Unit 3 Test - Madison County Schools
advertisement

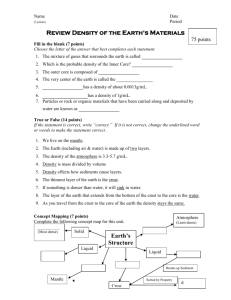
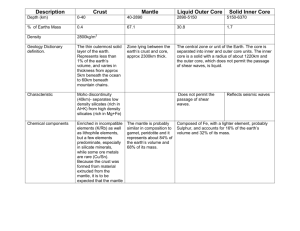
Unit 3 Test Review QUESTION 1 What causes the movement of the tectonic plates? a. Convection c. Subduction b. Radiation d. Convergence QUESTION 1 What causes the movement of the tectonic plates? a. Convection c. Subduction b. Radiation d. Convergence QUESTION 2 The upper portion of the mantle just below the lithosphere is called the: a. Mid Ocean Ridge c. Asthenosphere b. Rift Valley d. Mesophere QUESTION 2 The upper portion of the mantle just below the lithosphere is called the: a. Mid Ocean Ridge c. Asthenosphere b. Rift Valley d. Mesophere QUESTION 3 What is the name of the location within the Earth where an earthquake begins? a. Fold c. Epicenter b. Focus d. Core QUESTION 3 What is the name of the location within the Earth where an earthquake begins? a. Fold c. Epicenter b. Focus d. Core QUESTION 4 What is a break in a rock mass along which movements occurs? a. Fold c. Fault b. Earthquake d. Epicenter QUESTION 4 What is a break in a rock mass along which movements occurs? a. Fold c. Fault b. Earthquake d. Epicenter QUESTION 5 What is the source of heat that sets the plates in motion? a. The sun c. Radioactive Decay b. Friction d. Subduction QUESTION 5 What is the source of heat that sets the plates in motion? a. The sun c. Radioactive Decay b. Friction d. Subduction QUESTION 6 What does letter B represent in the above figure? a. The Outer Core c. The Crust b. The Inner Core d. The Mantle QUESTION 6 What does letter B represent in the above figure? a. The Outer Core c. The Crust b. The Inner Core d. The Mantle QUESTION 7 The two types of crust: a. Oceanic and Inner Core b. Continental and Inner Core c. Inner Core and Mantle d. Oceanic and Continental QUESTION 7 The two types of crust: a. Oceanic and Inner Core b. Continental and Inner Core c. Inner Core and Mantle d. Oceanic and Continental QUESTION 8 Which of the following statements is true regarding seismic waves? a. In the longitudinal S-wave, the energy moves perpendicular to the particles b. In the transverse S-wave, the energy moves perpendicular to the particles c. In the longitudinal P-wave, the energy moves perpendicular to the particles d. In the transverse P-wave, the energy moves parallel to the particles. QUESTION 8 Which of the following statements is true regarding seismic waves? a. In the longitudinal S-wave, the energy moves perpendicular to the particles b. In the transverse S-wave, the energy moves perpendicular to the particles c. In the longitudinal P-wave, the energy moves perpendicular to the particles d. In the transverse P-wave, the energy moves parallel to the particles. QUESTION 9 A subducting oceanic plate a. Is less dense than the plate it moves under b. Is pushed up and over the continental crust c. Sinks into the mantle, forming a trench d. Moves horizontally in the opposite direction past the other plate QUESTION 9 A subducting oceanic plate a. Is less dense than the plate it moves under b. Is pushed up and over the continental crust c. Sinks into the mantle, forming a trench d. Moves horizontally in the opposite direction past the other plate QUESTION 10 When 2 oceanic plates collide, which land feature forms? a. Mountain c. Volcano b. Rift Valley d. Hot Spot QUESTION 10 When 2 oceanic plates collide, which land feature forms? a. Mountain c. Volcano b. Rift Valley d. Hot Spot QUESTION 11 Which letter represents the epicenter of the earthquake in the figure above? a. Point A c. Point C b. Point B d. Point D QUESTION 11 Which letter represents the epicenter of the earthquake in the figure above? a. Point A c. Point C b. Point B d. Point D QUESTION 12 New ocean crust is formed along a. Mid-Ocean Ridges c. Mountain Belts b. Subduction Zones