Nutrition for the Critically Ill Neonate
advertisement

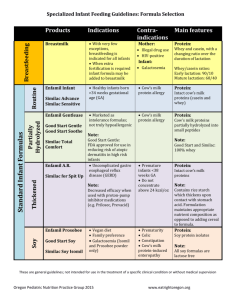
Formulas in the NICU Yvonne Sarson, MS, RD, CNSD Objectives NICU nurse will be able to Recognize the appropriate formula for his/her baby Identify key differences between infant formulas Identify babies who need routine vitamin and mineral supplements Nutrition Standards & Goals Nutritional Standards Standard for determining nutritional needs for term infants - human breast milk for preterm infants - growth rate that mimics in utero growth Adequacy of growth compared to standards – growth charts Birth weight charts – Babson, Fenton Growth charts - WHO Nutrition Goals Term Infant Enteral nutrition Preterm Infant Protein gm/kg Kcal/kg Protein gm/kg Kcal/kg 2.2 108 3.5 120 100 3.5 110 Parenteral nutrition 3 Energy needs Components of energy needs Kcal/kg/day BMR 40 - 62 Thermogenic effect of feeding 3 - 11 Activity 2- 4 Growth (15 gm/kg/day) 45 - 67 Total 90 – 130 (rarely 144) Fluid and Nutrition Needs - Term RDA for calories for term infant = 108 kcal/kg/day, 20 cal/oz breast milk has 68 kcal/100 ml, How much milk does the baby need to meet RDA? x ml/kg/day = 108 kcal ÷ 68 kcal X 100 ml = 160 ml/kg/day Fluids to meet nutritional needsenteral nutrition Formula KCAL density Volume to = 108 kcal/kg/day 120 kcal/kg/day 20 cal/oz (67.6 cal/100 ml) 160 ml/kg/day 180 ml/kg/day 22 cal/oz (74 cal/100 ml) 145 ml/kg/day 160 ml/kg/day 24 cal/oz (81 cal/100 ml) 135 ml/kg/day 150 ml/kg/day 27 cal/oz (91 cal/100 ml) 120 ml/kg/day 130 ml/kg/day 30 cal/oz (100 cal/100 ml) 110 ml/kg/day 120 ml/kg/day Comparison of nutrient concentrations of parenteral & enteral fluids Pro gm/dl Kcal/dl Expressed breast milk 1.1 68 Term Similac Advance, 20 cal/oz 1.4 68 Premature Enfamil Lipil, 20 cal/oz 2 68 Elecare, 20 cal/oz 2 68 PN 3 g Pro/kg, D15% @115 ml/kg 2.6 61 PN 3.5 g Pro/kg, D17%@ 115 ml/kg 3 80 PN 3 g Pro/kg, D12.5% @ 135 ml/kg 2.2 69 PN 3.5 g Pro/kg, D14.5% @ 135 ml/kg 2.6 81 Formula Ingredient Primer Carbohydrates Proteins Fats DHA ARA Prebiotics vs Probiotics Carbohydrates Polysaccharides – Starch and glucose polymers- from tapioca starch or cornstarch hydrolysis of carbohydrate polymers (cornstarch) by treatment with acid and then enzymes Cornstarch (complex) Maltodextrin Corn syrup solids Glucose polymers (or hydrolyzed cornstarch) Oligosaccharides – in breast milk (prebiotic effect) Influence microflora Alter bacterial adhesion Carbohydrates (cont.) Disaccharides – Lactose (glucose + galactose) Maltose (glucose + glucose) Sucrose (glucose + fructose) Monosaccharides – Glucose Galactose Fructose Protein sources Intact proteins Cow’s milk sources – milk protein concentrate, nonfat milk, Whey (whey protein isolate or concentrate) Casein Soy – soy protein isolate Protein hydrolysates – partially vs extensively Casein hydrolysates Whey protein hydrolysates Amino acids Fats of significance Medium chain triglycerides (6-12 carbon chain length) – ~12% of total fatty acids in human breast milk Added to all preterm formulas and some term formulas Long-chain triglycerides (>12 carbon chain length) Essential fatty acids (EFA) (18 carbon chain length); 4-5% of Kcal as EFA to prevent deficiency. Linoleic acid – 18: 2n6 Alpha-linolenic acid – 18: 3n3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids ARA (Arachadonic acid) – 20: 4n6; source is M. alpina Oil DHA (Docosohexanoic acid)- 22: 6n3; source is C. cohnii Oil, DHA and ARA Per 100 ml 24 cal DHA mg. ARA mg. Ratio Similac Special Care 11 17.6 1.6:1 Premature Enfamil Lipil 14 28 2:1 Nestle Good Start Premature 13.5 27 2:1 Prebiotics vs Probiotics Probiotics – Live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host. (WHO def.) Prebiotics – Non-viable food substances that stimulate the growth or activity of microbial flora (microbiota) in the digestive system which are beneficial to the health of the body. Most common now are non-digestible carbohydrates inulin, galacto-oligosaccharides and fructo-oligosaccharides Composition of Breast Milk and Formulas Human Breast Milk Gold standard for modeling term infant formulas Preferred source of enteral nutrition for all infants, including premature and sick newborns Protein – whey:casein ratio Contraindications- galactosemia, congenital lactase deficiency, maternal HIV or use of some medications early milk – 90:10 vs. mature milk – 60:40 CHO – lactose (40% of energy content) Fat – (40-50% of energy content); ~ 12% of fatty acids are medium chain Human Milk Fortification