The French and Indian War - Mrs. Hopkins History Class
advertisement

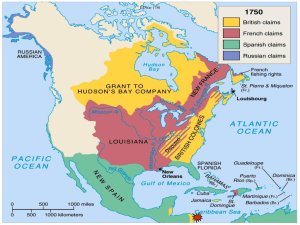
The French and Indian War French and Indian War Paintings by Nat Youngblood usccls.org The French and Indian War Or… • The Seven Years War Or… • La guerre de la Conquête Or… • Fourth Intercolonial War Or… • Great War for the Empire Who Fought? • God The French and Indian War was fought Save the by the British against the French and King!! their Indian (Native American) allies • The British had Indian allies too. • Remember, the colonists were Englishmen at this time. They were loyal subjects and did not think of themselves as anything but Englishmen The Albany Plan of Union The Albany Plan of Union • 7 of the 13 colonies sent representatives to a conference in Albany, New York • Benjamin Franklin proposed a Union so the colonies could: – Make decisions over Indian affairs – Handle trade issues – Defend themselves against the French The colonies said, “No thanks” Why did they Fight??? French claims Spanish claims English claims Remember the “G” in Glory! • England and France and Spain were all in competition with each other and with other European countries • France had long claimed the Ohio River Valley • As the 13 colonies prospered, many colonist began to look west toward lands that were claimed by the French One Part of a Bigger War The war was driven by the antagonism between Great Britain (in personal union with Hanover) and the Bourbons (in France and Spain), resulting from overlapping interests in their colonial and trade empires, and by the antagonism between the Hohenzollerns (in Prussia) and Hapsburgs (Holy Roman Emperors and Archdukes in Austria), resulting from territorial and hegemonial conflicts in the Holy Roman Empire. The Diplomatic Revolution established an Anglo-Prussian Camp, allied with some smaller German States and later Portugal, as well as an Austro-French Camp, allied with Sweden, Saxony and later Spain. The Russian Empire left its offensive alliance with the Habsburgs on the succession of Peter III, and like Sweden concluded a separate peace with Prussia in 1762. The war ended with the peace treaties of Paris (Bourbon France and Spain, Great Britain) and of Hubertsburg (Hohenzollerns, Habsburgs, Saxon elector) in 1763. The war was characterized by sieges and arson of towns as well as open battles involving extremely heavy losses; overall, some 900,000 to 1,400,000 people died. Just kidding… You don’t have to learn all that stuff! But… this was a World War England and her Allies France and her Allies George Washington • A young Major in the Virginia Militia, George Washington was sent into western Pennsylvania to counter the French • His group encountered a party of French scouts and there was a fight. A French officer was killed • This was one of the first events that sparked the world-wide conflict A young George Washington Washington-Custis-Lee Collection, Washington and Lee University, Lexington, Virginia Peace Before After England’s North American Territory is now HUGE!! • France cedes (gives up) all land EAST of the Mississippi to England • France gives New Orleans to Spain • Spain gives Florida to England (who will later give it back, but that’s another story) • In North America, the only possessions France has are some islands in the Caribbean (West Indies) The Result? • England is in debt (big time!) • England needs money to pay for the war • Fighting Indians would be too expensive So….. England’s Plan • Enforce existing taxes on the colonists (The state of Salutary Neglect was over) • Impose new taxes (after all, the war was to protect the colonists, so they should pay. Right???) • Declare that there would be no settlements west of the Proclamation Line of 1763. (England was too broke to fight any Indian wars!) Vocabulary • Salutary Neglect: The unofficial policy England had toward her colonies; tax and trade restrictions were loosely enforced (the colonists liked it!) • The Proclamation of 1763: Colonists were forbidden to settle west of the Appalachian Mountains because England wanted to avoid wars with Indians The Proclamation of 1763 Colonial Reaction TEKS 8.4A: analyze causes of the American Revolution, including the Proclamation of 1763, the Intolerable Acts, the Stamp Act, mercantilism, lack of representation in Parliament, and British economic policies following the French and Indian War