Business Process Reengineering pertemuan 13
advertisement

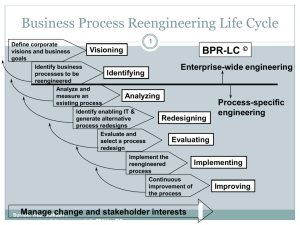
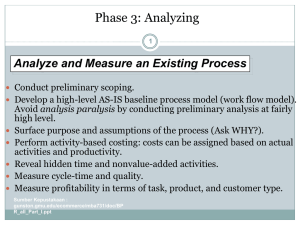
Phase 6: Implementing 1 Implement the reengineered process Plan IT implementation Plan organization implementation Conduct a pilot project Develop a prototype system Technical Design Social Design Evaluate results from the pilot project and the prototype Prepare large-scale roll out Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP R_all_Part_I.ppt Phase 7: Improving 2 Improve the process continuously Develop performance measurement and reward systems in the reengineered process Monitor process performance constantly Improve the process on a continuous basis Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP Elements of Integrated Process Management Integrated Process Management 3 Process Reengineering Process Monitoring Process Improvement Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP Target Design Visioning: Price Waterhouse Vision High-Level Goals • Desired end state • Scope of vision Business Analysis Level • Strategic • Tactical • Operational Information • Facts • Problems • Opportunities 4 • People & culture • • • • Processes Systems & IT Organization & Structure Performance measures & targets Visioning Workshop Process Design • Facilitation • Participation • Consensus • Segment processes • Select high-return process redesign opportunities • Perform detailed redesign of business processes External View • • • • Best practices BPR principles Technologies Industry & functional Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BPR_all_Part_I.ppt Target Environment Design • People & culture • Processes • Systems & IT • Organization & structure Rapid Re Approach Solution: Technical Design Preparation Recognize need Develop executive consensus Train team Plan change Identification Model customer Define & measure performance Define entities Model processes Map organization Map resources Prioritize processes Vision Understand process structure Understand process flow Identify value-adding activities Benchmark performance Determine benchmark drivers Estimate opportunities Envision and integrate the internal & external ideal Source: Adapted form Manganelli & Klein, The Sumber Kepustakaan : AMACOM, 1994. Reengineering Handbook, gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP 5 Model data & reexamine process linkages Instrument and informate Consolidate interfaces & information Redefine alternatives Relocate & retime controls Modularize & specify deployment Apply technology Plan implementation Solution: Social Design Empower customer contact personnel Define jobs, teams, skills, Specify management structure, org. boundaries, & transitional org. Specify job changes & career paths Deign change mgmt prog. Design incentives Plan implementation Transformation Build & test the system Train staff Pilot new process Define transition Continuous improvement Enterprise Engineering - A Framework for Change 6 Organization and Culture Development Continuous Process Improvement Business Process Redesign Learning Organization Business Strategic Re-engineering Visioning Information Infrastructure Development Sumber: Adapted from James Martin & Co., Business Re-engineering Quick Reference Guide, 1993. Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BPR_all_Part_I.ppt BPR Team Structures 7 BPR Leader (Champion) BPR Czar Methodologist Tools Experts BPR Steering Commitee Change Master BPR Team BPR Team Sebagai contoh Struktur tim : “The LEADER appoints the PROCESS OWNER, who convenes a REENGINEERING TEAM, with assistance from the BPR CZAR and under the auspices of the BPR STEERING COMMITTEE.” (Hammer and Champy, 1993) Process Owner Team Leader BPR Experts Domain Experts Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP IS Experts BPR Team Stakeholders of the Reengineering Project 8 End users, operators, managers of the process Gainers and losers of benefits Employees who may be affected Decision makers Controllers of resources Suppliers and customers of the process Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP BPR Team 9 Size: up to 8 members in the core team augmented by subject-matter experts when needed. Commitment: half- to full-time. Skills: team skills, process engineering, quality, information systems, benchmarking, organizational and job design, and change management. Composition: Employees, customers, suppliers, and external consultants. Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP Facilitated BPR Meetings 10 Centered around a workshop: It is an organized, controlled, and structured process Participated by users, managers, and IS personnel (if necessary) User orientation Management direction IS technical assistance Facilitated by a BPR facilitator to ensure thorough analysis Employ a BPR analysis and design methodology to ensure usable requirements or specifications Focused on a consensus-based decision making process Use multi-media audio-visual equipment or BPR tools to bridge knowledge gap among participants Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP Qualifications of a BPR Facilitator 11 Is skillful in team building and leading Manages group process and dynamics Has energetic and outgoing personality Summarizes discussion Is a good communicator (listening and speaking) Has project management ability Has mastered facilitation skills Understands BPR methods Sumber Kepustakaan : gunston.gmu.edu/ecommerce/mba731/doc/BP R_all_Part_I.ppt