Commercial human milk fortifiers – cow’s milk based for infants <34 weeks or <1500-1800 gm at birth until ~2.5 kg. Higher calorie preparations or use in larger infants can provide excessive protein, fat-soluble vitamins & minerals Available as powders Commercial human milk fortifier – human milk based (Prolacta) designed to increase to 22-24 cal/oz, iron content varies Ex. - Similac or Enfamil Human Milk Fortifier Targeted for <1250 gm @ birth, for first 2 months of life Nutritionally comparable to Similac Human Milk Fortifier (low iron) Available as liquid – 4 different formulations designed to increase caloric density from 24 cal/oz – 30 cal/oz in 2 cal/oz increments Other powdered formulas and modular supplements may be used to fortify human milk for term infants or growing premature infants Major Formula Brands Enfamil (Mead Johnson Nutrition) Similac (Abbott Nutrition) Nestle Good Start (Nestle Nutrition) Higher levels of DHA & ARA supplementation than Abbott; now market standard with exception of Abbott All infant cow’s milk protein formulas contain only partially hydrolyzed whey protein as protein source (`5 formulas) Bright Beginnings (PBM Nutritionals) PBM also manufactures store brand infant formulas (`5 formulas) Standard Infant Formulas Protein – CHO – Source-lactose Fat – Source – cow’s milk Whey:casein ratio- 60:40 – 70:30, except Good Start (100% partially hydrolyzed whey) Source – variety of vegetable & tropical oils, DHA, ARA Examples – Enfamil Lipil, Nestle Good Start Gentle Plus, Nestle Good Start Nourish Plus*, Similac Advance or Advance EarlyShield, Bright Beginnings Milk *no DHA/ARA Premature Formulas Protein Source – cow’s milk protein – whey protein concentrate and non-fat milk CHO Whey:casein ratio- 60:40 Source-lactose & glucose polymers or corn syrup solids Fat – Source – MCT, soy & coconut oils or,high-oleic sunflower and safflower, DHA, ARA Vitamins & Minerals – higher fat-soluble vitamins esp. A & D, Ca & PO4 Indications – BW < 1800 gm & prematurity until hospital d/c or wt. ~ 2.7 kg. Examples – Enfamil Premature Lipil, Similac Special Care Advance, Nestle Good Start Premature 24 Premature Follow-up Formulas Protein – Source – cow’s milk protein – whey protein concentrate and non-fat milk Whey:casein ratio- 50:50 to 60:40 CHO – Source-lactose & glucose polymers or corn syrup solids Fat – Source – MCT, soy & coconut oils, DHA, ARA Indications – BW < 1800 gm until corrected age of 9 mos. Examples – Enfamil Enfacare Lipil, Similac Neosure Advance, Bright Beginnings Neocare Lactose-free cow’s milk formula CHO – Source- corn syrup solids; corn maltodextrin and sucrose (in Similac products) Lactose-free Indication – secondary lactase deficiency as after course of antibiotics carbohydrate malabsorption after colectomy Congenital lactase deficiency (exceedingly rare disease occurring in Finland Examples Enfamil Lacto-free, Similac Sensitive & Similac Sensitive R.S. Bright Beginnings Lactose-free (All soy, elemental & semi-elemental formulas are also lactose-free) Term formulas with Prebiotics Oligosaccharides (def.) – complex carbohydrates naturally occurring in human milk stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria support mucosal immune function Galacto-Oligosaccharides Early Shield (Similac), Premium (Enfamil) Term formulas with Probiotics Examples Good Start Protect Plus Bifidobacterium lactis Enfamil Nutramigen Lipil with Enflora LGG– Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) Cow’s Milk Formulas with rice starch Added rice starch Indications- formulas with rice starch added to provide nutritionally balanced feedings where providers would add rice cereal (not suitable for oral dysphagia) Examples Enfamil AR, Similac Sensitive RS Enfamil Restfull Cow’s Milk – low mineral Low mineral Indications- hypocalcemia or renal failure with hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia Similac PM 60/40 Cow’s Milk Formulas – Low LCT Low long chain fat – (High protein) Indications- Chylothorax Examples Portagen- powdered form, not marketed for infants, 4.7 gm fat/100 cal with 87% MCT 3.1% of calories as linoleic acid, trace alpha-linolenic acid Enfaport- liquid form (30 cal/oz as packaged), 5.4 gm fat/100 cal with 84% MCT 3.2% of calories as linoleic acid,0.5% of calories as alpha-linolenic acid Partially hydrolyzed protein Protein – Cow’s milk protein molecules partially broken down, but not as small peptide chains as semi-elemental hydrolyed Indications – marketed as easier to