Chapter 6 Study Guide
advertisement

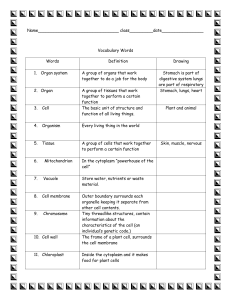
Chapter 6 Study Guide Vocabulary: Word Roots: centro- = the center -soma = a body chloro- = green cili- = hair cyto- = cell -ell = small endo- = inner eu- = true extra- = outside flagell- = whip glyco- = sweet lamin- = sheet/layer h lyso- = loosen micro- = small -tubul = a little pipe nucle- = nucleus -oid = like phago- = to eat -desma = a band or bond pro- = before karyo- = nucleus pseudo- = false -pod = foot thylaco- = sac or pouch trans- = across Key Terms: actin: A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells. cell wall: A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and some protists. In plant cells, the wall is formed of cellulose fibers embedded in a polysaccharide-protein matrix. central vacuole: A membranous sac in a mature plant cell with diverse roles in reproduction, growth, and development. chloroplast: An organelle found only in plants and photosynthetic protists that absorbs sunlight and uses it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water. chromosome: A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins. collagen: A glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix of animal cells that forms strong fibers, found extensively in connective tissue and bone contractile vacuole: A membranous sac that helps move excess water out of the cell. crista: (plural, cristae) An infolding of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electron transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP. cytoplasm: The entire contents of the cell, exclusive of the nucleus, and bounded by the plasma membrane. cytoplasmic streaming: A circular flow of cytoplasm, involving myosin and actin filaments, that speeds the distribution of materials within cells. cytoskeleton: A network of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments that branch throughout the cytoplasm and serve a variety of mechanical and transport functions. cytosol: The semifluid portion of the cytoplasm. desmosome: A type of intercellular junction made of intermediate filaments in animal cells that functions as an anchor. endomembrane system: The collection of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles. eukaryotic cell: A type of cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membraneenclosed organelles, present in protists, plants, fungi, and animals; also called eukaryote. extracellular matric (ECM): The substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded, consisting of protein and polysaccharides. flagellum: (plural, flagella) A long cellular appendage made of microtubules specialized for locomotion. food vacuole: A membranous sac formed by phagocytosis. gap junction: A type of intercellular junction in animal cells that allows the passage of material or current between cells. glycoprotein: A protein covalently attached to a carbohydrate. Golgi apparatus: An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of stacks of flat membranous sacs that modify, store, and route products of the endoplasmic reticulum. granum: (plural, grana) A stacked portion of the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast. Grana function in the light reactions of photosynthesis. intermediate filament: A component of the cytoskeleton made of subunits of keratin that includes all filaments intermediate in size between microtubules and microfilaments. lysosome: A membrane-enclosed sac of hydrolytic enzymes found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. microfilament: A solid rod of actin protein in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells, making up part of the cytoskeleton and acting alone or with myosin to cause cell contraction. microtubule: A hollow rod of tubulin protein in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells and in cilia, flagella, and the cytoskeleton. mitochondrial matrix: The compartment of the mitochondrion enclosed by the inner membrane and containing enzymes and substrates for the citric acid cycle. mitochondrion: (plural, mitochondria) An organelle in eukaryotic cells that serves as the site of cellular respiration. nuclear envelope: The membrane in eukaryotes that encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm. nuclear lamina: A netlike array of protein filaments that maintains the shape of the nucleus. nucleoid: A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell. nucleolus: (plural, nucleoli) A specialized structure in the nucleus, formed from various chromosomes and active in the synthesis of ribosomes. nucleus: The chromosome-containing organelle of a eukaryotic