3.4 The Circulatory System Student Copy
advertisement

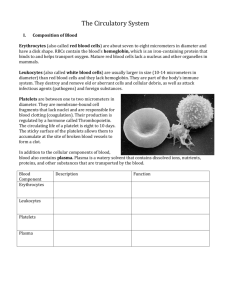
The Circulatory System The human circulatory system is made up of the blood, the heart, and the blood vessels. The function of the circulatory system is to transport substances around the body. It moves nutrients absorbed from the intestine to all of the body’s cells. Blood flows through the lungs to pick up oxygen and then flows through the body to deliver it to active cells. Blood also carries wastes from the body tissues for disposal. It carries carbon dioxide to the lungs, where it is released into the air. Other waste substances are carried to the kidneys where the substances are filtered out and excreted. Among the circulatory system’s other vital functions are the regulation of body temperature and the transport of disease-fighting white blood cells to areas of the body where there are viruses or bacteria. BLOOD Blood is a type of connective tissue that circulates throughout all parts of your body. The blood consists of four components: Red blood cells are the most plentiful of the body’s blood cells. Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which allows them to transport oxygen throughout the body. Hemoglobin makes the cells appear red. White blood cells are infection fighting cells. They recognize and destroy invading bacteria and viruses. They are the only blood cells to have a nucleus. Platelets are tiny cells that help in blood clotting. Plasma is a protein rich liquid that carries the blood cells along. THE HEART The heart is made up of three different types of tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. All of the cardiac muscle tissue in each part of the heart contracts at the same time. This makes the heart contract and moves the blood around the body. The heart pumps with a regular beat. The frequency of the beat (the heart rate) changes depending on physical activity and other factors such as stress, temperature and your general health. BLOOD VESSELS Three types of blood vessels form a network of tubes throughout the body to transport the blood. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Because the blood in the arteries is being pumped away from the heart, it is under greater pressure than the blood in the other blood vessels. The walls of arteries are thicker than the walls of other blood vessels to withstand this pressure. Veins carry blood toward the heart. This blood is at lower pressure, so the walls of the veins are not as thick. Arteries and veins are linked by the capillaries Capillaries are tiny blood vessels with very thin walls that allow substances to diffuse between the blood and other body fluids and tissues. Oxygen and nutrients diffuse from the blood into the surrounding tissues. Carbon dioxide and other wastes pass from the body tissues into the blood to be carried away for disposal.