d. Trenches QUESTION 12 New ocean crust is formed along a. Mid-Ocean Ridges c. Mountain Belts b. Subduction Zones d. Trenches QUESTION 13 P waves pass through the outer core but S waves do not. This is because: a. The temperature of the outer core is too high for S waves to pass through b. S waves are transverse and the outer core only allows longitudinal waves to pass through c. The outer core is radioactive and the rest of the Earth is not d. The outer core is liquid and S waves do not pass through a liquid QUESTION 13 P waves pass through the outer core but S waves do not. This is because: a. The temperature of the outer core is too high for S waves to pass through b. S waves are transverse and the outer core only allows longitudinal waves to pass through c. The outer core is radioactive and the rest of the Earth is not d. The outer core is liquid and S waves do not pass through a liquid QUESTION 14 At colliding continental plates, which land feature forms? a. Mountain c. Volcano b. Rift Valley d. Hot Spot QUESTION 14 At colliding continental plates, which land feature forms? a. Mountain c. Volcano b. Rift Valley d. Hot Spot QUESTION 15 A narrow valley that forms along mid ocean ridges where the plates separate: a. Mountain c. Volcano b. Rift Valley d. Hot Spot QUESTION 15 A narrow valley that forms along mid ocean ridges where the plates separate: a. Mountain c. Volcano b. Rift Valley d. Hot Spot QUESTION 16 The process which scientists believe causes tectonic plates to move is: a. Subduction c. Conduction b. Convection d. Radiation QUESTION 16 The process which scientists believe causes tectonic plates to move is: a. Subduction c. Conduction b. Convection d. Radiation QUESTION 17 The hypothesis that the continents move slowly over Earth’s surface and once were joined into one supercontinent is called: a. Seismology c. Sea-Floor Spreading b. Continental Drift d. Subduction QUESTION 17 The hypothesis that the continents move slowly over Earth’s surface and once were joined into one supercontinent is called: a. Seismology c. Sea-Floor Spreading b. Continental Drift d. Subduction QUESTION 18 Which choice lists the 3 main interior layers of the Earth from coolest to hottest? a. Core, Mantle, Crust b. Crust, Mantle, Core c. Mantle, Core, Crust d. Crust, Core, Mantle QUESTION 18 Which choice lists the 3 main interior layers of the Earth from coolest to hottest? a. Core, Mantle, Crust b. Crust, Mantle, Core c. Mantle, Core, Crust d. Crust, Core, Mantle QUESTION 19 Plates slide past each other, and crust is neither created nor destroyed, at a: a. Convergent Boundary b. Divergent Boundary c. Mid-Ocean Ridge d. Transform Fault Boundary QUESTION 19 Plates slide past each other, and crust is neither created nor destroyed, at a: a. Convergent Boundary b. Divergent Boundary c. Mid-Ocean Ridge d. Transform Fault Boundary QUESTION 20 Which type of earthquake wave has circular motion? a. Transverse Wave c. Primary Wave b. Longitudinal Wave d. Surface Wave QUESTION 20 Which type of earthquake wave has circular motion? a. Transverse Wave c. Primary Wave b. Longitudinal Wave d. Surface Wave QUESTION 21 Stress in Earth’s crust is caused by: a. Folds b. Plate Movements c. Earthquakes d. Faults QUESTION 21 Stress in Earth’s crust is caused by: a. Folds b. Plate Movements c. Earthquakes d. Faults QUESTION 22 Geologists have inferred that Earth’s outer core is liquid because: a. P waves cannot pass through the outer core b. S waves speed up in the outer core c. P waves are bent downward as they travel through the outer core d. S waves cannot pass through the outer core QUESTION 22 Geologists have inferred that Earth’s outer core is liquid because: a. P waves cannot pass through the outer core b. S waves speed up in the outer core c. P waves are bent downward as they travel