Muscular strength
advertisement

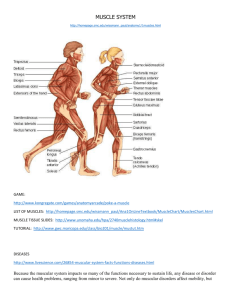
Chapter 6: Muscular Strength & Endurance Muscular Strength and Endurance Defined Muscular strength The ability of a muscle or muscle groups to exert maximal force against a resistance one time through the full ROM One repetition maximum (1RM) Muscular endurance The ability of a muscle or muscle group to exert sub-maximal force repeatedly over a period of time We often use muscular endurance to predict muscular strength Isometric (no movement) Isokinetic (same speed) or Isotonic (same resistance) 2 Benefits of Strength Training Health-Related Benefits Prevention of CVD Reduction and control of obesity & hypertension Improved self-confidence & self-image Development of good posture Improved body comp Improved flexibility Establishment of lifetime interest in fitness Skill-Related Benefits – Improved ability to perform basic motor skills – Possible prevention of injuries – Greater ease & efficiency of sport skill performance – Early development of coordination & balance – Better performance on nationwide fitness tests 3 Myths About Muscular Strength and Endurance Protein Women and lifting Spot training The weight loss balance Body building vs. weight training Size ≠ Strength Supplementation 4 Major Muscles in The Human Body How the Muscles Work Muscular contraction (pull only, no push): -cock-connect-pull-release (cross-bridge cycling) http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/movies/actin_myosin_gif.html 6 Principles of Weight Training Overload Doing more than you are used to Progression Gradually increasing overload (frequency, intensity, time or some combination) Specificity Choose activities that target desired systems Regularity “Use it or lose it” Individuality Start at your base fitness level, using your own goals and keep your genetics in mind FITT ○ Frequency (how often) ○ Intensity (how hard) ○ Time (how long) ○ Type (mode) 7 FITT Guidelines Applied to Muscular Fitness Table 6.1 AGES 9-11 YEARS 12-14 YEARS 15-16 YEARS 17+ YEARS FREQUENCY 2 -3 days / week 2 -3 days / week 2 -3 days / week 2+ days / week INTENSITY Very light weight Or body weight Light Weight Moderate Weight Light to heavy weight (based on type selected) TIME At least 1 set (may do 2 sets) At least 1 set (may do 3 sets) At least 1 set (may do 3 or 4 sets) Min. 1 set 6-15 reps 6-15 reps 6 – 15 reps 20-30 minutes 20-30 minutes 20-30 minutes 8-12 reps (based on type selected) Major Muscle groups Major Muscle groups Major Muscle groups Major muscle groups 1 exercise per muscle or muscle group 1 exercise per muscle or muscle group 2 exercises per muscle or muscle group 8 – 10 exercises TYPE select muscular strength, power or endurance 8 Professional Guidelines & Recommendations Professional position statements on youth strength training (ACSM, 2006; AAP, 1990; NSCA, 2007). ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Proper supervision & technique instruction are critical Focus on technique development & affective domain Emphasize a variety of activities & skill development Avoid the use of maximal lifts with children & adolescents Sample training protocol: Initial focus on lifting technique High reps & light weight 1-3 sets x 6-15 reps 8-10 different exercises 2-3 nonconsecutive days per week 9 General Resistance Guidelines ACSM 10 Basic Structure of WT Session Dynamic Warm up - Not many static stretches Total body or isolated resistance training Cool down - Lots of static stretches 11 Exercise Safety Guidelines Train all major muscle groups Large small Opposing muscle groups Strengthen the core Never lift alone Warm-up & cool-down properly Control speed (2-1-4 second count) Use the full range of motion Avoid breath-holding Pay attention to pain and excessive fatigue Assessment of Muscular Strength 1 Rep Max Testing Max Conversion Using Factors Should only be done Number of Reps Factor 2 1.025 3 1.05 4 1.075 5 1.10 10 RM max 6 1.125 2 – 12 rep max 7 1.150 Pg. 92 chart 8 1.175 9 1.20 10 1.225 11 1.250 12 1.275 in lab setting HS WT Two ways: Strength Training Programs Can Include Strength training exercises Dietary guidelines Core strength training Pilates exercise system Stability exercise balls Resistance bands Medicine balls Body weight exercise Plyometrics Resistance Training for Elementary Students It is NOT developmentally appropriate to lift heavy weights ○ Body weight training ○ Light weight / High reps ○ Partner resistance training ○ Resistance bands ○ Medicine balls 15 Things to Remember Use training principles - FITT, Progression, Overload, Specificity, etc… Benefits How Muscles work Structure of each type of workout Safety guidelines and myths 16