Earth Science August 15, 2012 1.2 A View of the Earth Hydrosphere
advertisement

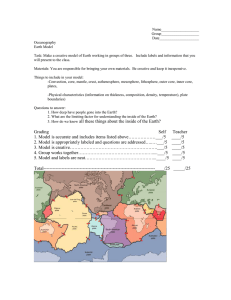
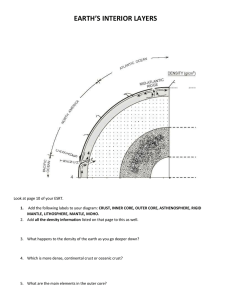
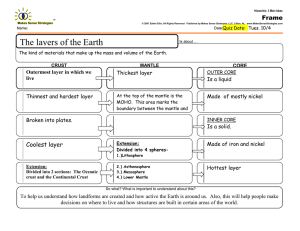
Earth Science August 15, 2012 1.2 A View of the Earth Hydrosphere water portions of the planet Atmosphere Earth’s gaseous envelope Geosphere The core, the mantle, the crust Biosphere All life on Earth Core Inner core (center) 1220 KM Outer core Mantle Lower 2260 Km 2890 Km Upper Km Crust not the same thickness difference is between 5 – 70 Km around the Earth (oceanic/continent Lithosphere The crust and uppermost mantle make a rigid outer layer Asthenosphere Under the lithosphere rocks become partially molten or melted due to uneven distribution of heat Lower Mantle Underneath the asthenosphere Destruction Forces Weathering/erosion work to wear down the high points/flatten out surfaces Constructive Forces Build up the surfaces by raising land/depositing new material in the form of lava Ex. Mountains, volcanoes Plate Tectonics The theory that the motion of the plates move slowly and continuously which generates earthquakes, volcanic activity and the deformation of large masses of rock into mountains