Story Elements PowerPoint
advertisement

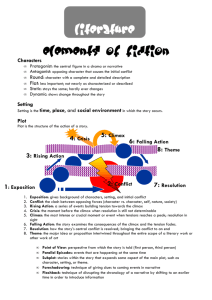
Important Parts of a Novel • Setting • Characters • Plot • Theme • Point of View Setting Tells when (time) and where (place) the story takes place Specific: The summer of 2002 in Voorhees, N.J. General: A large city sometime in the future Setting Clues: characters, lifestyles, transportation, dress, speech Novels can have more than one setting – each has a time (when) and place (where) Characters The people or animals in a story Described by how they look, act, think, or feel Major Characters/Minor Characters How the characters are revealed: What they say or think What they do What others say Physical characteristics/personality traits Plot Series of events created by the author to tell a story Elements of a plot: Exposition/Conflict – the basic problems, main goals Rising Action – suspense, events before the climax Climax – turning point, most exciting part Falling Action – events after the climax Conclusion/Resolution – how everything turns out, how the conflict was solved Plot Diagram Climax Rising Action Exposition/ Conflict Falling Action Resolution/Conclusion Theme • The underlying message or point the author is trying to make • Ties the plot setting or characters together – Example: Cinderella – Evil is punished, good is rewarded Point of View The position from which the events in a story are told 1st Person – the narrator is a character in the story Clues: I, me, mine, we, ours 3rd Person – the narrator is someone outside the story Clues: he, she, him, her, they, them, theirs Sequence of Events The order in which events happen Chronological – the order in which events actually happen Interrupted – the events are listed in an order different than they actually happened Cause and Effect Cause – something that makes something else happen, happens first Effect – what happens because of the cause, happens last Examples: Cause The boy kicked the ball. He teased the dog. Effect The ball rolled. The dog growled. Sam studied very hard. Sara became tired. Sam earned an A. Sara went to bed. Fictional Genres Realistic Fiction – everything in the story is fiction, but could actually happen in real life Tall Tale – a story based on possible occurrences but is exaggerated enough that it could not be true Legend – a story about a person and heroic deeds or about a place surrounded by mystery. The story starts with a real event or person, but over the years the story grows and changes Symbolism A symbol in literature is an object that represents and idea or entire set of ideas Peter Pan’s shadow is a symbol of reality. When he loses his shadow, it shows us how he has lost his sense of reality from being in Neverland. Allusions An allusion is a reference to someone or something that is known from literature, history, religion, mythology, politics, sports, or any other field that most people are familiar with. Allusions enrich the reading experience and broaden the meaning of what is said or written. Examples: He is a real Scrooge. You are opening up Pandora’s box. Hers is a real Cinderella story. Writers expect readers to recognize the allusions. Elements of a Good Story Setting Plot Conflict Climax Resolution Theme Characterization