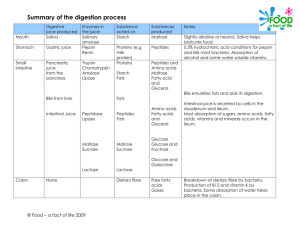
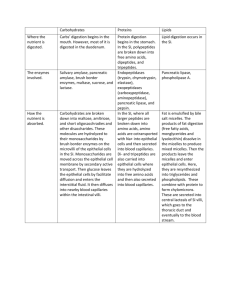
Digestion in the Sma..
advertisement
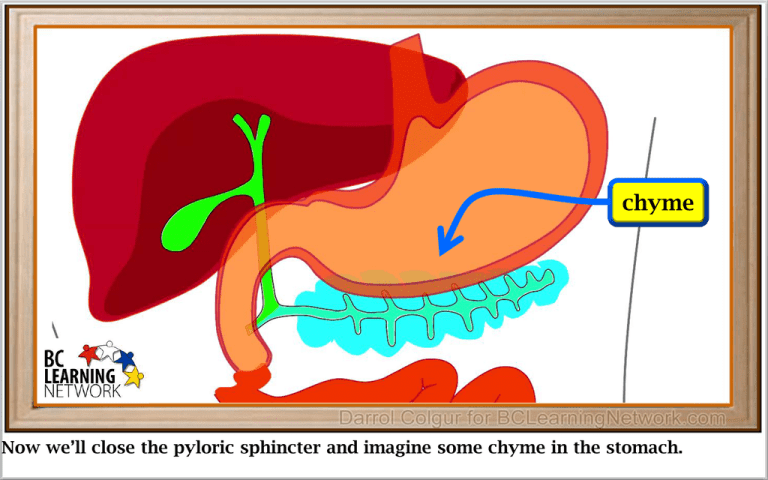
chyme Now we’ll close the pyloric sphincter and imagine some chyme in the stomach. The sphincter opens briefly and lets some chyme into the duodenum. Bile is secreted from the bile duct into the duodenum large fat particle Partially digested food at this point contains some large fat particles. (pause) We’ll show one here. Bile physically breaks up larger fat particles into smaller ones. . This process is called emulsification. large fat particle Bile physically breaks up large fat particles into smaller ones. Bile physically breaks up larger fat particles into smaller ones. . This process is called emulsification. large fat particle This process is called emulsification. emulsification large fat particle smaller fat particles Here’s how it works…We see the large fat particle breaking up into smaller particles. No chemical reactions occur during emulsion. This is a type of physical digestion. Chyme changes colour The presence of bile also causes the chyme to change colour during its time in the duodenum very large surface area Speeds up the action of enzymes Looking at the small fat particles (pause), we see they have a very large combined surface area. (click) This greatly speeds up the action of enzymes, which break down fats chemically. Now, we’ll move back over here… At the same time as bile is secreted, pancreatic juice also enters the duodenum from the pancreatic duct. We’ll discuss what pancreatic juice does. Functions of Pancreatic Juice 1. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3–) in pancreatic juice are basic, so they neutralize the excess acid in the chyme. 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens further down in the small intestine. Pancreatic juice is a complex mixture of bicarbonate ions and a number of enzymes. It is very important for digestion in the duodenum of the small intestine. We’ll look at some of its main functions here. Functions of Pancreatic Juice 1. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3–) in pancreatic juice are basic, so they neutralize the excess acid in the chyme. 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens further down in the small intestine. Chyme comes from the stomach, and is therefore highly acidic, containing many H + ions Functions of Pancreatic Juice 1. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3–) in pancreatic juice are basic, so they neutralize the excess acid in the chyme. 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens further down in the small intestine. Bicarbonate ions in the pancreatic juice move into the duodenum. Functions of Pancreatic Juice 1. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3–) in pancreatic juice are basic, so they neutralize the excess acid in the chyme. 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens further down in the small intestine. And they come in contact with the acid present, Functions of Pancreatic Juice 1. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3–) in pancreatic juice are basic, so they neutralize the excess acid in the chyme. 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens further down in the small intestine. And neutralize it. Now the chyme is no longer acidic, and it will not harm the intestinal walls. Functions of Pancreatic Juice 1. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3–) in pancreatic juice are basic, so they neutralize the excess acid in the chyme. 2. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down proteins into amino acids. 3. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 4. Pancreatic juice contains enzymes which break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. 5. Amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens further down in the small intestine. So we’ll summarize here that bicarbonate ions coming in with pancreatic juice are basic and therefore they neutralize excess acid in the chyme.