Analysis of Vinegar by Titration
advertisement

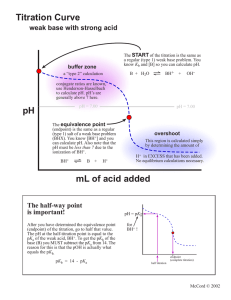
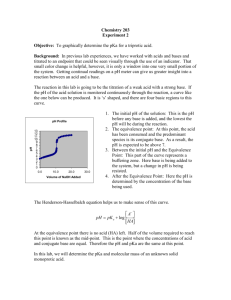
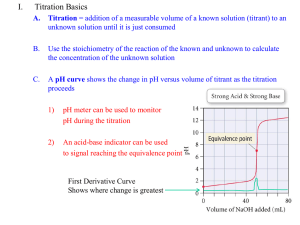
ANALYSIS OF VINEGAR BY TITRATION Lab 4 PURPOSE Students will use a pH probe to perform potentiometric titrations to determine the mass percent of acetic acid in vinegar and the pKa of acetic acid. POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATIONS Potentiometric titrations can be used to determine: proticity (how many acidic hydrogens are donated to solution) the amount or concentration of acid or base present (using MaVa= MbVb) pKa (the “– log” of the acid dissociation constant) PROTICITY Titration curve of a monoprotic acid such as HCl (hydrochloric acid) Titration curve of a diprotic acid such as H2SO3 (sulfurous acid) Titration curve of a triprotic acid such as H3PO4 (phosphoric acid) PROTICITY CONTINUED Acetic acid is a monoprotic weak acid that reacts with NaOH or KOH in a 1:1 ratio and produces a single sigmoidal curve. 12.00 11.00 10.00 9.00 8.00 pH 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 Volume, mL 20.00 25.00 EQUIVALENCE 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0.00 12.00 11.00 10.00 9.00 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 Volume, mL 20.00 25.00 pH Derivative The equivalence point volume is determined by plotting a derivative curve of the titration curve. The steepest point on the derivative curve corresponds to the equivalence point volume. (Find the exact value on your spreadsheet!) SPREADSHEET Time, s 0.01 35.95 60.24 79.47 103.54 142.46 151.31 187.66 222.13 268.71 pH Vol, mL 3.02 0.02 4.15 1.97 4.65 5.21 4.74 10.44 5.16 13.45 5.34 16.11 8.50 20.89 10.58 21.52 11.35 22.95 11.73 25.36 Deriv 0.001 0.000 0.003 0.000 0.002 0.010 18.750 1.960 0.001 0.000 pKa Half-equivalence Point Volume Highest derivative Equivalence Point Volume EQUIVALENCE POINT VOLUME The concentration of acetic acid can be determined from: the equivalence point volume of the base the concentration of the base the volume of the acid used in the titration The equation to use is: MaVa = MbVb PKA The pKa of acetic acid is the pH at the half-equivalence point volume of the titration, because: For a weak acid: HA H+ + A- H A and Ka = HA At the half-equivalence point, half the acid has been converted to its salt, so: [HA] = [A-] Ka = [H+] pKa = pH VINEGAR TITRATION Make the required dilution of vinegar. Calibrate your pH probe. Titrate the specified aliquots to obtain titration curves. Determine the volume of base delivered at each time point, using the base delivery rate. Graph the derivative of your titration curves following the instructions in the manual. Make up a spreadsheet that will allow you to calculate the indicated values. Perform statistical analysis on your data and complete your report form. EQUIPMENT SETUP SAFETY CONCERNS Reagents: Acetic Acid (1 N) Sodium Hydroxide (0.1 N) / Potassium Hydroxide (0.1 N) Eye Contact: Irritation, tearing, redness, pain, impaired vision, severe burns and irreversible eye injury. Skin Contact: Severe skin irritation, soreness, redness, destruction of skin (penetrating ulcers) . May cause sensitization and / or allergic reaction. Inhalation: May cause coughing, serious burns, pneumonitis, pulmonary edema, and coma. Ingestion: Toxic. Corrosive to mucous membranes. May cause perforation of the esophagus and stomach, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, general gastro-intestinal upset. WASTE Dispose of waste in the appropriate waste receptacles. Acidic and basic solutions / waste need to be disposed in the acid/base waste container in the fume hood. Solutions with a pH between 6 and 8 can be disposed down the drain. LAB 5 REMINDER Read the required reading sections in your textbook and lab manual as you prepare for the next experiment. Complete and submit the pre-lab questions. Study for your quiz. Submit your Lab 4 Report.