Chapter 24 and Chapter 25 Thunderstorm Hurricane Tornado Air
advertisement

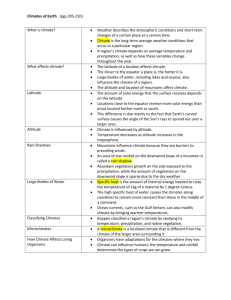
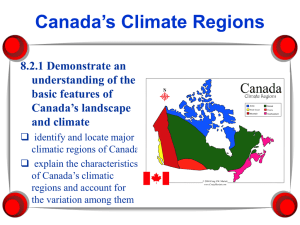
Chapter 24 and Chapter 25 Station model Thermometer Barometer Anemometer Wind vane Radiosonde Radar Cold front Chapter 8 and Chapter 9 Warm front Stationary front Occluded front Midlatitude cyclone Thunderstorm Hurricane Tornado Air mass(es) Climate Specific heat El Nino Monsoon Topical climate Middle latitude climate Microclimate Climatologist Global warming http://my.hrw.com/index.jsp?url=http://my.hrw.com/tabnav/controller.jsp?isbn=0030931509 24. Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how ari masses affect the weather of North America (different parts.) Compare the characteristic weather patterns of cold fronts with those of warm fronts. Describe how a mid-latitude cyclone forms. Describe the development of hurricanes, thunderstorms, and tornadoes. Identify four instruments used to measure lower atmospheric weather conditions. Describe how scientists measure conditions in the upper atmosphere. Explain how computers help scientists understand weather. Explain how weather stations communicate weather data. Explain how a weather map is created. Explain how computer models help meteorologists forecast weather. List three types of weather that meteorologists have attempted to control. On the white board, draw a current U.S. weather map showing symbols for fronts and wind. 25. Identify how major factors used to describe climate. Explain how latitude determines the amount of solar energy received on Earth. Describe how the different rates at which land and water are heated affect climate. Explain the effects of topography on climate. Describe the three types of tropical climates. Describe the five types of middle-latitude climates. Describe the three types of polar climates. Explain why city climates may differ from rural climates. Compare four methods used to study climate change. Describe four factors that may cause climate change. Identify potential impacts of climate change. Identify ways that humans can minimize their effect on climate change.