Minerals and Energy/China - Denver Climate Study Group
advertisement

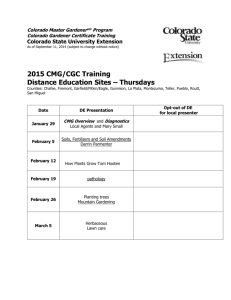
The Global Scramble for Minerals and Energy— Its Impact on Colorado Vince Matthews Director Colorado Geological Survey Harris D. Sherman, Executive Director YOUR Geological Survey !!! Geology of Water Resources Geologic Hazards Colorado Avalanche Information Center Educate Assist State and Federal Agencies Promote Mineral and Energy Resources Everything you need to know about Mineral and Energy in Colorado Production of Natural Resources is an Important Part of Colorado’s Economy $12.0 billion Revenue comparison of Colorado’s Important Economic Sectors (2005) 48% $ Billion 96% Minerals & Energy Tourism Distribution of Colorado Mineral & Energy Value 2007 ($ Billions) Uranium Coal 0.00 Minerals 1.1 Oil 1.8 1.5 CO2 0.5 7.0 Natural Gas Production of Natural Resources has Always been an Important Part of Colorado’s Economy Boulder 1902 Just off 51st Street China India U.S. Population Comparison 1400 China 1200 India 1000 800 600 400 U.S. 200 0 China U.S. India Land Area Comparison 10 9 China U.S. 8 7 6 5 4 India 3 2 1 0 China U.S. India GDP Comparison - 2007 13.8 14 U.S. 12 10 8 6 4 2 3.2 China 1.1 India 0 China Source: World Bank US India GDP Growth Comparison 2004-06 12 10.4 10 China 8.1 8 India 6 3.5 4 U.S. 2 0 Source: World BankChina US India World Electrical Growth World 8.3 terawatts increase (+70%) China/India/U.S. 4.4 terawatts World Electrical Growth U.S. 1.1 India 0.5 China 2.8 World Electrical Growth Africa EuropeEurasia South & Central America AsiaPacific Middle East North America China’s Share of World Mineral Production in 2005 Industrial minerals: Cement Fluorspar Rare earths Metals: Aluminum Antimony Copper Gold Lead Magnesium Molybdenum Silver Steel, crude Tin Tungsten Zinc % Rank 45 51 96 1 1 1 24 86 16 9 32 75 22 12 31 35 87 26 1 1 2 4 1 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 Source: USGS, Menzie and Tse China’s Production and Consumption of Copper 3.5 Copper production 3.0 Copper consumption Production supplemented by imports 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 2005e 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 0.0 1990 Million metric tons 4.0 Year Source: USGS, Kenzie, et al Global Impact 457% Global Impact Global Impact 307% Global Impact 457% 307% Colorado Impact Difficulty in manufacturing of copper products Increased copper thefts Increased costs to the consumer Copper mine reopening China’s Share of World Mineral Production in 2005 Industrial minerals: Cement Fluorspar Rare earths Metals: Aluminum Antimony Copper Gold Lead Magnesium Molybdenum Silver Steel, crude Tin Tungsten Zinc % Rank 45 51 96 1 1 1 24 86 16 9 32 75 22 12 31 35 87 26 1 1 2 4 1 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 Source: USGS, Menzie and Tse Leading Importers of Iron Ore— 1980–2003 160 Million metric tons 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 Year China Germany Japan United States Republic of Korea Sources: U.S. Geological Survey Minerals Yearbook; United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Trends in Demand for Steel Million metric tons 300 250 China Other Asia Europe Americas 200 150 2001 2002 2003 Year Source: International Iron and Steel Institute. 2004 China 2005 – Opened 70,000 new supermarkets 2006 – Became #3 car manufacturer 11th Five-year plan – 42% increase in capital investment - Plan to build the equivalent of three Manhattan Islands Price of Scrap Iron 559% Ball mill gets real Leadville welcome Image courtesy of Leadville Herald Democrat U.S. molybdenum exports Molybdenum Exports 41,400 45,000 40,000 34,500 35,000 30,000 21,900 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 0 2003 2004 2005 MOLYBDENUM Price 997% Ball mill gets real Leadville welcome Image courtesy of Leadville Herald Democrat MOLYBDENUM Price 997% MOLYBDENUM Price MOLYBDENUM Price ~ 100 Known Occurrences of Molybdenum Precious & Base Metal Increases Platinum 255% Aluminum 144% 01/03 - 01/09 Gold Silver 205% 367% Palladium 284% Lead 800% Nickel 630% Tin 229% Zinc 497% Antimony Bismuth 159% 671% Germanium Iridium 411% 193% Selenium Tellurium 1620% 8 1123% Cadmium 908% Chromium 581% 719% Magnesium 