cell. organelle: One of several formed bodies with specialized functions, suspended in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. phagocytosis: A type of endocytosis involving large, particulate substances, accomplished mainly by macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells. plasma membrane: The membrane at the boundary of every cell that acts as a selective barrier, thereby regulating the cell’s chemical composition. plasmodesma: (plural, plasmodesmata) An open channel in the cell wall of plant through which strands of cytosol connect from an adjacent cell. plastid: One of a family of closely related plant organelles that includes chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and amyloplasts. prokaryotic cell: A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea. pseudopodium: (plural, pseudopodia) A cellular extension of amoeboid cells used in moving and feeding. ribosome: A cell organelle constructed in the nucleolus and functioning as the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm; consists of rRNA and protein molecules, which make up two subunits. rough ER: That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes. smooth ER: That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes. stroma: The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; involved in the synthesis of organic molecules from carbon dioxide and water. thylakoid: A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy to chemical energy. tight junction: A type of intercellular junction in animal cells that prevents the leakage of material between cells. tonoplast: A membrane that encloses the central vacuole in a plant cell, separating the cytosol from the vacuolar contents transport vesicle: A tiny membranous sac in a cell’s cytoplasm carrying molecules produced by the cell. vacuole: A membrane bound vesicle whose specialized function varies in different kinds of cells vesicle: A sac made of membrane inside of cells. Chapter 6 Important Points: 2 major types of cells: Prokaryotic: Bacteria, Archaea Domains o Smaller, simpler than eukaryotic o Lack membrane bound organelles including nucleus (have DNA in concentrated nucleoid region instead) Eukaryotic o Animal, Plant, Fungi, Protist Kingdoms o Larger and more complex than prokaryotic o Have many specialized membrane bound organelles including membrane bound nucleus All cell types have: Plasma membrane DNA Ribosomes Cytoplasm Structures unique to animal cells vs. plant: Lysosomes Centrosomes with centrioles Flagella (except some plant sperm) Gap junctions, tight junctions, desmosomes Structures unique to plant cells vs. animal: Cell wall Plasmodesmata in cell wall Central vacuole Chloroplasts Amyloplasts Chromoplasts 1.) Plasma membrane Function: Selective barrier that controls what can enter and leave cell, contains cytoplasm, defines cell as separate from environment Structure: Double layer of phospholipids w/ proteins embedded in them; carbohydrate side chains on outside 2.) Nucleus Function: Contains genes (DNA) Structure: Enclosed by double layer nuclear membrane Membrane has pores: protein structure called pore complex lines pore, controls what can enter or leave nucleus Nuclear lamina: lines inside of nuclear membrane, has protein filaments intermediate filaments), maintains shape of nucleus 3.) Nucleolus Function: area w/in nucleus where ribosomal components synthesized Structure: dense area w/in nucleus near chromatin 4.) Ribosomes Function: Site of protein synthesis Structure: Made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) & protein; 2 subunits 2 types: A. Free ribosomes: in cytosol, proteins they make are used in cytoplasm B. Bound ribosomes: attached to endoplasmic reticulum; makes proteins exported out of cell or used w/in other cell organelles Endomembrane System Various membrane structures that are responsible for protein and lipid synthesis and detoxification of poisons; May be directly connected or use vesicles to move cellular products between members Members: nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles/vesicles, plasma membrane 5.) