Bacteria & Archaebacteria
advertisement

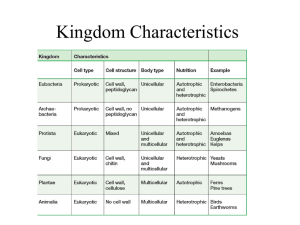
CLASSIFICATION OF ORGANISMS THE 6 KINGDOMS Kingdom Bacteria Where are bacteria found? – Members of this kingdom are found in soil, water, and other living things Kingdom Bacteria All bacteria are single celled organisms that do not have a nucleus! What do we call organisms with these characteristics? Bacteria have cell walls Genetic material Cell Membrane Kingdom Bacteria Bacteria can be one of three main shapes. – Rod-shaped (bacilli) – Spherical-shaped ( cocci) – Spiral-shaped (spirilla) Kingdom Bacteria Reproduce by Binary Fission – one bacteria duplicates its genetic material and then splits into 2 separate cells – the new cell is identical to the parent Kingdom Bacteria Some bacteria reproduce sexually through conjugation – Two parents – Transfers some of its genetic material – Offspring are genetically different from parents Kingdom Bacteria Different types of bacteria are classified by how they get their food – Autotrophic – Heterotrophic – Decomposers Kingdom Bacteria Roles/Uses – 99% of bacteria are helpful to humans Produce foods such as cheese, apple cider, and sauerkraut Some can even clean up oil spills and gasoline leaks – Bacteria cause food to spoil – Some are decomposers Can Bacteria Help Us? Bacteria help us – Digest food – Make vitamin K Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Where are archaea found? – Most organisms in this kingdom are found in extreme environments, such as hot springs – Can be found in ponds and swamps – Most archaea prefer environments with little or no oxygen Kingdom Archaebacteria All archaea are prokaryotic organisms They reproduce using binary fission Kingdom Archaebacteria There are 3 main types of archaea – Heat Lovers—live in extremely hot water like that found in ocean vents and hot springs – Salt Lovers--live in environments with high levels of salt (ex. Dead Sea and Great Salt Lake) – Methane Makers—live in swamps and animal intestines; give off methane gases