digest Examples Nestle Good Start Gentle Plus, Protect Plus, Nourish Plus, Enfamil Gentlease Bright Beginnings Gentle Partially hydrolyzed protein • Protein – – Cow’s milk protein molecules partially broken down, but not as small peptide chains as semi-elemental hydrolyed • Indications – marketed as easier to digest • Examples – Nestle Good Start Gentle Plus, Protect Plus, Nourish Plus, – Enfamil Gentlease – Bright Beginnings Gentle Soy formula Protein- soy CHO – lactose-free contraindicated in premature infants due to phytate content, lower protein bioavailability aluminum content Indication – term infant with galactosemia, vegetarian diet Elemental and Semi-elemental Formulas Protein – CHO – Source- sucrose, modified tapioca starch, corn syrup solids, or modified cornstarch Fat – slightly higher protein content than standard formulas Source – casein hydrolysates and/or L- amino acids Source – MCT, variety of vegetable and tropical oils Indications – protein sensitivity and/or malabsorption Semi-elemental Formulas Extensively hydrolyzed proteins Enfamil Nutramigen Lipil (no MCT) Enfamil Pregestimil Lipil, Enfamil Product 3232A (for CHO malabsorption, needs added CHO source) Similac Alimentum Advance Elemental Formulas Amino acids Neocate (SHS) Elecare (Abbott) Nutramigen AA (Enfamil) Increased Caloric Density Formulas Less water to powder increases nutrient intakes Additives may decrease other nutrient intakes Modular Additives Protein Beneprotein – 1.3 gm protein/tsp Carbohydrates Polycose - 8 kcal/ tsp Rice cereal – 4 kcal/tsp Karo syrup - 4 kcal/cc but not under 6 months old Fat Corn or safflower oil - 8 kcal/ml MCT oil - 7.7 kcal/ml Microlipid (safflower oil emulsion)- 4.5 kcal/ml Dietary Supplementation Vitamin D needs at NICU discharge Feeding Wt at discharge Vitamin D supplement dose* Predominantly breastmilk All 400 units Term formula < 6.2 kg. 200 units > 6.2 kg none < 4.2 kg 200 units > 4.2 kg none Neosure or Enfacare •Poly-vi-sol drops, 400 units Vitamin D per 1 ml •Enfamil D-Vi-Sol Vitamin D (D3) Supplement Drops, 400 units per 1 ml (50 ml bottle costs ~$11) Term Infants – Additional supplements Healthy Breast fed Iron after 4-6 months (usually enriched cereal) Fluoride after 6 months Formula fed – depending on intake Chronic diseases Multivitamin for chronic intake < 500 kcal/day Seizures treated with phenobarbital – extra Vitamin D Abnormal GI losses– ?need for zinc, copper, fat-soluble vitamins and electrolytes Preterm Infants – Stable, Growing No daily multivitamin mineral supplements premies on preterm formulas or human milk fortifiers Ex-premies on transitional/premature discharge formulas <4.2 kg If standard term infant formula or breast milk – multivitamins, folic acid, calcium, phosphorus, and zinc may be needed Need for iron supplements depends on milk & presence of anemia Bone meds Prevent need with optimal nutrition throughout NICU stay Refer to Calcium and phosphorus supplements used to treat osteopenia Target intake – 200 mg elemental calcium/kg/day 115 mg elemental phosphorus/kg/day Doses must be staggered to prevent formation of calcium-phosphorus precipitates Iron supplements Iron source Formulas provide ~ 2 mg/kg/day elemental iron per 160 ml/kg/day Growing, preterm infants @ 1-2 months or 2X BW. Healthy, term infants @ 4-6 months Dose (elemental iron) Preterm = 4-6 mg/kg/day Term = 2 mg/kg/day Max= 15 mg/day of supplemental iron Additional Issues Formula handling Enterobacter sakazakii - meningitis resulting in death linked to formula contamination; especially a concern with of cow’s milk protein formulas mixed from powder Tube feeding breastmilk Syringe pump vs kangaroo bag Home on continuous breastmilk feedings? Evaluation growth with Kangaroo pump vs obtain appropriate pump – Zevex Infinity Orange Sucrose containing formulas Fructose absorption –not fully matured in young infant Sucrose disaccharide (glucose+fructose) Fruit juice malabsorption is dose dependent Symptomatic malabsorption above 10 ml/kg/day Fructose content may be excessive for young infant if this is sole nutrition source (malabsorption/diarrhea Infant formulas containing sucrose Similac Alimentum – 2.2 gm/100 ml Similac Organic – 1 gm/100 ml Similac Sensitive – 3.3 gm/100 ml Similac Sensitive R.S. – 1.4 gm/100 ml Portagen – 2.9 gm/100 ml Formula company web sites Mead Johnson www.mjn.com Nestle nutrition www.nestleinfantnutrition.com Abbott nutrition Abbottnutrition.com PBM nutritionals www.brightbeginnings.com Nutricia www.neocate.com