Name: Section, page numbers Main Ideas from the section in italics
advertisement

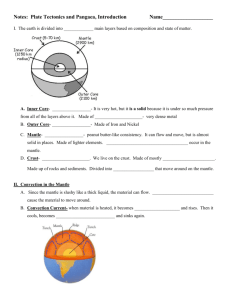
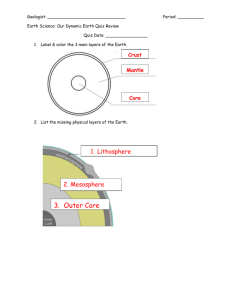
Name: Section, page numbers Main Ideas from the section in italics. Feel free to fill in your own (optional). Earth’s Interior 6 Questions for guided notes. If there is a dot next to a question, you must answer it in the space to the right. What happens to the lava when it flows over land? How have geologists found what is in Earth’s interior? Evidence from Rock Samples How do geologists get rocks from inside the Earth’s structure? Evidence from Seismic Waves Define seismic wave: How do seismic waves help geologists determine what is inside the Earth? What are the three main layers of the Earth? Exploring Inside Earth 7 A Journey to the Center of Earth Main Idea: Earth’s surface is constantly changing. Geologists use many methods to help identify what the layers of the Earth are made of. Main Idea: There are 3 different layers that make up in side of our Earth. Responses to vocab, questions and fill in the blanks. Seismic Wave: 1 2 3 Temperature As you go deeper into the Earth, what happens to the temperature? Name: Pressure Define Pressure: *The high inside Earth are the result of left over from the formation of the planet. Pressure: *The you go, the greater the pressure. The Crust (10) The crust is the outer layer of the Earth’s interior. In this layer are mountains and rocks. Define Crust: Is the crust the center, middle, or outside layer of the interior of Earth? Crust: On the crust you find and s. The crust also includes and water that cover large parts of Earth’s surface. The outer rind of rock is thinner/thicker (circle one) than the layer that lies beneath it. What is oceanic crust? Name: What are the 2 rocks that are found in this layer of the Earth? The Mantle 11 1. 2. Define Mantle Overall, the mantle is how many miles thick? The lithosphere Define lithosphere: Lithosphere: How many miles thick is the lithosphere? The asthenosphere Define asthenosphere Asthenosphere: Is the asthenosphere soft or hard? Lower Mantle The Core 12 What is the lower mantle like? The core is the inner layer of the Earth’s interior. What is the core made of? There are 2 parts of the core. What are they? Outer and Inner Core How thick is the core? Define outer core: 1. 2. Outer Core: Name: Define inner core: Inner Core: What do scientists believe the core is made up of? The Core and Earth’s Magnetic Field What layer do scientists believe gives us a magnetic field? Convection and the Mantle 14 Define heat transfer: Types of Heat Transfer 15 Main Idea: Heat always moves from a warmer/cooler substance to a warmer/cooler substance. Radiation What are the 3 types of heat transfer? Define Radiation: 1. 2. 3. Radiation: Conduction What are a few examples of radiation mentioned in the book? Define Conduction Conduction: What is an example of conduction from the book? Be specific Name: Convection Define Convection Convection: Heat can also be moved through and gases. Density: Convection Currents 16 Main Idea: Define Density: How do convection currents work through soup to heat it up? Be specific. Define Convection Current Convection Currents in Earth 17 Convection Current: Convection currents will continue as long as is added. Heat from the core and the mantle itself causes in the mantle. Main Idea: How do scientists believe convection currents are working in our mantle? What is happening to the rocks? Drifting Continents 18 Main Idea: Columbus and other individuals helped influence the idea of Pangaea by noticing all the In the 1700s, geologists believed that the continents had always in the same place. In the 1900’s, one scientists believed that the Name: continents fit together like a puzzle. Continental Drift 19 Main Idea: Wegener is a scientist who came up with the idea of Continental Drift. continents could have once been in a single landmass. What scientist hypothesized that Earth’s continents had moved? What did his hypothesis state? This idea became known as what? Define Pangaea: Pangaea: According to Wegener, Pangaea existed about million years ago. Wegener gathered from different scientific fields to his ideas about continental drift. He studied land features, , and evidence of change. Evidence from Land Features Evidence from Fossils Evidence from Climate What did Wegner notice when he pieced together maps of Africa and South America? Define fossil Fossil: As a continent moves toward the , its climate becomes warmer. As a continent moves towards the poles, its climate becomes Name: . Deep scratches in showed that continental glaciers once covered South Africa. Wegener concluded that when Pangaea existed, South Africa was much to the South Pole. This led Wegener to conclude that climates changed because the landmasses had moved. Wegener’ Hypothesis Rejected 22 Main Idea: Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift were rejected by scientists due to his inability to explain certain parts of his theory. What did Wegener have a difficult time explaining in his theory? For geologists to accept continental drift, they would also have had to change their ideas about how form.