Circulatory System - Educational Excellence
advertisement

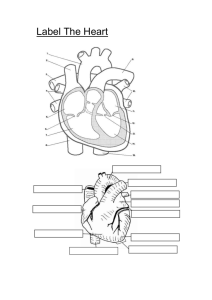
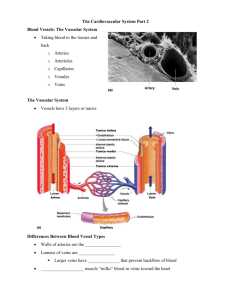
The Circulatory System Veterinary Medical Applications c6A Anatomy of the Circulatory System • • • • • • Heart Veins Capillaries Arteries Lymph vessels Lymph glands Anatomy of the Circulatory System • Each of its components work together to supply the body tissues with nutrients and to collect waste. Functions • • • • • • Distribute nutrients Transport and exchange oxygen an CO2 Remove waste Distribute secretions of the endocrine glands Prevent infection Assist in the regulation of body temperature The Heart • Hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood to all parts of the body • Located in the thoracic cavity • Contained in a pericardial sac The Heart • The pointed end, called the apex, is directed toward the abdomen The Heart • The Heart wall has three layers – Epicardium – Endocardium – Myocardium The Heart • Mammals and birds have a 4 chambered heart that contains: – Right atrium – Left atrium – Right ventricle – Left ventricle • The two sides are separated by a ventricular septum The Heart • The atrioventricular valves (AV) separate the atrium and ventricle on each side • They have flaps of tissue called cusps which open and close to allow blood to flow in only one direction, preventing backflow • Right AV is called tricuspid • Left AV is called bicuspid The Heart • Pulmonary Valve and aortic valve prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles The Heart • AV Valves • Pulmonary and Aortic Valves Sinoatrial Node • Controls the beat of the heart • Sends electrical signals to make the heart pump Vascular System • Made up of 3 types of Blood Vessels: – Arteries – Capillaries – Veins Vascular System • Arteries – Blood vessels that carry oxygen rich blood from the heart to the body – Thick walls enable them to withstand the pressure of the beating heart – They branch out into arterioles – Arterioles branch into small vessels called capillaries Vascular System • Capillaries – Tiny, thin walled vessels that connect arteries to veins – Located in all bodily tissues – Allow nutrients, oxygen, and water to diffuse to the tissues – Waste products, like CO2, diffuse from the tissues into the blood Vascular System • Veins – Blood vessels that return blood to the heart from all parts of the body – Capillaries come together to create small veins called venules – Venules join together to form larger veins – For every artery, there is a larger vein counterpart Vascular System • Veins – Have valves that aid in the prevention of backflow – Assist in the return flower of blood to the heard with pressure is low Circulation • Two Types – Pulmonary – Systemic Pulmonary Circulation • Takes the blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen • Oxygenated blood returns to the heart Systemic Circulation • The flow of oxygenated blood from the heart to all of the tissues of he body • And the return of the un-oxygenated blood back to the heart Circulation Circulation • Using your textbook or computer, trace both the systemic and pulmonary circulation of blood Blood • Blood is connective tissue • 50-65% Plasma • 35-50% Non-Plasma (cellular) Blood • Plasma – Straw colored liquid containing 90% water and 10% solids (salts, antibodies, hormones, vitamins, glucose, proteins) Blood • Non-Plasma – Cellular portion of the blood is made up of: • White blood cells • Red blood cells • Platelets Blood • Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) – Carry oxygen from the lungs to various organs – Contain hemoglobin which provides for the red color – Biconcave shape provides for oxygen exchange – Produced in the marrow Blood • White Blood Cells (leukocytes) – Two types • Granulocytes – Neutrophils- produced by marrow, fight infection – Eosinophils-combat infection by parasites and allergens, contain histamines – Basophils- rarest of the granulocytes, responsible for inflammation • Agranulocytes- produced by lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and other lymph tissues – Lymphocytes-produce and release antibodies – Monocytes- absorb diseases like bacteria through phagocytosis Blood • Platelets – Also called thrombocytes – Formed in the bone marrow – Help prevent blood loss by forming clots Blood