Carbohydrates: Chemistry & Identification
advertisement

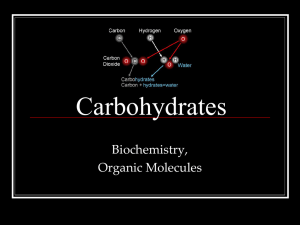
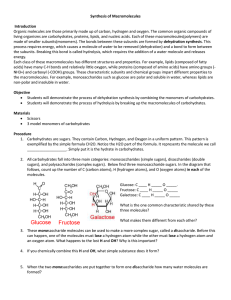
Name ___________________________________ Date ______________ Block _________ Carbohydrates: Chemistry & Identification Sugar, the building block of carbohydrates!! Carbohydrates are molecules made up of smaller molecules called sugars. The major function of carbohydrates in the body is for “quick energy”. There are 3 sizes of carbohydrates depending on the amount of sugars included in the carbohydrate. 1. Give the adjective for each of the following carbohydrates according to the amount of sugars in the molecule. a. 1 sugar: ___________________________________ b. 2 sugars: __________________________________ c. Many sugars: _______________________________ Carbohydrates are made of the elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen are in a ratio of 1:2 no matter what size of carbohydrate is being discussed. Refer to figure below for the structural formulas of 3 of the single sugar carbohydrate molecules. 2. What is the molecular formula for the the following monosaccharides? a. glucose: C ____ H ____ O _____ b. fructose: C ____ H ____ O _____ c. galactose: C ____ H ____ O _____ 3. What do you notice about the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in each monosaccharide? _____ 4. What is the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in the molecule water? __________________________ 5. What do you notice about all of the monosaccharide molecular formulas? ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. What is the difference between the monosaccharides? ________________________________ 7. What do the straight lines between the atoms in each molecule represent? ________________ 8. What does it mean when there are two lines in between atoms? _________________________ 9. When you put atoms together with the straight lines, are you storing or releasing energy? ______________________________________________________________________________ 10. What functional group is contained in a carbohydrate? _______________________________ When you want to make a disaccacharide, you must remove a hydroxyl group from one monosaccharide and a hydrogen atom from another. This leaves a place open on each of the molecules then to connect to each other. This process is called dehydration synthesis. Humans usually do this when they have already digested plant polysaccharides into their monosaccharides and now they want to make human disaccharides or polysaccharides. 11. In the figure below, what are the monosaccharides represented? _______________________ 12. What molecule has to be removed in the figure below in order to connect the two monosaccharides? ______________________________________________________________ 13. What is the name of the process shown in the figure below? __________________________ Name of process shown here?