Drugs
advertisement

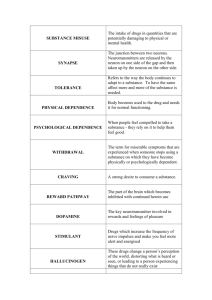
The three myths of addiction: 1. Addictive drugs can quickly corrupt: i.e. morphine taken for pain can often leads to heroin abuse. 2. Addictions cannot be overcome voluntarily 3. Addiction as a concept can be applied to many other repetitive, pleasure-seeking behaviors Psychoactive drugs, 198 What are depressants and what are their effects? Depressants drugs that slow or calm neural activity Disinhibition; slowed neural processing; memory disruption Reduced self-awareness and self-control; expectancy effects Alcohol impairs judgment and inhibitions; people who think they are drinking alcohol exhibited less sexual restraints Abrams and Wilson Rutgers experiment: if people believe they are drinking alcohol they will behave as if they are. Alcohol increases sexual aggression and casual sex. Barbiturates (tranquilizers) similar to alcohol because it lowers SNS activity; large doses can cause death Opiates (morphine, heroin) depress brain activity and bring pleasure with addiction; pain results with withdrawal because the brain stops producing its own endorphins; the two are chemically similar What are Stimulants and what are their effects? These speed up and excite bodily activity 12. Caffeine increases heart and breathing boosting mood/athletic performance 13. Nicotine: tobacco products are as addictive as cocaine and heroin; triggers the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine reducing appetite and increasing alertness 14. Amphetamines after these wear off the user experiences a crash: headaches, tiredness, even depression; methamphetamine (speed) 15. Cocaine most powerful stimulant: blocks the re uptake of dopamine because it is chemically similar; neurotransmitters (remains in the synapse, leading to intense mood) Ecstasy: MDMA, both a stimulant and hallucinogen; it releases stored serotonin and blocks its reabsorption; taking this drug even once can lead to serotonin neuron destruction. What are Hallucinogens and what are they effects: They distort perceptions and evoke vivid images 17. LSD (PCP) leads to intense emotions and seeing of colors, shapes, even out-of-body experiences; chemically similar to serotonin; synthetic substance; Albert Hoffman created this in 1943 Hallucinations during LSD usage can include experiences like near death experiences, a separation from the body feeling 18. Marijuana; natural substance a. contains an organic compound called THC that causes euphoric high, relaxation, increased sensitivity to colors b. Impairs judgment; causes lung damage; disrupts memory, decreases reaction time; lowers sex hormones Influences on drug use, 208 Why do some people become regular users of psychoactive drugs? 1. biology: alcoholism influenced by heredity; identical v. fraternal twins 2. psychology: the feeling that life is meaningless 3. psychology: stress and/or depression; failure People in poverty use to mask pain of being poor; wealth use because they can afford 4. sociology and culture : Peer culture; behavior v. belief Teens may feel their own behavior is not destructive; they attribute their own behavior to the situation and blame others for their own problems (rather than the situation); they’ll say they take drugs due to outside factors but assess others’ behavior based on internal factors; this is known as the fundamental attribution error. VI. Near Death Experiences 1. A state of consciousness reported after being close to death. 2. May see bright tunnel 3. LSD or oxygen deprivation are similar experiences 4. Dualism mind and body are two distinct parts separating after death 5. Monism we cannot exist without our bodies