354% Manganese 580% Titanium Cobalt Rhenium 685% Tungsten Vanadium 2060% 600% 531% Increase in Coal Spot Price 37 40 35 30 25 20 17 15 2004 10 5 0 2005 2005 Coal Price Spot versus Contract 2007 $29.75 37 40 35 30 24.4 25 20 15 10 5 0 Contract Spot Metal prices fall further than during Great Depression The price of key industrial metals has fallen further over the last four months than occurred during the worst years of Great Depression between 1929 and 1933, according to research by Barclays Capital. By Ambrose Evans-Pritchard Last Updated: 7:29AM GMT 03 Dec 2008 “Chinese companies and their rivals are scouring the globe from Australia to Africa for access to the raw materials needed to sustain the Asian nation’s growth as commodity prices surge.” --June 23, 2006 (Bloomberg) Renewable Energy WIND - Neodymium - Molybdenum - Iron Ore SOLAR - Cadmium - Tellurium - Indium - Germanium - Gallium - Selenium - Silicon - Copper Strategic and Critical Materials with uses in Alternative Energy applications for which the U.S. is dependent on imports for 50% or more of consumption Commodity Antimony Barium Bismuth Cobalt Gallium Germanium Indium Manganese Nickel Platinum group Rare Earths Scandium Selenium Strontium Tantalum Tellurium Tin Titanium Vanadium Zinc Primary Sources China China China, Mexico Kinshasa,Australia China Belgium,Canada China, Canada Gabon, S. Africa Canada South Africa China China, Russia Canada Mexico Brazil Belgium, Germany Peru Australia, S. Africa Czech Rep., S. Africa Canada, Mexico Applications in Alternative Energy Thermoelectric/paraelectric materials Thermoelectric/paraelectric materials Thermoelectric/paraelectric materials Photovoltaics (solar cells) Photovoltaics, paraelectric materials Photovoltaics (solar cells) Solar cells, thermo/paraelectric materials Photovoltaics Fuel cells Fuel cells, para/thermoelectric mtrls Fuel cells, para/thermoelectric mtrls Thermoelectric/paraelectric materials Solar cells, thermoelectric materials Thermoelectric/paraelectric materials Thermoelectric/paraelectric materials Solar cells, thermoelectric metrls, semiconductors Thermoelectric materials Solar cells Fuel cells Photovoltaics, fuel cells, thermoelectric mtrls 120 Percent imported 100 80 60 40 20 0 In um i d S e el um i n Te llu m ir u V a an um i d R EE um l A a in al G li um M G P n Zi c r e e v in li S om r B REE = Rare Earth Elements = 15 + 2 neodymium, lanthanum, terbium, dysprosium Toyota Prius “The biggest user of rare earths of any object in the world!” HONG KONG — China is set to tighten its hammerlock on the market for some of the world’s most obscure but valuable minerals. --August 31, 2009 (The New York Times ) World faces hi-tech crunch as China eyes ban on rare metal exports –August 24, 2009 (London Telegraph) China Tightens Grip on Rare Minerals –August 31, 2009 (New York Times) As hybrid cars gobble rare metals, shortage looms –August 31, 2009 (Reuters) China Considers Rare-Earth Reserve in Inner Mongolia –September 2, 2009 (Bloomberg News) 2004 2003 Cement producers 1. China 2. India 3. U.S. 22% Imported China Consumes ½ of all the concrete in the world U.S. cement manufacturing is 81% foreign owned Fertilizers Potash $50/ ton > $200/ ton in 2008 Nitrogen urea $1000/ ton. Sulfur $50/ ton > $500/ ton in one year Energy Fertilizers Agriculture Sep-08 May-08 Jan-08 Sep-07 May-07 Jan-07 Sep-06 May-06 Jan-06 Sep-05 May-05 Jan-05 Sep-04 May-04 Jan-04 Sep-03 May-03 Jan-03 Sep-02 May-02 Jan-02 Sep-01 May-01 Jan-01 Sep-00 May-00 Jan-00 ( 2000 = 100 ) 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Metals/minerals Dr Colin Thirtle, Professor of Development Economics, Imperial College London U.S. Energy Split Coal Oil Natural Gas U.S. Energy Split 94% 6% Commodity Percent of U.S. energy supply Coal 22.8 381 0 Oil 39.8 306 67 8.4 481 89 Natural Gas 23.6 206 16 Hydroelectric Biomass Solar Wind Geothermal 2.5 3.6 .1 .3 .3 - - Uranium Percentage Price Increase 2003-07 Percent Imported (2007 Net) Source: EIA, Annual Report 2007 World Coal Consumption COAL Consumption- China China’s Production and Consumption of Coal 2,100 Coal production Coal consumption 1,700 1,500 1,300 1,100 900 700 Year 2005e 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 500 1990 Million metric tons 1,900 Coal Spot Price 2/06 – 2/09 $38China per ton begins importing coal $140 per ton COAL Consumption- India COAL U.S. China/U.S. Coal 54% of world production. 