Digestion Essential Question Chart
advertisement
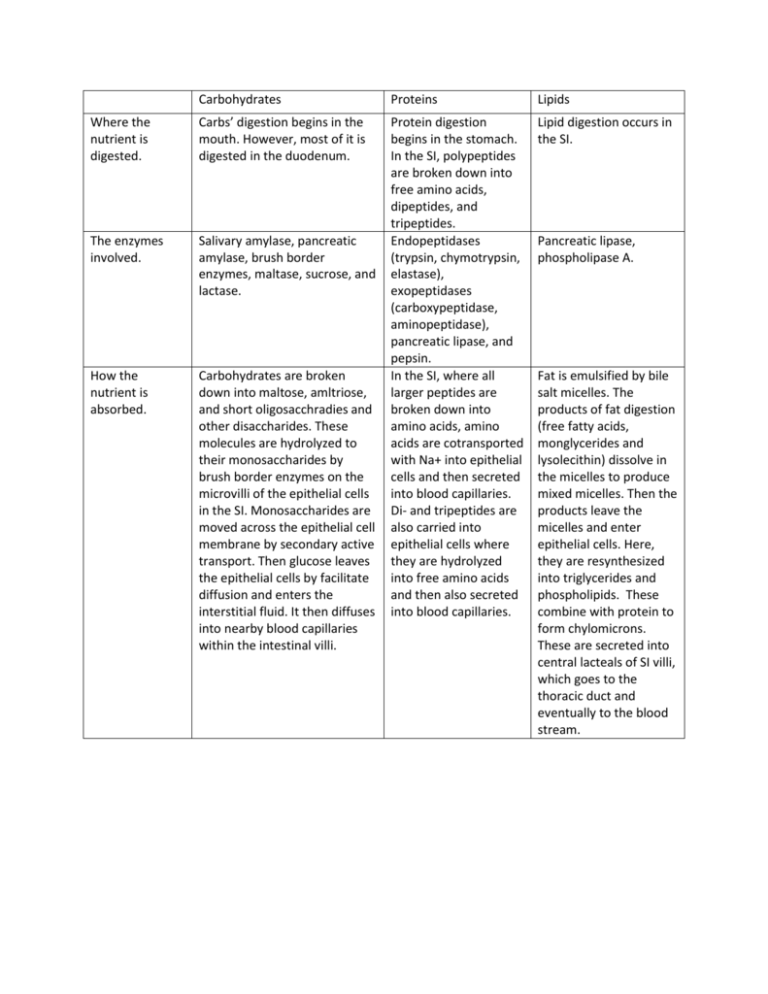
Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Where the nutrient is digested. Carbs’ digestion begins in the mouth. However, most of it is digested in the duodenum. Lipid digestion occurs in the SI. The enzymes involved. Salivary amylase, pancreatic amylase, brush border enzymes, maltase, sucrose, and lactase. How the nutrient is absorbed. Carbohydrates are broken down into maltose, amltriose, and short oligosacchradies and other disaccharides. These molecules are hydrolyzed to their monosaccharides by brush border enzymes on the microvilli of the epithelial cells in the SI. Monosaccharides are moved across the epithelial cell membrane by secondary active transport. Then glucose leaves the epithelial cells by facilitate diffusion and enters the interstitial fluid. It then diffuses into nearby blood capillaries within the intestinal villi. Protein digestion begins in the stomach. In the SI, polypeptides are broken down into free amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides. Endopeptidases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase), exopeptidases (carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase), pancreatic lipase, and pepsin. In the SI, where all larger peptides are broken down into amino acids, amino acids are cotransported with Na+ into epithelial cells and then secreted into blood capillaries. Di- and tripeptides are also carried into epithelial cells where they are hydrolyzed into free amino acids and then also secreted into blood capillaries. Pancreatic lipase, phospholipase A. Fat is emulsified by bile salt micelles. The products of fat digestion (free fatty acids, monglycerides and lysolecithin) dissolve in the micelles to produce mixed micelles. Then the products leave the micelles and enter epithelial cells. Here, they are resynthesized into triglycerides and phospholipids. These combine with protein to form chylomicrons. These are secreted into central lacteals of SI villi, which goes to the thoracic duct and eventually to the blood stream. How the body uses the molecule. The glucose is absorbed from the intestines into the blood and transported to the liver, muscles, and other sites where it is converted to another glucose polymer, glycogen, and stored. Glycogen helps maintain the proper amount of glucose in the blood by removing and storing excess glucose derived from ingested food or by supplying it to the blood when it is needed by the body cells for energy. (http://www.diet-andhealth.net/Nutrients/carbohyd rates.html) Antibodies defend the body from germs. Contractile proteins are responsible for movement in muscle fibers. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions. Storage proteins store amino acids. Some are used as hormones, some as transporters, some as structural support (elastin, collagen, keratin). The body uses lipids to store energy fuel, insulate body tissues, cushion and protect organs, produce ketone bodies - the primary energy source for the heart and brain, and as cell membranes (phospholipid membrane). (http://wiki.answers.co m/Q/How_does_the_b ody_use_lipids_or_fats)