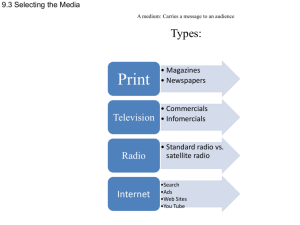
Marketing Activities
advertisement

1 Radio Advertising is Good when...... You need to reach local markets You have enough budget to advertise on several stations You have a simple message 2 Cost and efficiency Selectivity Flexibility Mental Imagery Integrated marketing opportunities 3 Creative limitations Fragmentation Chaotic buying procedures Limited research data Limited listener attention Clutter 4 You need to reach several segments that are fairly similar or they are going through the same hierarchy of effects You need to convey a dynamic message or one with strong visual imagery Your message can be grasped in 30 seconds You have an ample budget 5 Costs Lack of selectivity Fleeting message Clutter Limited viewer attention Distrust and negative evaluation 6 Creativity and impact Coverage and cost effectiveness Captivity and attention Selectivity and flexibility 7 You need to target special interest groups Magazine readers regularly read the ads A static, visual message can work well Customers are looking in the magazine for information on products they are seeking 8 Selectivity Reproduction Quality Creative flexibility Permanence Prestige Consumer receptivity and involvement Services 9 Costs Limited reach and frequency Long lead time Clutter and competition 10 Your target market segments are local A special interest group lines up well with a particular newspaper section An incentive is being advertised, or A special event of somewhat broad interest is being advertised 11 Extensive penetration Flexibility Geographic selectivity Reader involvement and acceptance Services offered 12 Poor reproduction Short life span Lack of selectivity Clutter 13 When price promotion is consistent with brand image or positioning When introducing a new product When trying to move inventory, or trying to get the most out of a bad idea (e.g. a clothing line that didn’t work out) Be careful what message is conveyed 14 - It is an incentive to get customers, channel members, or the sales force to take some action (like buying) There are 2 types Price reduction effect (e.g. rebates, coupons) Incentive based on something other than price (e.g. a contest) Always conveys one or more messages, intended or unintended 15 Getting attention Getting trial Getting purchase But again, be careful what message is conveyed 16 It is an extra incentive It is a sales accelerator, often The channel is the target It can be consumer oriented, trade oriented, or aimed at business customers 17 Power of retailers Lower brand loyalty More sensitivity to promotion More brands Fragmented consumer market Short term view More accountability Competition Clutter 18 Manage relationship with publics e.g. : Consumers Government Community Investors Employees General public Industry News media Publicity is managing relationships with news media 19 Credibility Cost Avoid clutter Generate leads Access to small groups Images building 20 Loss of control Hard to measure Incomplete communication 21