51% of world consumption. Colorado’s Coal is becoming increasingly desirable Colorado Impact Colorado Coal Production 1960-2007 Colorado is the seventh largest coal producer in the nation. Colorado has the seventh largest bituminous coal reserves in the nation. Colorado has the largest reserves of bituminous compliance coal in the nation. World Nuclear Consumption NUCLEAR- China NUCLEAR- India China : 32 new plants by 2020 4 per year through 2015 9 GW to 60 GW India: 17 new reactors by 2012 NUCLEAR- U.S. The last nuclear power plant came on line in 1996 Since then has U.S. nuclear generation -Increased? Decreased? Remained flat? NUCLEAR- U.S. Last nuclear power plant came online. And, the largest nuclear power generator in the world? The United States generates as much nuclear energy as— France, Germany, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom combined! World Nuclear Power Consumption 436 Plants Operating 44 Under Construction 50 - 60 Countries Applied to IAEA The world’s existing 436 nuclear reactors currently need 180 million pounds of uranium each year. 180 80 million pound gap 160 140 120 100 Million Pounds 80 60 40 20 0 Needed Produced Uranium prices Source: Cameco Uranium-vanadium districts and mines, Colorado Colorado Impact Three new mines opened in Colorado in 2008 10,000+ claims filed on federal lands in Colorado in 2005-6. 10,000+ claims filed on federal lands in Colorado in 2007. World Oil Consumption OIL CONSUMPTION- China Source: BP OIL- CONSUMPTION India Source: BP OIL- U.S. Consumption U.S. OIL PRODUCTION - 1900 to 2050 1.6 billion barrels PEAK 1970 40% less 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050 U.S. OIL PRODUCTION - 1900 to 2050 GONE: 2/3 OF U.S. OIL HAS BEEN USED. IT’S HISTORY. 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050 How do you communicate what “2/3 of something gone” means? In 1969, M. King Hubbert Predicted that World Production would Begin Declining in 2000. 90% 2004 80% 2000 50% of the OIL Consumed by the Human Race Used Since 1986 90% of the OIL Consumed by the Human Race Used Since 1959 1094 Billion barrels Consumed 70% 1995 60% 1990 50% 1986 40% 1980 30% 1975 20% 1969 10% 1959 Start 1859 1% 1924 5% 1948 (data from Arnulf Grubler, 1998; BP Statistical Review of World Energy, 2008) Copyright J. D. Hughes GSR Inc, 2008 Population Per Capita Consumption Total Consumption 45 times 8.6 times 5.3 times OIL OIL COAL HYDRO WOOD Year Year Renewable 11% COAL Non-Renewable 89% Percentage of 2007 GAS Year (data from Arnulf Grubler, 1998; BP Statistical Review of World Energy, 2008; U.S. Bureau of Census, 2008) Copyright J. D. Hughes GSR Inc, 2008 85% of the world’s oil comes from just 20 of the 65 producing countries 54 of the 65 producing countries are in decline Mexico’s declining production at Cantarell field accelerating Mexican state oil company Pemex said Wednesday that production at its Cantarell oil field, the world’s second-largest, will drop faster than expected. 08/03/06 2005 producing 2.2 million barrels per day 2009 producing 0.6 million barrels per day 1 of 65 producing countries USA Peak 1970 Source: BP Annual Energy Report 5 of 65 producing countries Mexico Norway UK Indonesia Peak 1997 Source: BP Annual Energy Report USA 50 of 65 producing countries Peak ~2000 Source: BP Annual Energy Report 45 small producers USA 61 of 65 producing countries Brazil Algeria Canada China Kuwait Iraq UAE Venezuela Nigeria Iran Libya Peak 2004 Source: BP Annual Energy Report 45 small producers USA 63 of 65 producing countries Qatar Angola Flat 2004 Source: BP Annual Energy Report 45 small producers USA 64 of 65 producing countries Source: BP Annual Energy Report Flat? 45 small producers USA 65 of 65 producing countries Source: BP Annual Energy Report Slight Increase FSU Former Soviet Union nations 45 small producers USA Crude Oil Prices Wattenberg oil well near Longmont 16th Largest oil field Colorado Impact 50.0 Colorado Oil Production - 1960-2006 45.0 40.0 35.0 30.0 25.0 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 Rangely still has large reserves (57R/65P). Commerce City refinery will be processing Canadian oil sands. 