The Islamic Empires
advertisement

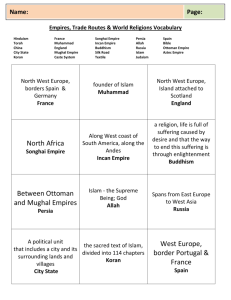
* Chapter 27 Formation of the Islamic Empires (Ottoman, Safavid, Mughal) The Ottoman Empire Osman & Ottoman Expansion • Founder of dynasty • 1289-1923 • bey=chief, semi-nomadic Turks • Osman & followers strive To be ghazi=Muslim religious Warriors • Waged holy wars • Capitals: Bursa & Edirne • Bursa became major Commercial and intellectual Center • Ghazi two forces: light Cavalry & volunteer infantry • Devrshirme: conversion Of Christian boy to Administration or Janissaries= Military soldiers • Gunpowder weapons Mehmed the Conqueror • 1451-1481 • Captured Constantinople= New Ottoman capital and New name Istanbul • Istanbul became Commercial center • Not just warrior but emperor • “two lands” “two seas” • Tightly centralized • Absolute monarchy • Military face no rivals Suleyman the Magnificent • 1512-1520 • Continued to expand Empire SW Asia & Europe • Became major naval Power • Was able to challenge Christian and Portuguese vessels Safavid Empire The Safavids • Shah Ismail (1252-1334) • Manipulated rise to Power story • Ancestry traced back to Sufi religious leader • Changed religious Preference several times Before settling, due to Nomadic Turkish tribes Twelver Shiism • 12 infallible imams After Muhammed Starting with prophet’s Cousin Ali • Qizilbash=red heads • Suggested Ismail Was a hidden imam or Incarnation of Allah • Most Muslims saw This as blasphemous • Qizilbash felt Invincible in battle Battle of Chaldiran & Shah Abbas the Great • Battle between Shiite Safavids & Sunni Ottomans • Ottomans led with heavy Artillery & Janissaries • Safavids thought they were Protected • Intermittent for 2 centuries • After Ismail, successor s Abandon radicalism & lean to More conventional Twelver Shiism • Shah Abbas the Great (15881629) • Encouraged trade, reformed Administration & military Mughal Empire Babur • Claimed descent From Chinggis Khan & Tamerlane • Attempted to expand Authority into India through Firearms and gunpowder Weapons • Cared little for land of India Take spoils and leave • Began Mughal empire= Persian for Mongol . • Embrace almost all Indian subcontinent Akbar • 1556-1605 • Killed Adham Khan • Didn’t tolerate those That challenged him • Centralized administration w/ministries to watch over Provinces • Allowed for religious toleration (Hindu & Muslim) • Called for syncetic religious blend That would focus emperor as a Common ruler to all Aurangzeb • 1659-1707 • Reached greatest Extent • Presided over Troubled empire • No religious Toleration • Destroyed Hindu Temples & taxed Hindus • Local leaders Begin rebellions & resistance Imperial Islamic Society The Dynastic State The Emperors & Islam • Empires were military Creations based off of Possession • Prestige & authority Derived from piety & Military • Devotion of Islam leads To expansion of new lands • Ghazi’s fight infidels Steppe Traditions • Early emperors often Did as pleased with disregard For religious and social norms • Steppe practices lead to Problems of succession • Problems:Conflicts, rebellions, challenges • In Ottoman empire legal to Kill brother • Sons received administrive Power in provinces in the Ottoman empire Women and Politics • In Islam women have No role in public affairs • Influence was often Private • In Ottoman empire, Emperor’s mother & Chief wife receive Privileges Agriculture and Trade Food Crops • Agricultural economies • Financed armies and Bureaucracies • Colombian exchange Brought American crops But little effects • Encouraged consumption Of tobacco and coffee Tobacco • Introduced by English Merchants, medicinal • Entrepreneurs est. Coffeehouses for coffee and Tobacco • Some in society were Against tobacco and coffee • Attempted to get rid of It, proved unsuccessful Population Growth & Trade • Population in empires Increased due to intensive Agriculture • 1600 Ottoman empire Declines due to loss of land • Long-distance trade successful In the Islamic empires • Ottoman empire had commercia Capital Bursa • Safavids had commercial Center Isfahan • Mughals allowed trading stations In their land Religious Affairs in the Islamic Empires Religious Diversity • Religious and ethnically Diverse, had to be kept under Control • Ottomans: Christian & Jews • Safavids: Zoroastrian, Jews Christians • Mughals: Muslims & Hindus Christian Mission in India Akbar’s Divine Faith • Portuguese Goa center Of Christian mission in India • Attempt to attract converts (schools) • Attempt to convert Akbar • Emperor declined to commit To exclusive faith • Wanted religious Synthesis to unify Empire • “Divine Faith”= loyalty To emperor w/different Religious traditions • Mostly drew on Islam, Monotheistic • “Lord of Wisdom” Religious Affairs in the Islamic Empires Status of Religious Minorities • Est method to deal w/nonMuslims in the empire • “dhimmi”=protected people, Paid “jizya”=tax • Retained personal freedoms • “millet”=autonomous religious Communities retaining their civil laws Promotion of Islam • Policies of religious tolerance Not popular with Muslims • Worried it would lead to Hindu Absorption in caste system • Mughals created Islamic state wit Islamic law • Aurengzeb reinstates jizya create Cultural tensions Cultural Patronage of the Islamic Emperors Istanbul • Capital cities and royal Palaces were visible Expressions of imperial Majesty • Ottoman pride in Istanbul • Prosperous city • Topkapi palace=gov’t Offices, mint, meeting Places, sultan’s residence Isfahan • One of the most precious Jewels of urban architecture • Palaces emphasized Natural settings with gardens And pools, inner courts and gates • Mughal’s regarded their capital Wherever their ruler was Fatehpur Sikri & the Taj Mahal • Private residence and Retreat for ruler • Mughal display of piety And devotion • Incorporated Indian Elements • Tah Mahal was a Mugha monument The Empires in Transition Deterioration of Imperial Leadership Dynastic Decline • All 3 dynasties had incompetent Rulers who cared more for themselves Than their empire • Late 17th c. provoked mutinies in Armies, revolts, political corruption, Economic oppression and insecurtiy Religious Tensions • Political troubles arose from religious Tensions. • Ottoman: disaffected religious students Often joined the Janissaries in revolt Economic and Military Decline Economic Difficulties • The cost of military and Administration led to decline In Islamic empires • Became difficult to support Empire that was limited in Resources • Empires lost control over Provinces, raised taxed after Losing revenues, bribery, selling offices Military Decline • Military decline because they did Not seek to improve their technologies • European technology was advancing So quickly that it became difficult For empires to keep up. Cultural Conservatism Piri Reis • Ottoman reconoittered The Indian Ocean Basin from East Africa to Indonesia • Produced large scale maps And navigational texts Cultural Confidence • Believed in their superiority And felt they had nothing to Learn from Europeans • Remained oblivious to European Culture and developments The Printing Press • Resistance from Conservatives to the new Inventions of the Europeans • Printing press was Not as popular in Islamic Empires as in Europe • Aesthetics were more Preferred • Feared what the printing Press could do to the Islamic society