CARBOHYDRATE NOTES 2011
advertisement

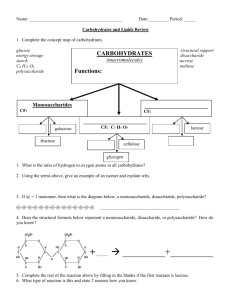
CARBOHYDRATE NOTES Carbohydrates Compounds containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Example: C6H12O6 Examples: Sugars & Starches Functions in the body Main source of energy Building Blocks – the basic building block of carbohydrates Example: Sugars Monosaccharide – single sugars; C6H12O6 Examples: Glucose (plants), Galactose (milk), Fructose (fruits) Saccharide Building Blocks, cont. Disaccharides – double sugars; C12H22O11 Examples: Sucrose (table sugar), maltose (malt sugar), lactose (milk) Check for Understanding In the reaction represented below, which molecules are considered the reactants? monosaccharide + monosaccharide --> disaccharide + water 1 monosaccharide and monosaccharide 2 disaccharide and water 3 monosaccharide and water 4 monosaccharide and disaccharide Building Blocks, cont. Polysaccharides – many saccharide units Examples: starches, glycogen (animal starch), cellulose (plants) Which molecule is an example of a carbohydrate? Food Energy 1 gram of carbohydrates is 4 calories Healthy Living Fact: •The best sources of carbohydrates—whole grains, vegetables, fruits and beans—promote good health by delivering vitamins, minerals, fiber, and a host of important phytonutrients. •Easily digested refined carbohydrates from white bread, white rice and other refined grains, pastries, sugared sodas, and other highly processed foods may contribute to weight gain, interfere with weight loss, and promote diabetes and heart disease. Check for Understanding Normally, when the concentration of glucose in the blood falls below a certain level, stored glucose reenters the blood until the original concentration is reached again. This regulation of the concentration of blood glucose is part of the process known as 1 synthesis 3 pinocytosis 2 respiration 4 homeostasis Color Code Instructions Glucose – red OH ends – blue Fructose – orange H ends - blue You have 5 minutes to color