File
advertisement

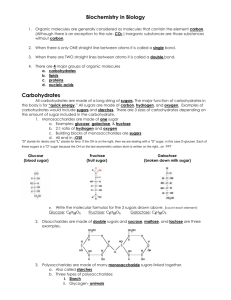
Biology Study Guide Section 2.3 Carbon Compounds Biological Macromolecules 1) What are the four groups of organic molecules that make up most of your body? a) _______________________ b) _______________________ c) _______________________ d) _______________________ 2) The molecules listed in question “9” are so large that they are referred to as ___. ______________________________________________________ 3) Look at the diagram to the right. What do you call the small molecules at the top? 4) What is a generic name for a whole bunch of tiny molecules linked together in a long chain? 5) What do you call the name of the process that links many monomers together to create polymers? _____________________________________________________________ Carbohydrates (pages 45 and 46) 6) What 3 elements make up carbohydrates? a) b) c) d) In what ratio do these atoms occur? _____ : _____ : _____. 7) Fill in the blank subscripts of the carbohydrate formulas below a) C6H____O_____ b) C____H8O4 c) C____H____O7 d) C8H____O____ 8) Which would NOT be a valid formula for a carbohydrate? a) C3H6O3 b) C3H8O3 c) C4H8O4 d) C5H10O5 9) Circle the letter of each sentence that that is TRUE about carbohydrates. a) starches and sugars are carbohydrates b) living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy c) the basic unit of carbohydrates are monosaccharides d) plants can use carbohydrates for energy AND strength 10) Look at the diagram to the right. When 2 monosaccharides are linked together, the polymer produced is called a a) monosaccharide b) disaccharide c) polysaccharide 11) A certain polymer is made of 200 monosaccharides linked together. It is known as a(n) a) monosaccharide b) disaccharide c) polysaccharide 12) Polysaccharides are long __________________ of monosaccharide monomers all linked together in huge chains. Plants and animals use these for __________________ storage. 13) How do plants and animals store excess sugars that they will use for ENERGY later (circle all that apply)? a) in long polymers called polysaccharides b) as starches c) as glycogen d) as cellulose (like in wood and paper) 14) How do plants and animals store excess sugars that they will use for STRUCTURE later (circle all that apply)? a) in long polymers called polysaccharides b) as starches c) as glycogen d) as cellulose (like in wood and paper) 15) Which of the following can be digested by your bodies? a) monosaccharides like fructose (found in fruits) b) disaccharides like sucrose (table sugar) c) polysaccharides like flour or oats d) polysaccharides like cellulose (found in paper and wood)