20 06 20 04 20 02 20 00 19 98 19 96 19 94 19 92 19 90 19 88 19 86 19 84 19 82 19 80 19 78 19 76 19 74 19 72 19 70 19 68 19 66 19 64 19 62 19 60 0.0 Oil shale is being seriously re-appraised. World Natural Gas Consumption NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION - China NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION - India NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION - U.S. Natural Gas – America’s Silver Bullet? Natural Gas Electrical Generation vs Natural Gas Imports 5000000 Electricity from Natural Gas 4500000 4000000 3500000 3000000 Imports 2500000 Electrical 2000000 1500000 1000000 Natural Gas Imports 500000 0 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 U.S. Monthly Natural Gas Production 2000000 8,900 30,180 Well Completions 1800000 1600000 Rockies Trends 1200000 1000000 Avg Reserves per Well Reserves Average Initial Production IP 1200 600 800000 1000 1128 500 528 800 400 600000 600 300 400 400000 439 200 200000 286 200 100 0 0 1998 2007 1998 2007 0 Ja n95 Ju l-9 5 Ja n96 Ju l-9 6 Ja n97 Ju l-9 7 Ja n98 Ju l-9 8 Ja n99 Ju l-9 9 Ja n00 Ju l-0 0 Ja n01 Ju l-0 1 Ja n02 Ju l-0 2 Ja n03 Ju l-0 3 Ja n04 Ju l-0 4 Ja n05 Ju l-0 5 Ja n06 Ju l-0 6 Ja n07 Ju l-0 7 Million Cubic Feet of Gas 1400000 Colorado Drilling Permits Approved Colorado Drilling Rigs Source: Baker-Hughes Source: Baker-Hughes Colorado Impact 1,600 1,400 1,200 1,000 Colorado Natural Gas Production 1960-2007 800 600 400 200 0 Colorado is the seventh largest gas producer in the nation. Colorado has the fifth largest gas reserves in the nation. Colorado has the largest reserves of coalbed methane in the nation. Location of the 78,000+ wells that have been drilled for oil and gas. About half are dry holes. Natural Gas Prices 8 $6.50 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 $2.00 +/- $0.50 21st Century Natural Gas Prices Colorado has all, or parts, of seven of the top 50 natural gas fields in the nation! Gas Price Needed to achieve a 10% IRR Piceance Basin Morgan Stanley Encana Morgan Stanley IHS 4/08/09 Delta Petroleum Drilled 163 Colorado wells Last month announced a loss of $459.7 million Next day stock dropped 41% Natural Gas – America’s Silver Bullet? 60% From Most Recent FOUR YEARS (data copyright IHS Energy, Diagram prepared and copyright by EOG Resources Inc., 2006) Natural Gas – America’s Silver Bullet? Conservation Natural Gas Oil Wind Solar Geothermal Biomass Efficiency Coal Hydro Nuclear Hydro Generation - China Hydro Generation – U.S. Geothermal Energy Direct Use Electric Generation Geoexchange Heat Pumps Below the 690 apartments—not to mention the gyms, bars, dry cleaners and movie theater—that make up the 15-acre Linked Hybrid residential complex in Beijing, China, are 660 geothermal wells that eliminate the need for air conditioners and boilers. Each well funnels water 325 feet beneath the ground into bedrock, where the constant 55ºF temperature either heats or cools it before it’s pumped back to the surface and piped through the building’s concrete floors. The system will reduce energy costs by up to 30 percent in the summer and up to 40 percent in the winter. The Escalator Dilemma Natural Forces are Working Against Our Goals The future is here! Are we ready? Overall Impacts Coloradans will suffer from effects of inflation Coloradans may see increasing shortages of critical raw materials Pressures will mount to develop more of Colorado’s natural resources Conflicts may arise with multi-national corporations operating in Colorado How do we turn lemons into lemonade? So– What is CGS doing? Working with GEO on geothermal electrical generation. Encouraging the use of Geoexchange heat pumps. Studying the potential of CCS. Studying the potential of alternative energy minerals in Colorado Trying to reduce our energy consumption Trying to increase public understanding of our energy situation. “The world is a football field now and you’ve got to be sharp to be on the team which plays on that field. If you’re not good enough, you’re going to be sitting and watching the game. That’s all.” --Rajesh Rao, founder and CEO of Dhurva Interactive The End! Of the talk, that is.