through the outer core d. S waves cannot pass through the outer core QUESTION 23 The above diagram displays what type of fault? a. Strike-Slip c. Reverse b. Thrust d. Detachment QUESTION 23 The above diagram displays what type of fault? a. Strike-Slip c. Reverse b. Thrust d. Detachment QUESTION 24 What causes the magma inside a volcano to rise toward the surface? a. It is a thick liquid, denser than the surrounding rock b. It does not contain dissolved gasses c. It is less dense than the surrounding rock d. It is cooler than the surrounding rock QUESTION 24 What causes the magma inside a volcano to rise toward the surface? a. It is a thick liquid, denser than the surrounding rock b. It does not contain dissolved gasses c. It is less dense than the surrounding rock d. It is cooler than the surrounding rock QUESTION 25 The area where magma collects inside a volcano before an eruption is called: a. A Crater c. A Vent b. A Caldera d. A Magma Chamber QUESTION 25 The area where magma collects inside a volcano before an eruption is called: a. A Crater c. A Vent b. A Caldera d. A Magma Chamber QUESTION 26 The amount of energy released by an earthquake is measured on the a. Richter Scale b. Moment Magnitude Scale c. Modified Mercalli Scale d. Seismic Scale QUESTION 26 The amount of energy released by an earthquake is measured on the a. Richter Scale b. Moment Magnitude Scale c. Modified Mercalli Scale d. Seismic Scale QUESTION 27 What determines whether a volcano erupts quietly or explosively? a. The size of the volcano b. The age of the volcano c. The characteristics of the magma d. The magnitude of nearby earthquakes QUESTION 27 What determines whether a volcano erupts quietly or explosively? a. The size of the volcano b. The age of the volcano c. The characteristics of the magma d. The magnitude of nearby earthquakes QUESTION 28 Composite volcanos are produced by a. Quiet eruptions of lava b. Explosive eruptions of lava and ash c. Explosive eruptions of ash and cinders d. Quiet eruptions that alternate with explosive eruptions QUESTION 28 Composite volcanos are produced by a. Quiet eruptions of lava b. Explosive eruptions of lava and ash c. Explosive eruptions of ash and cinders d. Quiet eruptions that alternate with explosive eruptions QUESTION 29 P Waves: a. Cause Earth to vibrate in the direction of the waves motion b. Cause Earth to vibrate at right angles to the direction the wave moves c. Travel along Earth’s surface d. Move in a rolling motion similar to ocean waves QUESTION 29 P Waves: a. Cause Earth to vibrate in the direction of the waves motion b. Cause Earth to vibrate at right angles to the direction the wave moves c. Travel along Earth’s surface d. Move in a rolling motion similar to ocean waves QUESTION 30 A steep-sided volcano formed entirely of ash and cinders is a: a. Shield Volcano b. Composite Volcano c. Ash-Cinder Cone d. Hot Spot QUESTION 30 A steep-sided volcano formed entirely of ash and cinders is a: a. Shield Volcano b. Composite Volcano c. Ash-Cinder Cone d. Hot Spot QUESTION 31 Which one represents a Convergent (Colliding) Boundary? QUESTION 31 Which one represents a Convergent (Colliding) Boundary? QUESTION 32 Which one represents a Convergent (Subducting) Boundary? QUESTION 32 Which one represents a Convergent (Subducting) Boundary? QUESTION 33 Which one represents a Transform Fault Boundary? QUESTION 33 Which one represents a Transform Fault Boundary? QUESTION 34 What are the names of the tectonic plates at 9, 10, 11 & 12? QUESTION 34 9 – Caribbean Plate 10 – Arabian Plate 11 – Philippine Plate 12 – Cocos Plate QUESTION 35 The New Madrid Fault is closest to what US State? a. California b. Kentucky c. Texas d. Connecticut QUESTION 35 The New Madrid Fault is closest to what US State? a. California b. Kentucky c. Texas d. Connecticut