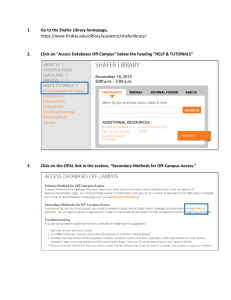
Week 1 slides - File Storage
advertisement

CS181 Introduction to
Database and the
Web
Class hour: 9:55AM-10:45AM MWF.
Hyer Hall 210
Course Objectives
• Create databases, tables, queries, forms and
write reports using RDBMS
• Develop and publish web sites using HTML,
and CSS.
Textbook/Technology requirement
Textbook:
1. HTML for the World Wide Web with XHTML and
CSS. Elizabeth Castro. 2003. Peachpit Press.
2. Special Edition Using Microsoft Access 2002.
Roger Jennings. 2002. Que Press.
Software:
Microsoft Access
Introduction
Tell me about yourself and what you expect
to get out from this course
Self-Introduction
• Recently graduated from the
University of Connecticut (05
Class), Ph.D in Computer
Science and Engineering
• Master of Computer Science
from UW-Milwaukee (96-99)
• Bachelor of Science from
Hanoi University of
Technology (86-91)
Self-Introduction
• Research Experience:
– User Modeling, Information Retrieval,
Decision Theory, Collaborative Filtering,
Human Factors
• Teaching Experience:
– CS181, 271, 172 Fall 05 at UWW
– Introduction courses at UOP and Devry
– TA for Computer Architecture, OO Design,
Compiler, Artificial Intelligence
Self-Introduction
• Teaching philosophy:
– Interactive
– Adaptive
– Pro-active
– Collaborative
• Other hobbies (non-academic related)
– Movies
– College Basketball
– Family activities
Contact information
nguyenh@uww.edu
Baker Hall 324
Office Hours: 2:15-4:15pm,
MWF or by appointment
262 472 5170
Course detail - Topics
Develop simple
three tier application
Database
(back-end)
HTML & Java script
(front-end)
Connecting these
two together
Course detail - Evaluation
GRADABLE
POINTS
WEIGHTING
Project 1
300
30%
Project 2
200
20%
Midterm
200
20%
Final exam
300
30%
Totals
1000
100%
What does it take to success
• Hard working, well-organization,
pay attention to detail
• Participate in the class discussion
• Practice, practice, practice!!!
Questions?
Introduction to Database and
Database Design
Introduction to Database
• Why are databases important?
• How do databases represent
information?
• Who works with databases?
• How do databases support the World
Wide Web?
• What database concepts and terms
do you need to know?
Why Are Databases Important?
• Importance to business
– Walmart: Records of retail business
• Size of warehouses
• Size of inventory
• Average sales per $ of inventory
– Amazon.com: Records of customers
• Importance to Web
– Records of interactions/transactions
– Example of auction site, customers’s
preferences/behaviors
Importance of Databases to Economy
• Expanding use of databases in retail sales
– Walmart, retail sales information tracking
• Examples of analyses
– Sales of items
• Comparisons between daily totals of items sold and items in
inventory; seasonal variations in sales of specific and similar
items; relative sales of similar items with different features
– Market-basket collections (all items in a single
purchase)
• Average and variation in total purchase amount/number &
price of items.
• Correlation between sales of items in a single purchase
– Customer analysis
• Behavior of average customer
• Preferences of individual customers
How Do Databases Represent
Information?
• The physical database:
– a collection of files containing the data content
• The schema:
– a specification of the physical database’s information content
and logical structure
• The database engine:
– software that lets people access and modify the database
contents
• The data definition and manipulation languages:
– programming languages, such as Java or SQL (Structured
Query Language), that let software developers define the
schema and access the database
How Do Databases Represent Information?
• Relational database management
system (RDBMS)
– Tables of data
– Schema
• Name of table
• Names and types of attributes
– Contents
• Row is a fact
• Attribute value is a characteristic
Example of storing information of a department
Department
table
Dept
Manager Description
101
017-110031
018-212131
019-411231
102
103
Marketing
Accounting
Customer
service
Schema
Depts(dept,manager,description)
Table creation
statement
create table depts(dept
char(3), manager char(11),
description char(25))
Example of storing information of a department
Insert data
into
table
insert into depts (dept,
manager,description)
values ('001','017-11-0031',‘marketing');
Practice
• Open Microsoft Access
• Name your database as Example
• Create a new table “By Design
View” named Department with 2
fields:
– Dept: text (3 characters)
- Manager: text (11 characters)
- Description: text (100 characters)
Who Works with Database Systems?
•
•
•
•
•
Database designers
Applications developers
Web-application developers
Web-site designers
Database administrators
How Do Databases Support the World Wide
Web?
• Maintain information that is published in the
site
• Track the ways in which site visitors use that
information
• Track the number of site visitors and
customers
• Store information collected from input forms
such as requests for customer addresses
• Store the structure and content of Web
pages
Information Systems
• Three separate types of
functionality:
– Data Management
– Application logic
– Presentation
Single-tier architecture
• All functionality combined into a
single tier (e.g mainframe where
users access through dumb
terminal or stand-alone machine
where there is no server)
• Pros: easy maintenance and
administration
• Cons: missing GUI, single point
failure
Client-server architecture
• Thin client
– Client implements only the GUI
– Server implements business logic
and data management
• Pros: easy maintenance and
implementation
• Cons:can’t separate between
business logic and data
management
Client-server architecture
• Thick client
– Client implements both GUI and
business logic
– Server implements data
management
• Cons: no central place to update
the business logic
– Security: trust clients
– Scalability: problems with 100s of
clients
Three tier architecture
Presentation
tier
Middle tier
Data
management
tier
Client program
Application server
Database server
Three tier architecture
• Pros:
– Heterogeneous systems
– Thin clients
– Integrated data access
– Scalability
– Development:
• Code for business logic is centralized
• Interaction between tiers through welldefined APIs.
Timeline for Database Systems
Developments
• before 1960 transition from punched card and tape
• 1960s, from file management to databases
• 1970s, CODASYL and Relational Model
– Codd (IBM) Relational Model
– Chen introduced Entity Relationship Model
– Query languages developed (SQL)
• 1980s, Client/Server DBs, Oracle, DB2
• 1990s, web-based information delivery
– Trends: expert DBs, object DBs, distributed DBs
• 2000s, Enhancing database technology for Web
storage and access
– Bioinformatics: genetic and protein information,
medical records
– Using the Web as a database
Questions?