diesel oil Cholesterol, Fats and Oils, Salt and Calories in Foods (per 100g) Food Cholesterol Beef, raw Chicken Cheese (cheddar) Corn oil Eggs, whole Hot dog, all beef Milk, whole Olive oil Margarine (Becel) Butter Tuna (canned) Salmon (canned) Peanut butter (unsalted) Yogurt (plain, skim milk) Oil or Fat (grams) Salt mg Satur Mono-un Poly-un mg 91 85 105 0 548 51 14 0 0 215 63 35 0 6 2.7 1.3 21.1 12.7 3.4 12.7 2.3 13.5 10.0 50.5 0.2 1.0 9.7 1.0 54 70 615 0 142 1026 40 0 700 576 338 487 17* 77 2.7 1.5 9.4 24.2 4.5 14.8 1.1 73.7 30.0 23.4 0.1 1.8 23.3 0.4 0.5 1.0 0.9 58.7 1.4 1.2 0.1 8.4 40.0 3.0 0.2 2.7 15.2 0.04 Cal 152 165 400 884 143 296 60 884 700 720 116 140 588 56





