keynote4.26.06post
advertisement

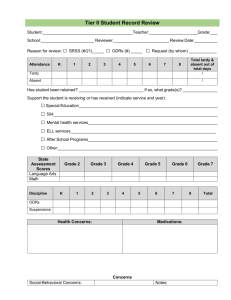
SWPBS: Where Did the Triangle Come From? George Sugai OSEP Center on PBIS University of Connecticut May 17, 2006 www.pbis.org www.swis.org George.sugai@uconn.edu OBJECTIVES • Celebrate your accomplishments & progress • Review SWPBS features that relate to sustainability & expansion • Look at some recent data OSEP Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports • USF, KU, UK, MU, UNC, UF, UO & UConn • IL EBD-PBIS Network, ShepperdPratt, May Institute • www.pbis.org Center Logic: SWPBS Successful individual student behavior support is linked to host environments or school climates that are effective, efficient, relevant, & durable (Zins & Ponti, 1990) PBS Foundations Behaviorism ABA PBS • Behavior & physiology • Learned behavior • Behavior & environment • Behavior lawfulness • Observable behavior • Socially important questions • Applied settings • Functional relationship Continuum of Behavior Support Science of Human Behavior Systems Change & Durability Local Context & Culture PBS Features Natural Implementers Prevention Logic EvidenceBased Practices Supporting Social Competence & Academic Achievement 4 PBS Elements OUTCOMES Supporting Decision Making Supporting Staff Behavior PRACTICES Supporting Student Behavior CONTINUUM OF SCHOOL-WIDE INSTRUCTIONAL & POSITIVE BEHAVIOR SUPPORT ~5% ~15% Primary Prevention: School-/ClassroomWide Systems for All Students, Staff, & Settings ~80% of Students Tertiary Prevention: Specialized Individualized Systems for Students with High-Risk Behavior Secondary Prevention: Specialized Group Systems for Students with At-Risk Behavior Designing School-Wide Systems for Student Success Academic Systems Behavioral Systems Intensive, Individual Interventions •Individual Students •Assessment-based •High Intensity 1-5% Targeted Group Interventions •Some students (at-risk) •High efficiency •Rapid response Universal Interventions •All students •Preventive, proactive 5-10% 80-90% 1-5% Intensive, Individual Interventions •Individual Students •Assessment-based •Intense, durable procedures 5-10% Targeted Group Interventions •Some students (at-risk) •High efficiency •Rapid response 80-90% Universal Interventions •All settings, all students •Preventive, proactive Brief Primer on “Triangle” Why? • It’s showing up beyond Center website • “Basics” are being overlooked • It’s a guide, not a standard Kutash, K., Duchnowski, A. J., & Lynn, N. (2006). School-based mental health: An empirical guide for decision makers. Tampa, FL: University of South Florida. The Louis De la Parte Florida mental Health Institute, Department of Child and Family Studies, Research and Training Center for Children’s Mental Health. http://rtckids.fmhi.usf.edu “Triangle” ?’s you should ask! • Where did it come from? • Why not a pyramid or octagon? • Why not 12 tiers? 2 tiers? • What’s it got to do w/ sped? • Where did those % come from? Original logic: Public Health & Disease Prevention Commission on Chronic Illness, 1957; Larson, 1994; Mrazek & Haggerty, 1994) • Tertiary (FEW) – Reduce complications, intensity, severity of current cases • Secondary (SOME) – Reduce current cases of problem behavior • Primary (ALL) – Reduce new cases of problem behavior Prevention Logic for All (Walker et al., 1996) • Decrease development of new problem behaviors • Prevent worsening of existing problem behaviors • Redesign learning/teaching environments to eliminate triggers & maintainers of problem behaviors • Teach, monitor, & acknowledge prosocial behavior Mean Percentage of Students by Major ODR rate 04-05 673 schools Grades K-6 (292,021 students) 100% 3 (4) 9 (6) 90% 80% 70% 88 (10) 60% 6+ ODRs 50% 2-5 ODRs 40% 0-1 ODR 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 Mean Percentage of Students by Major ODRs 04-05 255 schools, Grades 6-9 (170,700 students) 9 (7) 100% 90% 16 (7) 80% 70% 75 (13) 60% 6+ ODRs 50% '2-5 ODRs 40% '0-1 ODRs 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 Mean Percentage of Students by Major ODRs 04-05 67 schools, Grades 9-12 (62,244 students) 100% 11 (12) 90% 20 (12) 80% 70% 60% 6+ ODRs 50% '2-5 ODRs 69 (21) 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 '0-1 ODRs Mean Percentage of Students by Major ODRs 04-05 167 schools, Grades K- (8-12) (65,862 students) 100% 8 (8) 90% 15 (12) 80% 70% 60% 77 (16) 6+ ODRs 50% '2-5 ODRs 40% '0-1 ODRs 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 SWIS summary 04-05 (Majors Only) 1210 schools, 595,742 students Grade Range Number of Schools Number of Students Mean ODRs per 100 per school day K-6 673 292,021 .39 (sd=.43) Mean = 434 6-9 255 170,700 .96 (sd=.72) Mean = 669 9-12 67 62,244 1.28 (sd=1.32) Mean = 929 K-(8-12) 167 65,862 .88 (sd=.96) Mean = 394 Alt/JJ 48 3,915 Mean = 82 11.89 (9.03) SWIS summary 04-05 (Out of school suspensions [OSS]…Events) Grade