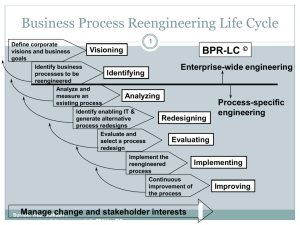
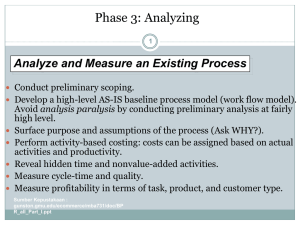
Business Process Reengineering: Principles, Methods, and Tools
advertisement

BPR Principles 1 Organize around outcomes, not tasks. Have those who use the output of the process perform the process. Subsume information-processing work into the real work that produces the information. Treat geographically dispersed resources as though they were centralized. Link parallel activities instead of integrating their results. Put decision points where the work is performed and build controls into the process. Capture information once and at the source. Source: Michael Hammer, “Reengineering Work: Don’t Automate, Obliterate,” Harvard Business Review, July-August, 1990, pp. 104-112. Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP BPR Principles - Derived 2 Redesign process steps such that they are perform in a correct order. Combine several process steps into one. Design for parallel subprocesses whenever possible to reduce waiting time between tasks. Integrate subprocesses. Processes may have multiple versions. Remove complex, exceptions, and special cases. Empower human potentials. Give front-line workers the responsibility to make decisions. Provide mechanism in the process to encourage individual, team, and organizational learning Source: Derived from Michael Hammer and James Champy, Reengineering the Corporation: A Manifesto for Business Revolution, HarperCollins Publishers, Inc., 1993 Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP Informating, Not Automation 3 An individual without information cannot take responsibility; an individual who is given information cannot help but take responsibility. Sumber : Jan Calzon CEO, Scandinavian Airlines Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP BPR Principles - Derived (Continued) 4 Perform the work where it makes sense. Reduce controls and checks. ==> Build in feedback mechanisms at each steps to minimize the need for the checkpoints and control. Minimize reconciliation. Eliminate multiple external contact points. ==> Use case managers to provide a single point of contact for customers. One-stop customer service or customer service center. Design processes with centralized and decentralized operations. Coordinate inventory, buffers, and other assets by sharing data cross organization boundaries. JIT, continuous replenishment, supplier shelf management. Strive for “doing things right the first time”. Eliminate rework and iteration. Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP R_all_Part_I.ppt A BPR Framework Organization Job skills Structures Reward Values Technology 5 – – – – Process – Core business processes – Value-added – Customer-focus – Innovation Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP Enabling technologies IS architectures Methods and tools IS organizations