Taxes and Financial Planning
advertisement

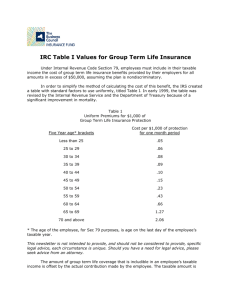
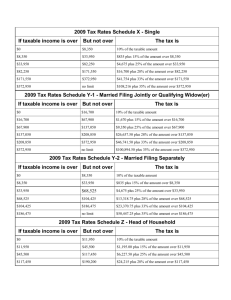
Taxes and Financial Planning •Common goals related to tax planning: –Know current tax laws –Maintain complete records –Make financial decisions that can reduce tax liability •Principal purpose of taxes is to finance government activities. •About 1/3 of your earnings go to pay taxes. Taxes on Purchases • State and local taxes are added to the purchase price of goods. • Excise tax is imposed on specific goods and services – – – – – – Gasoline Cigarettes Alcohol Tires Air travel Telephone service Taxes on Property • Real estate property tax is based on the value of land and buildings. • Personal property taxes on the value of automobiles, boats, furniture, and farm equipment are imposed in some areas. Taxes on Wealth • Estate tax-imposed on the value of an individual’s property at the time of death. • Inheritance tax-levied on the value of property bequeathed by a deceased individual. • Gift amount greater than $13,000 are subject to federal tax. Taxes on Earnings • Social Security • Income Tax – Federal tax – State tax in all but 7 states • • • • • • • Alaska Florida Nevada South Dakota Texas Washington Wyoming Determining Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) • Taxable income-net income after deductions, on which income tax is computed • Types of income subject to taxation: – Earned income-wages, salaries, commissions, fees, tips, bonuses – Investment income-dividends, interest, rent – Passive income-business activities that you do not direectly participate-limited partnership – Alimony, awards, lottery winnings, prizes Taxable Income • Total income is affected by exclusions – Exclusions are amounts not included in gross income – Exclusions can also be tax-exempt income • Total income is affected by tax deferred income Computing Taxable Income • Adjusted Gross Income-income after certain deductions including: – Contributions to a traditional IRA or Keogh – Alimony payments – Student loan interest, tuition and fee deductions – Tax-deferred retirement plans Taxable Income • Deduction-an amount subtracted from AGI to arrive at taxable income. – Standard deduction – Itemized deduction Exemption-a deduction from AGI for yourself, your spouse, and qualified dependents. Taxes Owed • Use your taxable income in conjunction with the appropriate tax table or tax schedule. • Marginal tax rate-the tax on the last dollar of income. • Average tax rate-total tax due divided ty your taxable income. • Tax credit-amounts subtracted from the amount of tax owed. The Progressive Nature of the Federal Income Tax If your filing status is Single If your taxable income is: Over: But not over -- The tax is: Of the amount over-- $0 $7,150 ------------ 10% $0 7,150 29,050 $715.00 + 15% 7,150 29,050 70,350 4,000.00 + 25% 29,050 70,350 146,750 14,325.00 + 28% 70,350 146,750 319,100 35,717.00 + 33% 146,750 319,100 ---------- 92,592.50 + 35% 319,100 The Tax Rate Schedule is shown so you can see the tax rate that applies to all levels of taxable income. It is not used to figure ones’ taxes. Tax Payments • Payroll deductionspay-as-you-go (W-4) Tax Credit Versus Tax Deduction • $100 tax credit reduces your taxes by $100 • $100 tax deduction reduces taxes by your tax bracket. For instance, if a person is in the 25% tax bracket it would reduce your taxes by 25%