Blood Vessels: The Vascular System
advertisement
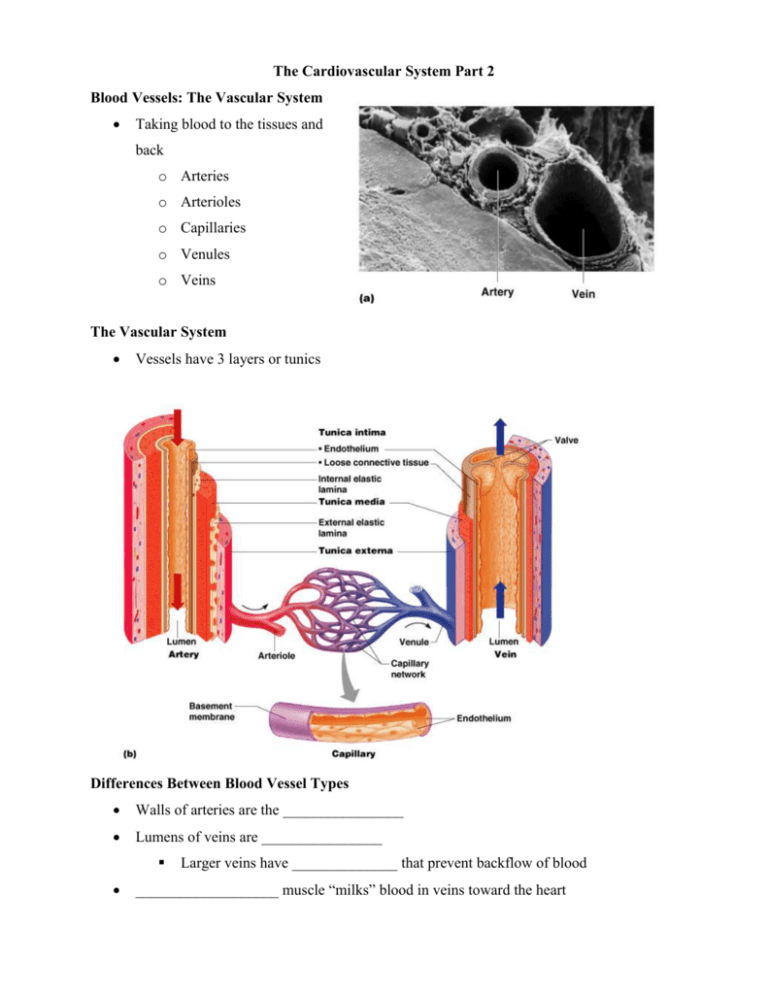
The Cardiovascular System Part 2 Blood Vessels: The Vascular System Taking blood to the tissues and back o Arteries o Arterioles o Capillaries o Venules o Veins The Vascular System Vessels have 3 layers or tunics Differences Between Blood Vessel Types Walls of arteries are the ________________ Lumens of veins are ________________ Larger veins have ______________ that prevent backflow of blood ___________________ muscle “milks” blood in veins toward the heart Walls of capillaries are only ___________________ layer thick to allow for exchanges between blood and tissue Movement of Blood Through Vessels Most _____________ blood is pumped by the heart ____________ use the milking action of muscles to help move blood Capillary Exchange Substances exchanged due to ________________ _____________________ o ____________ and _______________ leave the blood o _______________________ and other wastes leave the cells Capillary Exchange: Mechanisms Direct ______________ across plasma membranes ______cytosis or _____cytosis Some capillaries have _______ (intercellular clefts) o Plasma membrane not joined by tight junctions Fenestrations of some capillaries o Fenestrations = __________ Diffusion at Capillary Beds Special Circulations: Hepatic Portal Circulation Veins of the _______________ portal circulation drain the digestive organs, spleen and pancreas and deliver this blood to the liver via _________________________________ Liver processes _____________, ________ and ____________ before they enter the systemic circulation Some nutrients are removed to be ______________ for later release to the blood _____________ feed the liver circulation Special Circulations: Circulation to the Fetus Lungs and digestive system are ________ functional All nutrient, excretory and gas exchanges occur through the ________________ Umbilical cord contains ____ blood vessels o ____ large umbilical __________ Carries nutrients and ________________ the fetus o ____ smaller umbilical ______________ Carries ____________________ and __________ from fetus to placenta As blood flows to the fetal heart, most of it ____________ the _____________________ via the ductus venosus and enters the inferior vena cava and is carried to the right atrium Since _______________________________________, 2 shunts bypass them o Blood entering right atrium is shunted into the left atrium via _______________ _________________, an opening in the interatrial septum o Blood that enters the right ventricle is pumped out the pulmonary trunk and shunted into the ductus arteriosus, which connects it to the aorta _________________ carries blood to fetal tissues and ultimately back to the placenta via the umbilical arteries Shortly after birth, the foramen ovale closes and the ductus arteriosus collapses and is converted to the ______________________________________________ Developmental Aspects of the Cardiovascular System A simple “tube heart” develops in the embryo and pumps by the ______________ week The heart becomes a ____________________________ organ by the end of _________ weeks Few structural changes occur after the seventh week Pulse Pulse – pressure ___________ of blood Monitored at “_______________________________” where pulse is easily palpated Resting pulse averages ______________ beats/min Blood Pressure Measurements by health professionals are made on the pressure in large arteries o Systolic – pressure at the peak of ventricular _____________________ o Diastolic – pressure when ventricles ______________ Pressure in blood vessels ___________ as the distance away from the heart ___________ Measuring Arterial Blood Pressure Comparison of Blood Pressures in Different Vessels Blood Pressure: Effects of Factors Neural factors o Autonomic nervous system adjustments (sympathetic division) cause ____________________________, which ______________________ BP Renal factors o Regulation by altering blood _________________ Allowing more water to leave as urine, __________________ BP Retaining water ____________________ BP o _______________ – hormonal control - _______________ BP (vasoconstriction) Temperature o Heat has a _____________________________ effect o Cold has a _____________________________ effect Chemicals o Various substances can cause increases or decreases _______________ BP – epinephrine and nicotine _______________ BP – alcohol and histamine Diet Factors Determining Blood Pressure Variations in Blood Pressure Human normal range is variable o Normal 140–110 mm Hg ________________ 80–75 mm Hg ________________ o ______tension (low BP) ________ systolic (below 100 mm HG) Often associated with long life and an old age free of illness Chronic hypotension may hint at poor ________________ o _______tension ___________ systolic (above 140 mm HG) Can be dangerous if it is _____________