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Overall structure: Network of membranes arranged in sacs (cisternae); Has internal compartments (ER lumen) that is separate from cytosol 2 distinct regions: 1. Smooth ER: Function: Synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates, detoxification of drugs; makes sex hormones Structure: No ribosomes give “smooth” appearance 2. Rough ER: Function: Secretion of specialized proteins Rough ER packages proteins into transitional ER then into bubbles called transport vesicles which move to Golgi Structure: Contains ribosomes giving “rough” appearance 6.) Golgi Apparatus Function: Accepts transport vesicles containing cellular products from ER; Clearing house---modifies, sorts, ships proteins ready to be secreted or for use somewhere else in cell; places ID tags on outside of vesicles leaving Golgi to arrive at correct location Structure: flat membranous sacs (cisternae) o 2 opposite sides: Cis face (receiving); Trans face (shipping) 7.) Lysosome Function: Contains enzymes which digest macromolecules o Enzymes work in pH of about 5 so it’s separated from rest of cell o Autophagy: recycling of cell’s own organic materials o Phagocytosis: digestion of large food particles; food vacuoles merge w/ lysosomes for digestion Structure: Membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes 8.) Vacuoles (larger), vesicles Structure: large membrane bound sacs 3 Types: 1. Food vacuoles: Function: formed by phagocytosis; allow digestion of large food particles 2. Contractile: Function: Freshwater protists use to pump out excess internal water 3. Central: Function: in plant cells, enclosed by tonoplast membrane; Storage, disposal of wastes; pigments; poisons; growth; holds water 9.) Mitochondria Function: site of cell respiration (process of extracting energy from food) Structure: enclosed by 2 membranes o Outer membrane smooth; inner convoluted (Cristae: increases surface area) o Intermembrane space: b/t inner and outer membranes o Mitochondrial matrix: w/in inner membrane o Mitochondria have own DNA, ribosomes; can reproduce itself 10.) Chloroplasts Function: site of photosynthesis (conversion of sun energy into chemical energy/glucose) in plants and algae Structure: Has 2 membranes o Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment in thylakoids (sacs of membranes) o Grana: stacks of thylakoids o Stroma: fluid outside thylakoids o Contains own DNA and ribosomes 11.) Other plastids Function: storage of various cellular materials o Amyloplasts: colorless; stores starch o Chromoplasts: stores plant pigments that give flowers and fruits colors Structure: Double membrane organelle 12.) Cytoskeleton Function: Overall: network of fibers in cytoplasm; organizes and anchors organelles, gives structural support 3 types of cytoskeleton 1.) Microtubules Function: Compression resistant for maintaining shape of cell o Provides organelle “tracks” o Moves chromosomes during cell division o Cell motility: Cilia and Flagella: locomotive appendages Structure: thickest of 3 types; hollow, made of tubulin o Can be disassembled and re-built from pieces 2.) Microfilaments Function: Bears tension (pulling forces), supports cell shape Muscle contraction: microfilaments of actin interact w/ another protein (myosin) Cleavage furrow: tightening band of microfilaments divides cell Gel-sol state: o Cytoplasm on periphery of cell thicker (gel); inner area is more fluid (sol) o Pseudopodia: cellular extensions of amoebas caused by localized breakdown of microfilaments from gel to sol state o Cytoplasmic streaming: flow of cytoplasm: sol to gel state; distributes substances w/in cell Structure: Solid, made of actin, twisted, double chain Can be assembled and re-built from pieces 3.) Intermediate Filaments Function: Provide shape and support of cell Organelle location (nucleus anchor) Makes up nuclear lamina (inside lining of nucleus) Forms desmosomes, rivets that hold cells together Structure: Larger than microfilaments, smaller than microtubules o Made of keratin o Permanent 13.) Cell Surfaces and Junctions: Plant cell walls: o Function: Gives shape, support, protection to plant cells o Structure: Fibrils of cellulose (polysaccharide) embedded in polysaccharide matrix, proteins Extracellular matrix (ECM) of an animal cell o Function: Gives support, adhesion, regulation to animal cells o Structure: Outside of plasma membrane Made mostly of glycoproteins (collagen is primary one) Bonded to integrins, proteins built into plasma membrane; allows communication b/t ECM and inside of cell Series of proteoglycan complex of polysaccharide molecules joined to protein cores Intercellular Junctions Plants: Plasmodesmata: channels in cell walls; connects cells; allows exchange of cytoplasm and cellular material b/t adjacent cells Animals: o Tight Junctions: fused continuous connection bonding cells together, sealed; prevents leakage between cells o Desmosomes: rivets that anchor cells together; made of intermediate filaments o Gap Junctions (communicating): communication; channels that connect cells; allows exchange of cytoplasm and cellular material b/t adjacent cells