PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter12
advertisement

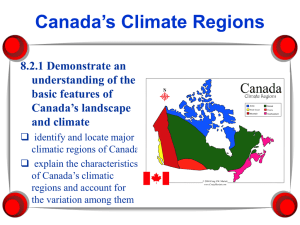
Chapter 12- Mid latitude climates seasonal temperature change greater than diurnal temp change I.e., winter to summer temp change is greater than daily min and max temperature ranges Two major source regions of contrasting air polar high = cold subtropical high = cold Mid latitude Temperature range Circulation is dominated by Westerlies- eastward motion associated with subtropical jet and polar jet Rossby waves- undulations in jetstream that enable airmass interaction Temperature is controlled by Insolation - higher in latitude the longer the daylight during summer Airmass origination- where the air gets its characteristics Wet all year (Dfa) Winter dry (Dfb) Summer dry (BWk) Most climate categories have several subcategories Cf ---> has Cfa, Cfb, Cfc, etc. Wet climates (no dry season) Climates dominated by sub-polar low pressure and frontal generated precipitation mid latitude cyclonic storms Typically located on the southeastern side of continents in Northern Hemisphere Cfa, Cfb, Cfc climate classifications Df climates in lower latitudes Winter dry climates (summer wet) Generally located in continental interiors loses effect of moisture from distant oceans during colder months e.g., northern Great Plains Mongolia Typically has extreme seasonal temperature ranges- related to lack of moisture & lat Continentality- a measure of influence of continental influence on moisture and temperature Summer dry climates (winter wet) Csa, Csb climates- commonly called a Mediterranean Climate as that region experiences this kind of climate also occurs along western margins of continents at higher latitudes •effects of oceans strongly influences climates Locations: California, southern Australia, and near the Mediterranean sea