Range Number of Schools Number of Students Mean OSS per 100 students K-6 673 292,021 11.35 (18) Mean = 434 6-9 255 170,700 46.38 (55) Mean = 669 9-12 67 62,244 54 (84) Mean = 929 K-(8-12) 167 65,862 34 (48) Mean = 394 Alt/JJ 48 3,915 Mean = 82 241 (216) SWIS summary 04-05 (Out of school suspensions [OSS]…Days) Grade Range Number of Schools Number of Students Mean Days of OSS per 100 students K-6 673 292,021 10.9 (19) Mean = 434 6-9 255 170,700 60 (72) Mean = 669 9-12 67 62,244 67 (67) Mean = 929 K-(8-12) 167 65,862 n/a Mean = 394 Alt/JJ 48 3,915 Mean = 82 314 (374) What’s SWPBS look like? • Team- & data-based school-wide implementation • 3-4 year commitment for systems change • Small # positively stated expectations (within 1 min.) visible, defined, taught, & encouraged • >80% of kids/adults state expectations & give behavioral example in context • >80% of kids receive at least weekly acknowledgement • >70% of kids received 0 or 1 major disciplinary referral • <10% received >2 major disciplinary referrals GENERAL IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS: “Getting Started” Team Agreements Data-based Action Plan Evaluation Implementation Working Smarter Team Matrix Initiative, Project, Committee Attendance Committee Character Education Safety Committee School Spirit Committee Discipline Committee DARE Committee EBS Work Group Purpose Outcome Target Group Staff Involved SIP/SID/ etc Sample Team Matrix Initiative, Committee Purpose Outcome Target Staff SIP/SID Group Involved Attendance Committee Increase attendance Increase % of students attending daily All students Eric, Ellen, Marlee Goal #2 Character Education Improve character Improve character All students Marlee, J.S., Ellen Goal #3 Safety Committee Improve safety Predictable response to threat/crisis All students Has not met Goal #3 School Spirit Committee Enhance school spirit Improve morale All students Has not met Discipline Committee Improve behavior Decrease office referrals All students Ellen, Eric, Marlee, Otis DARE Committee Prevent drug use All students Don EBS Work Group Implement 3tier model All students Eric, Ellen, Goal #2 Marlee, Goal #3 Otis, Emma Decrease office referrals, increase attendance, enhance academic engagement, improve grades Goal #3 Data: Big Ideas • Always develop questions first • Accuracy of data linked to quality of data systems • Context matters…interpret available data on local context • Link intervention decisions to local data interpretations & desired outcomes School-wide Positive Behavior Support Systems Classroom Setting Systems School-wide Systems Evidence-based Practices SW PBS Practices SCHOOLWIDE • Classroom-wide positive expectations taught & encouraged • Teaching classroom routines & cues taught & encouraged Continuum of procedures for encouraging expected behavior • Ratio of 6-8 positive to 1 negative adult-student interaction Continuum of procedures for discouraging inappropriate behavior • Active supervision • Redirections for minor, infrequent behavior errors Procedures for on-going monitoring & evaluation • Frequent precorrections for chronic errors • Effective academic instruction & curriculum 1 Common purpose & approach to discipline 2. Clear set of positive expectations & behaviors 3. Procedures for teaching expected behavior 4. 5. 6. CLASSROOM-WIDE SECONDARY/TERTIARY INDIVIDUAL NONCLASSROOM SETTINGS • • Positive expectations & routines taught & encouraged • Behavioral competence at school & district levels • Function-based behavior support planning Active supervision by all staff • Team- & data-based decision making • Comprehensive person-centered planning & wraparound processes • Targeted social skills & self-management instruction • Individualized instructional & curricular accommodations – Scan, move, interact • Precorrections & reminders • Positive reinforcement “Ohio Integrated Systems Model for Academic & Behavior Supports” • • • • • • • • • • Big Ideas in Beginning Reading DIBELS Florida Center for Reading Research Institute for the Development of Educational Achievement National Center for Culturally Responsive Educational Systems North Central Regional Educational Laboratory Oregon Reading First Positive Behavior Intervention and Supports School Wide Information Systems (SWIS) What Works Clearinghouse Other SWPBS Outcomes ODR Admin. Benefit Springfield MS, MD 2001-2002 2277 2002-2003 1322 = 955 42% improvement = 14,325 min. @15 min. = 238.75 hrs = 40 days Admin. time ODR Instruc. Benefit Springfield MS, MD 2001-2002 2277 2002-2003 1322 = 955 42% improvement = 42,975 min. @ 45 min. = 716.25 hrs = 119 days Instruc. time PBIS Messages • Measurable & justifiable outcomes • On-going data-based decision making • Evidence-based practices • Systems ensuring durable, high fidelity of implementation Have a great school year! George.sugai@uconn.edu www.pbis.org www.swis.org